160 Degrees Celsius Converted To Fahrenheit
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
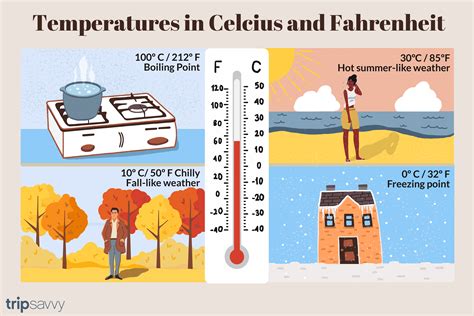
Table of Contents
160 Degrees Celsius Converted to Fahrenheit: A Deep Dive into Temperature Conversion
Knowing how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a fundamental skill, whether you're a chef perfecting a recipe, a scientist conducting experiments, or simply navigating daily life in a region that uses a different temperature scale. This article delves into the conversion of 160 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, explaining the process in detail, exploring the practical implications of this temperature, and offering insights into the broader context of temperature measurement and conversion.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
Before we dive into the conversion, let's briefly review the two temperature scales involved:
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, it's a metric temperature scale where 0°C is the freezing point of water and 100°C is its boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure. This is the most widely used scale globally.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This is an imperial temperature scale where 32°F is the freezing point of water and 212°F is its boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure. It's primarily used in the United States.
The Conversion Formula: From Celsius to Fahrenheit
The formula to convert Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F) is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This formula is crucial for accurate conversions. Let's apply it to our specific example of 160°C.
Calculating 160°C in Fahrenheit
Substituting 160°C into the formula:
°F = (160°C × 9/5) + 32
°F = (320) + 32
°F = 322
Therefore, 160 degrees Celsius is equal to 322 degrees Fahrenheit.
Practical Applications of 322°F (160°C)
A temperature of 322°F (160°C) has various applications across diverse fields. Understanding the practical implications of this temperature is essential for effective problem-solving and decision-making in various contexts:
Cooking and Baking
-
Baking: This temperature falls within the range used for baking many dishes. Many ovens reach this temperature for various baking applications. Consider baking bread, certain pastries, or roasting meats. This temperature will facilitate the Maillard reaction, creating a desirable browning and crust formation on many foods.
-
Caramelization: Sugars begin to caramelize at around 320°F (160°C), imparting a distinctive brown color and flavor to foods. This is crucial for making caramels, sauces, and certain desserts.
-
Deep Frying: While the exact temperature for deep frying varies by ingredient, 322°F (160°C) is often too low for many deep frying applications. This temperature might be more suitable for delicate items that wouldn't handle a higher temperature well.
Industrial Processes
-
Material Processing: Many industrial processes involve heating materials to specific temperatures. 322°F (160°C) might be utilized in processes involving plastics, polymers, or certain metals. Understanding the precise temperature is vital for quality control and preventing damage to the materials.
-
Sterilization: In some sterilization processes, particularly those used for certain medical or food-related applications, 160°C could be part of a temperature profile used to eliminate harmful microbes.
Scientific Experiments
- Laboratory Settings: In scientific research, precise temperature control is critical. 160°C might be a critical temperature for experiments involving chemical reactions, material science, or biological processes. Accurate temperature measurement and control are key to the reliability of experimental results.
Importance of Accurate Temperature Conversion
Accurate temperature conversion is paramount for several reasons:
-
Safety: Incorrect conversions can lead to serious consequences, especially in industrial settings or when handling potentially dangerous chemicals. Accurate temperature control is critical for ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.
-
Reliability: In scientific experiments and manufacturing processes, accurate temperature measurements are essential for reliable results and product quality. Inaccurate conversions can lead to flawed data or substandard products.
-
Consistency: Using consistent temperature measurements across different locations and projects is important for maintaining standardization and preventing misunderstandings. This applies especially to global collaborations and data sharing.
Beyond the Basic Conversion: Exploring Other Factors
While the formula provides a fundamental conversion, several factors can influence the accuracy of the temperature reading:
-
Atmospheric Pressure: The boiling and freezing points of water, which are the reference points for both Celsius and Fahrenheit, are slightly affected by changes in atmospheric pressure. At higher altitudes, water boils at a lower temperature.
-
Accuracy of Measurement Tools: The precision of the thermometers used to measure the temperature significantly influences the accuracy of the converted value. A reliable thermometer is essential for accurate readings.
-
Heat Transfer: The rate of heat transfer can affect the actual temperature of the substance being measured. Rapid heating or cooling can lead to temperature gradients within the material, making point measurements less representative of the overall temperature.
Expanding Knowledge: Advanced Temperature Concepts
Understanding the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is just one aspect of a broader understanding of thermometry. Further exploration can include:
-
Kelvin Scale: The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale, where 0 Kelvin represents absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases.
-
Thermodynamic Principles: A deeper understanding of thermodynamics helps explain the principles governing heat transfer, temperature changes, and energy interactions.
-
Heat Capacity: Knowing the heat capacity of a substance helps predict how its temperature will change in response to the addition or removal of heat.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Converting 160 degrees Celsius to 322 degrees Fahrenheit is a straightforward process using the established formula. However, understanding the practical implications of this temperature across various fields, acknowledging potential sources of error, and broadening your knowledge of temperature scales and related concepts are crucial for anyone who needs to work with temperature measurements regularly. This holistic approach ensures accurate conversions and a deeper appreciation for the importance of temperature in our daily lives and across numerous scientific and industrial applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Baking Soda A Mixture Or Pure Substance
Mar 10, 2025
-
122 Cm In Inches And Feet
Mar 10, 2025
-
Heat Of Formation Of Magnesium Oxide
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is 15 Inches In Mm
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is In A Half A Pound
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 160 Degrees Celsius Converted To Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
