4 To The Power Of 0
Kalali
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
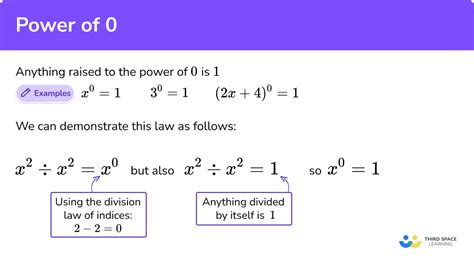
Table of Contents
4 to the Power of 0: Unraveling the Mystery of Exponents
The seemingly simple expression "4 to the power of 0," or 4⁰, often sparks confusion. While the answer is straightforward – it equals 1 – the underlying mathematical reasoning behind this result is surprisingly rich and connects to fundamental concepts in algebra and number theory. This article delves into the intricacies of this seemingly simple equation, exploring its meaning, its implications, and its relevance across various mathematical fields. We will unravel the mystery of zero as an exponent, explaining why it works and why it's so important.
Understanding Exponents: A Quick Refresher
Before we tackle 4⁰, let's briefly review the concept of exponents. An exponent, also known as a power or index, indicates how many times a base number is multiplied by itself. For instance:
- 4¹ = 4 (4 multiplied by itself once)
- 4² = 4 x 4 = 16 (4 multiplied by itself twice)
- 4³ = 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 (4 multiplied by itself three times)
This pattern is easily understood. We multiply the base number (4 in this case) by itself the number of times specified by the exponent. But what happens when the exponent is zero? This is where the intriguing nature of 4⁰ emerges.
The Rule of Zero Exponents: Why 4⁰ = 1
The core principle behind the rule of zero exponents is consistency within the mathematical system. Let's observe a pattern:
- 4³ = 64
- 4² = 16
- 4¹ = 4
Notice that as the exponent decreases by 1, the result is divided by the base (4). Continuing this pattern logically:
- 4⁰ = 4¹ / 4 = 4 / 4 = 1
This pattern preservation ensures that the rules of exponents remain consistent regardless of the value of the exponent. If we didn't define 4⁰ as 1, this elegant pattern would be broken.
The Algebraic Proof: Maintaining Consistency
We can further solidify this understanding through algebraic manipulation. Consider the following equation:
4ˣ / 4ˣ = 1
This equation holds true for any value of 'x' except zero, as division by zero is undefined. Using the rule of exponents for division (subtracting exponents), we can rewrite the equation as:
4ˣ⁻ˣ = 1
This simplifies to:
4⁰ = 1
This algebraic proof demonstrates that defining 4⁰ as 1 is essential to maintain the consistency and validity of exponent rules.
Extending the Concept Beyond 4: a⁰ = 1
The rule of zero exponents applies not just to 4 but to any non-zero base. In general:
a⁰ = 1, where 'a' is any non-zero number.
This is a fundamental rule in mathematics, crucial for various algebraic manipulations and calculations. The exception, as mentioned earlier, is when the base is zero. 0⁰ is an indeterminate form, a topic of considerable mathematical debate that often arises in calculus and analysis.
Implications in Various Mathematical Fields
The seemingly simple concept of 4⁰ = 1 has far-reaching implications across various mathematical disciplines. Let's explore some key areas:
1. Algebra and Polynomials:
Zero exponents play a critical role in simplifying and manipulating polynomial expressions. Consider a polynomial like:
3x³ + 2x² + x + 5
This can be rewritten as:
3x³ + 2x² + x¹ + 5x⁰
The inclusion of x⁰ emphasizes the constant term, showcasing the completeness and consistent structure of the polynomial.
2. Calculus and Limits:
Understanding zero exponents is crucial in calculus, particularly when dealing with limits and derivatives. The behavior of functions near zero often requires evaluating expressions involving zero exponents.
3. Combinatorics and Probability:
Combinatorial problems often involve the calculation of the number of ways to choose items from a set. These calculations frequently utilize binomial coefficients, which rely on factorials and zero exponents. For instance, the number of ways to choose 0 items from a set of n items is given by "n choose 0," which evaluates to 1. This is directly related to 0! = 1, a consequence of the consistent application of zero exponent rules.
4. Computer Science and Programming:
In computer science and programming, understanding exponents, including zero exponents, is fundamental for working with algorithms, data structures, and calculations involving large numbers or exponential growth and decay.
The Importance of Understanding 4⁰ = 1
The seemingly trivial concept of 4⁰ = 1 is, in fact, a cornerstone of mathematical consistency and elegance. Its implications extend far beyond basic arithmetic, impacting various advanced mathematical fields. Understanding this fundamental principle is vital for anyone aiming to master algebraic manipulations, delve into calculus, or work with any area of mathematics that involves exponents. It underscores the importance of consistent mathematical definitions and the elegant interconnectedness of mathematical concepts.
Dispelling Common Misconceptions
Several common misconceptions surround the concept of zero as an exponent. Let's address some of the most prevalent ones:
Misconception 1: 4⁰ = 0
This is a very common mistake. It stems from a possible intuitive but incorrect association with multiplication. However, as explained earlier, the definition of 4⁰ = 1 ensures consistency across the entire system of exponents.
Misconception 2: 0⁰ is undefined.
While it is true that 0⁰ is often considered indeterminate (meaning it could potentially take on several different values depending on the context), it's important to note that this is distinct from saying that it's strictly undefined. In most mathematical contexts, 0⁰ is either left undefined or assigned a value of 1 for convenience and consistency within certain operations. The reason for the indeterminate nature of 0⁰ involves subtle considerations of limits and calculus that extend beyond the scope of this article.
Misconception 3: Zero exponents are pointless.
This couldn’t be further from the truth! Zero exponents are not merely an arbitrary rule; they are fundamental to the internal consistency of mathematics and are vital for numerous calculations and operations across various mathematical branches.
Conclusion: A Foundation of Mathematical Consistency
In conclusion, understanding "4 to the power of 0" is far more than simply memorizing the answer. It's about grasping the underlying principle of mathematical consistency and the elegance with which the rules of exponents are designed. This seemingly simple concept serves as a foundational element in various branches of mathematics and is crucial for both theoretical understanding and practical applications. Mastering this concept solidifies a solid foundation for further exploration of advanced mathematical concepts. Its importance cannot be overstated, and appreciating its significance is key to becoming proficient in mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Ft Is 33 Inches
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 107 Inches
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 137 Inches
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 8 5 Feet
Mar 21, 2025
-
52 Cm Is What In Inches
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4 To The Power Of 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
