95 Degrees Fahrenheit Converted To Celsius
Kalali
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
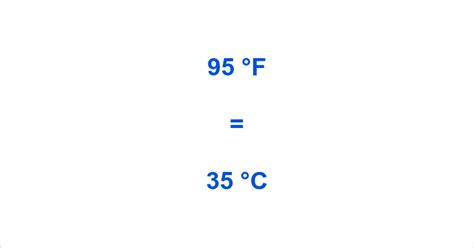
Table of Contents
95 Degrees Fahrenheit Converted to Celsius: A Deep Dive into Temperature Conversions
Converting temperatures between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a common task, whether you're checking the weather, baking a cake, or conducting scientific experiments. This article will delve deep into the conversion of 95 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, explaining the process, providing context, and exploring related temperature scales and their applications. We'll also touch upon the history of these scales and their ongoing relevance in our daily lives.
Understanding the Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
Before we dive into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two temperature scales involved:
Fahrenheit (°F): Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, this scale sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F, with 180 degrees separating them. It's still widely used in the United States, several Caribbean nations, and a few other places globally.
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius was developed by Anders Celsius in the 18th century. This scale defines the freezing point of water as 0°C and the boiling point as 100°C, with 100 degrees separating them. It's the standard temperature scale used by most of the world and in scientific contexts.
The Conversion Formula: From Fahrenheit to Celsius
The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 95°F to Celsius:
°C = (95 - 32) × 5/9 = 63 × 5/9 = 35°C
Therefore, 95 degrees Fahrenheit is equal to 35 degrees Celsius.
Understanding the Math Behind the Conversion
The formula's rationale lies in the different scales' intervals. Fahrenheit has 180 degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water, while Celsius has 100. The fraction 5/9 represents the ratio of these intervals (100/180 = 5/9). Subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature accounts for the difference in the freezing point of water between the two scales.
Practical Applications of the Conversion
Understanding the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is crucial in various applications:
-
Weather Forecasting: Many weather reports present temperatures in both Fahrenheit and Celsius, ensuring accessibility to a global audience. Knowing the equivalent Celsius temperature for a reported Fahrenheit temperature helps in understanding the actual weather conditions. For example, 95°F (35°C) signifies a hot and potentially uncomfortable day.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Converting between the two is essential for achieving accurate results in cooking. A slight deviation in temperature can significantly impact the outcome of baked goods.
-
Medicine and Healthcare: Body temperature, medication storage, and various medical procedures often require accurate temperature measurements in both Fahrenheit and Celsius. The conversion ensures proper communication and adherence to international medical standards.
-
Science and Engineering: Scientific experiments and engineering applications require precise temperature control and recording. Converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius is critical for data analysis and consistency across different geographical regions and research groups.
-
International Travel and Communication: Knowing the temperature conversion ensures smooth communication and understanding while traveling internationally. Understanding that 35°C is a warm day helps in planning accordingly.
Exploring Other Temperature Scales
While Fahrenheit and Celsius are the most widely used scales, several others exist:
-
Kelvin (K): This absolute temperature scale starts at absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. It's extensively used in scientific research and engineering. The conversion from Celsius to Kelvin is relatively simple: K = °C + 273.15. Therefore, 35°C equals 308.15 K.
-
Rankine (°R): Similar to Kelvin, Rankine is an absolute scale but is based on the Fahrenheit degree. The conversion is °R = °F + 459.67. Therefore, 95°F equals 554.67 °R.
-
Réaumur (°Ré): An older scale where the freezing point of water is 0°Ré and the boiling point is 80°Ré. It's rarely used today.
Understanding these various scales provides a broader perspective on temperature measurement and its historical development.
The History of Temperature Scales: A Journey Through Time
The development of temperature scales wasn't a singular event but rather a progressive process shaped by scientific advancements and the need for standardized measurements.
-
Early Attempts: Early attempts at measuring temperature relied on subjective observations and lacked standardization. The development of reliable thermometers was crucial for creating consistent scales.
-
Fahrenheit's Scale: Fahrenheit’s scale, developed around 1724, used a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride as its zero point and human body temperature as another reference point. While arbitrary, its wider adoption for a time established a common standard.
-
Celsius's Scale: Celsius's scale, developed around 1742, is more intuitive, using the easily reproducible freezing and boiling points of water as its reference points. Its simplicity and logical structure contributed to its widespread adoption.
-
Kelvin's Absolute Scale: Lord Kelvin's absolute temperature scale, developed in the 19th century, addressed the limitations of relative scales like Fahrenheit and Celsius by defining a theoretical zero point, absolute zero. This scale has become crucial in fields requiring precise temperature measurements.
The Ongoing Relevance of Temperature Conversion
The need for temperature conversion remains critical today due to the continued use of both Fahrenheit and Celsius globally. This highlights the importance of understanding the conversion formulas and the practical implications of using different scales. Moreover, the advancement of technology and its application in diverse fields constantly require accurate and consistent temperature measurements, highlighting the significance of conversion between these temperature scales.
Tips for Accurate Temperature Conversion
- Use the correct formula: Ensure you use the appropriate formula for the conversion you're performing (Fahrenheit to Celsius, Celsius to Fahrenheit, etc.).
- Double-check your calculations: Accuracy is key when dealing with temperature conversions. Recalculate to verify your results.
- Utilize online calculators: Many online calculators can perform temperature conversions quickly and accurately. This can be especially useful for quick conversions.
- Understand the context: Consider the context of the temperature measurement to avoid misunderstandings. A temperature of 35°C feels very different from 35°F.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions for a Seamless Experience
Mastering the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a crucial skill across various fields. From understanding weather conditions to cooking and baking, scientific research to everyday life, the ability to accurately convert temperatures is essential for clear communication, accurate results, and successful outcomes. By understanding the underlying principles and applying the formula correctly, you can easily navigate the world of temperature measurement, improving your efficiency and understanding in various contexts. Remember to utilize the available resources and practice regularly to enhance your skills and ensure accurate conversions. The ability to confidently convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a valuable asset in today's interconnected world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which State Of Matter Is The Most Dense
Apr 01, 2025
-
85 Cm Is What In Inches
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 95 Degrees Fahrenheit Converted To Celsius . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
