A Common Medium Used For Growing Fastidious Bacteria Is
Kalali
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
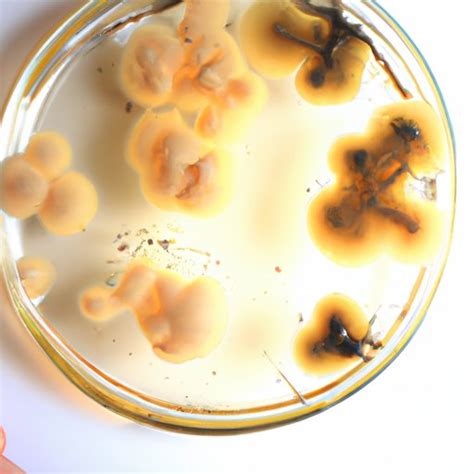
Table of Contents
A Common Medium Used for Growing Fastidious Bacteria Is: Blood Agar
Fastidious bacteria, by definition, are organisms with complex nutritional requirements that exceed those provided by standard media like nutrient agar. Their cultivation requires specialized growth media enriched with specific nutrients, growth factors, and other components to support their growth and survival. A common and exceptionally versatile medium used for cultivating these challenging microbes is blood agar. This article will delve into the composition, preparation, uses, and advantages of blood agar in the context of cultivating fastidious bacteria.
Understanding Blood Agar: Composition and Preparation
Blood agar, a type of enriched medium, is created by supplementing a basal agar medium, typically tryptic soy agar or sheep blood agar base, with 5-10% sterile blood. The choice of blood type significantly impacts the medium's efficacy. Sheep blood is the most frequently employed due to its consistent quality, readily available supply, and ability to support the growth of a wide range of bacteria. However, other blood types such as horse or rabbit blood may be used depending on the specific needs of the cultivation.
The crucial components of blood agar include:
- Basal Agar: This provides the fundamental nutrients necessary for bacterial growth, including carbohydrates, nitrogen sources, and essential minerals. Tryptic soy agar (TSA) is a popular choice because of its rich nutrient profile.
- Blood: The addition of blood enriches the medium with essential growth factors, such as hemin (factor X) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD, factor V), crucial for the growth of many fastidious organisms. It also provides iron and other necessary nutrients.
- Sterility: Maintaining sterility throughout the preparation process is paramount to prevent contamination and ensure reliable results. All components must be sterile, and aseptic techniques must be rigorously followed during mixing and pouring.
The preparation involves several steps:
- Preparing the Basal Agar: The basal agar is prepared according to the manufacturer's instructions. This usually involves suspending the dehydrated medium in distilled water, heating to dissolve, and sterilizing by autoclaving.
- Cooling the Agar: The sterilized agar is then cooled to approximately 45-50°C to prevent hemolysis of the blood cells.
- Adding Sterile Blood: Sterile blood, typically obtained commercially, is aseptically added to the cooled agar. Gentle mixing is crucial to ensure even distribution without introducing air bubbles.
- Pouring the Agar: The blood agar is then poured into sterile Petri dishes, allowing it to solidify.
Hemolytic Reactions: A Key Feature of Blood Agar
One of the most significant uses of blood agar is its ability to differentiate bacteria based on their hemolytic activity – the ability to break down red blood cells. This property is visualized as distinct zones around bacterial colonies:
-
Beta-hemolysis (β-hemolysis): Characterized by complete lysis of red blood cells, resulting in a clear, transparent zone surrounding the colony. This is indicative of potent hemolysins produced by the bacteria. Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus) is a classic example of a beta-hemolytic bacterium.
-
Alpha-hemolysis (α-hemolysis): Partial lysis of red blood cells, resulting in a greenish discoloration around the colony. This is due to the oxidation of hemoglobin. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a common alpha-hemolytic bacterium.
-
Gamma-hemolysis (γ-hemolysis): No lysis of red blood cells; no change in the surrounding agar. These bacteria are non-hemolytic.
Observing hemolytic patterns is critical in identifying bacteria, particularly within the Streptococcus and Staphylococcus genera. The hemolytic reaction provides crucial information for diagnostic purposes, guiding clinicians towards the correct treatment.
Cultivation of Fastidious Bacteria Using Blood Agar
Blood agar's enrichment and the provision of essential growth factors make it ideal for cultivating a wide range of fastidious bacteria, including:
-
Streptococci: Many streptococcal species, including those responsible for strep throat, pneumonia, and other infections, require the enriched environment of blood agar for optimal growth. The hemolytic pattern further aids in species identification.
-
Haemophilus influenzae: This bacterium requires both factor X (hemin) and factor V (NAD) present in blood for growth. Blood agar provides these essential factors, making it crucial for its cultivation.
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae: This sexually transmitted bacterium requires the enriched environment of blood agar for optimal growth and isolation.
-
Other fastidious organisms: Numerous other fastidious bacteria, including some species of Brucella, Pasteurella, and Legionella, may benefit from cultivation on blood agar.
Advantages of Blood Agar in Microbiology
The widespread use of blood agar in microbiology laboratories stems from several significant advantages:
- Enrichment: Its enriched nature supports the growth of a wide spectrum of fastidious bacteria that fail to grow on basic media.
- Differentiation: The ability to differentiate bacteria based on hemolytic patterns is invaluable for diagnostic purposes.
- Simplicity: The preparation is relatively straightforward compared to other specialized media.
- Cost-effectiveness: While it is a more complex medium than basic agars, it remains relatively cost-effective compared to other specialized media required for fastidious organisms.
- Availability: Blood agar base and sheep blood are readily available from most microbiology supply companies, ensuring consistent and reliable supplies for laboratories.
Limitations of Blood Agar
Despite its numerous advantages, blood agar also has certain limitations:
- Overgrowth: Rapidly growing non-fastidious bacteria may overgrow slower-growing fastidious organisms, potentially masking their presence. Selective media may be necessary in conjunction with blood agar to address this.
- Hemolysis variability: Hemolytic reactions can be variable depending on factors such as the blood source, age of the blood, and incubation conditions. Consistency in preparation and incubation is therefore critical.
- Not universally suitable: While suitable for many fastidious organisms, some extremely fastidious bacteria may still require more specialized media formulations for successful growth. Chocolate agar, for instance, is often preferred for organisms like Haemophilus influenzae due to heat-inactivated blood providing even more accessible growth factors.
Conclusion
Blood agar is a cornerstone medium in microbiology laboratories worldwide. Its ability to support the growth of fastidious bacteria while allowing for differentiation based on hemolytic patterns makes it an essential tool for diagnostic purposes. Although it has some limitations, its versatility, relatively simple preparation, and readily available components solidify its status as a fundamental component of clinical and research microbiology. While it is not the only medium used for growing fastidious bacteria, its widespread application and reliability make it a common and valuable choice for cultivating a diverse range of these challenging microorganisms. Understanding its composition, preparation, uses, and limitations is essential for any microbiologist working with fastidious bacterial cultures. Further research and development in media formulations continue to improve the cultivation of even the most challenging bacteria, but blood agar remains a significant and reliable tool in the microbiologist's arsenal.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
12 To The Power Of 4
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Grams Is 1 8 Oz
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Cups In 16 9 Fl Oz
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 54 Inches
Mar 22, 2025
-
1 1 4 Cup Of Water
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Common Medium Used For Growing Fastidious Bacteria Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
