2 And 1 4 As A Decimal
Kalali
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
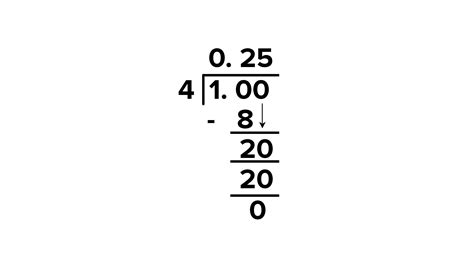
Table of Contents
2 and 1/4 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions and their decimal equivalents is fundamental to mathematics and numerous real-world applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the conversion of the mixed number 2 and 1/4 into its decimal form, exploring various methods and highlighting the significance of this conversion in different contexts. We will not only show you how to convert this specific fraction but also equip you with the knowledge to tackle similar conversions with confidence.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Decimals
Before diving into the conversion process, let's clarify some key terms.
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, such as 2 and 1/4 (often written as 2 1/4). It represents a value greater than one.
-
Decimal: A decimal number uses a base-ten system, employing a decimal point to separate the whole number part from the fractional part. For example, 2.25 is a decimal number.
Converting a mixed number to a decimal involves expressing the fractional part as a decimal and then combining it with the whole number part.
Method 1: Converting the Fraction to a Decimal Directly
This is the most straightforward method. We'll convert the fraction 1/4 to a decimal and then add the whole number 2.
1. Divide the Numerator by the Denominator:
The fraction 1/4 represents 1 divided by 4. Performing this division gives us:
1 ÷ 4 = 0.25
2. Add the Whole Number:
Now, we add the whole number part (2) to the decimal equivalent of the fraction (0.25):
2 + 0.25 = 2.25
Therefore, 2 and 1/4 as a decimal is 2.25.
Method 2: Converting the Mixed Number to an Improper Fraction First
This method involves first converting the mixed number into an improper fraction, then dividing to find the decimal equivalent.
1. Convert to an Improper Fraction:
To convert 2 and 1/4 to an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number (2) by the denominator (4) and add the numerator (1). The result becomes the new numerator, while the denominator remains the same.
(2 x 4) + 1 = 9
So, 2 and 1/4 is equivalent to the improper fraction 9/4.
2. Divide the Numerator by the Denominator:
Now, divide the numerator (9) by the denominator (4):
9 ÷ 4 = 2.25
This confirms that 2 and 1/4 as a decimal is 2.25.
Method 3: Using Decimal Equivalents of Common Fractions
Knowing the decimal equivalents of common fractions can significantly speed up conversions. For example, memorizing that 1/4 = 0.25, 1/2 = 0.5, and 3/4 = 0.75 is beneficial. Since we already know that 1/4 = 0.25, we can directly add the whole number 2 to get 2.25. This method relies on familiarity with frequently encountered fractions. This method, while quick, requires prior knowledge of these common fractional decimal equivalents.
The Significance of 2.25
The decimal representation 2.25 finds applications in various fields:
-
Finance: 2.25 could represent a quantity like 2.25 dollars, pounds, or euros.
-
Measurement: In metrics, 2.25 could represent 2.25 meters, centimeters, or liters, depending on the context.
-
Data Analysis: In statistical analysis or data visualization, 2.25 might be a data point or a result from a calculation.
-
Everyday Life: This decimal could represent quantities in cooking recipes (2.25 cups of flour), crafting projects (2.25 yards of fabric), or any number of other scenarios where precise measurements are required.
Beyond 2 and 1/4: Mastering Fraction-to-Decimal Conversions
The methods outlined above are applicable to converting any mixed number or fraction to its decimal equivalent. Here's a breakdown of the general process:
-
For Mixed Numbers: Convert the mixed number into an improper fraction (as shown in Method 2) or directly convert the fraction to a decimal and add the whole number (as shown in Method 1).
-
For Proper Fractions: Simply divide the numerator by the denominator. If the division results in a repeating decimal, you may choose to round to a certain number of decimal places depending on the context. For instance, 1/3 = 0.3333... which might be rounded to 0.33 or 0.333 depending on the level of precision needed.
-
For Improper Fractions: Divide the numerator by the denominator. The result will be a decimal greater than or equal to 1.
Dealing with Repeating Decimals:
Some fractions result in repeating decimals (e.g., 1/3 = 0.333...). In such cases, you can represent the repeating portion using a bar notation (e.g., 0.3̅) or round the decimal to a specified number of decimal places. The choice depends on the level of accuracy needed for your specific application.
Practicing Fraction-to-Decimal Conversions
To solidify your understanding, try converting the following fractions and mixed numbers to decimals:
- 3 and 1/2
- 1 and 3/4
- 5/8
- 7/10
- 2/3 (pay attention to the repeating decimal)
By consistently practicing these conversions, you'll build your proficiency and gain confidence in working with fractions and decimals.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The ability to convert fractions to decimals is crucial in many everyday situations:
-
Baking and Cooking: Recipes often call for fractional measurements (e.g., 1/2 cup of sugar), which need to be accurately converted to decimal equivalents if using a digital scale.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are paramount in these fields, requiring the accurate conversion of fractions to decimals for building plans, material calculations, and other engineering tasks.
-
Finance and Accounting: Calculating percentages, interest rates, and other financial metrics often involves converting fractions to decimals for calculations and analysis.
-
Data Science and Programming: Data analysis and programming frequently involve working with numerical data, where converting fractions to decimals is a necessary step in data processing and manipulation.
Conclusion
Converting 2 and 1/4 to its decimal equivalent (2.25) is a fundamental skill with far-reaching applications. Understanding the different methods outlined in this guide – direct division, improper fraction conversion, and using known decimal equivalents – allows for flexibility and efficiency in solving similar problems. Mastering these techniques not only enhances mathematical proficiency but also proves invaluable in numerous real-world situations requiring accurate numerical calculations. Continued practice and familiarity with the principles discussed here will solidify your understanding and enable confident navigation of fraction-to-decimal conversions in any context.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Half Of 1 And 3 4 Cup
Jul 02, 2025
-
How To Tell When Chorizo Is Done
Jul 02, 2025
-
Why Doesnt Christian Bale Remove His Mole
Jul 02, 2025
-
Somebody Once Told Me That The World Was Macaroni Lyrics
Jul 02, 2025
-
How Old Are You If Born In 1993
Jul 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 And 1 4 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.