A Ketogenic Diet Limits The Intake Of Which Macronutrient
Kalali
Mar 12, 2025 · 7 min read
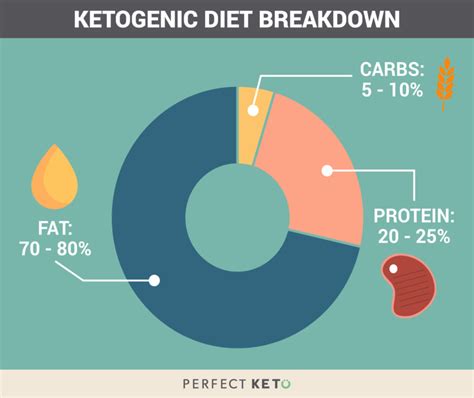
Table of Contents
A Ketogenic Diet: Severely Limiting Carbohydrate Intake for Weight Loss and Beyond
The ketogenic diet, often shortened to "keto," has exploded in popularity as a weight-loss strategy and for managing certain health conditions. But what exactly is a ketogenic diet, and which macronutrient does it drastically restrict? The answer is simple: carbohydrates. This article will delve deep into the ketogenic diet, explaining its principles, mechanisms, benefits, potential drawbacks, and how to successfully implement it.
Understanding the Macronutrients: Fats, Proteins, and Carbohydrates
Before we dive into the specifics of the ketogenic diet, let's review the three macronutrients: fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. These are the essential components of our food that provide energy to the body.
- Carbohydrates: These are the body's primary source of energy. They are found in various foods, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and sugars. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which fuels the cells.
- Proteins: Proteins are crucial for building and repairing tissues, making enzymes and hormones, and supporting various bodily functions. They are found in meat, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, and dairy products.
- Fats: Fats provide a concentrated source of energy and are essential for hormone production, cell function, and nutrient absorption. They're found in oils, nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty meats.
The Core Principle of the Ketogenic Diet: Carbohydrate Restriction
The ketogenic diet is characterized by a very low carbohydrate intake, typically less than 50 grams per day, although this can vary depending on individual factors like activity level and body composition. This severe restriction forces the body into a metabolic state called ketosis.
What is Ketosis?
Ketosis is a natural metabolic process that occurs when the body doesn't have enough carbohydrates for energy. Instead of relying on glucose (from carbohydrates), the liver begins to break down fats into ketones, which are used as an alternative fuel source for the brain and other organs. This shift in fuel source is what makes the ketogenic diet so effective for weight loss and other health benefits.
The Macronutrient Ratio in a Ketogenic Diet
While the exact ratio can vary, a typical ketogenic diet follows a macronutrient breakdown of approximately:
- 70-80% fat: This high fat intake provides the primary energy source during ketosis.
- 20-25% protein: Protein supports muscle mass and various bodily functions. It's important not to overdo protein, as excess protein can be converted into glucose.
- 5-10% carbohydrates: This severely restricted carbohydrate intake is crucial for inducing and maintaining ketosis.
Benefits of a Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet has shown promising results in several areas:
1. Weight Loss:
The primary reason many people adopt the ketogenic diet is for weight loss. By switching the body's primary fuel source from glucose to ketones, the body starts burning stored fat for energy, leading to significant weight loss. This is especially effective for individuals who have struggled to lose weight with other methods.
2. Blood Sugar Control:
The ketogenic diet can significantly improve blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. By reducing carbohydrate intake, it helps stabilize blood glucose levels and reduces insulin resistance.
3. Epilepsy Management:
The ketogenic diet has a long history of use in managing epilepsy, particularly in children who don't respond well to medication. The exact mechanism isn't fully understood, but it's believed that ketones may have anti-convulsive effects.
4. Improved Mental Clarity:
Some individuals report improved mental clarity and focus on the ketogenic diet. This may be due to the stable supply of energy from ketones, avoiding the blood sugar fluctuations associated with carbohydrate consumption.
5. Potential Benefits for Heart Health:
Some studies suggest that the ketogenic diet may improve certain heart health markers, such as reducing triglycerides and increasing HDL ("good") cholesterol. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Potential Drawbacks and Side Effects of a Ketogenic Diet
While the ketogenic diet offers several benefits, it's crucial to be aware of the potential drawbacks:
1. The "Keto Flu":
Many individuals experience a temporary set of symptoms known as the "keto flu" during the initial adaptation phase. These symptoms can include headache, fatigue, nausea, constipation, and dizziness. These usually subside within a few days as the body adjusts to ketosis.
2. Nutrient Deficiencies:
Restricting certain food groups can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned. It's essential to ensure adequate intake of vitamins and minerals through a diverse ketogenic diet or supplementation.
3. Kidney Stones:
Increased excretion of ketones can potentially increase the risk of kidney stones in susceptible individuals. Adequate hydration is vital to mitigate this risk.
4. Constipation:
A low-carbohydrate diet can lead to constipation due to reduced fiber intake. Increasing fiber intake through keto-friendly options like leafy greens and avocado can help prevent this.
5. Long-Term Effects: More Research Needed
While short-term benefits have been documented, long-term studies on the ketogenic diet are still limited. More research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects on overall health.
Transitioning to a Ketogenic Diet: A Step-by-Step Guide
Successfully transitioning to a ketogenic diet requires careful planning and preparation. Here's a step-by-step guide:
-
Gradual Reduction of Carbohydrates: Don't drastically cut carbs overnight. Gradually reduce your intake over several days or weeks to minimize the "keto flu" symptoms.
-
Increase Healthy Fat Intake: Prioritize healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
-
Maintain Adequate Protein Intake: Ensure you're getting enough protein to support muscle mass and overall bodily functions.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out ketones and prevent constipation.
-
Monitor Ketone Levels: Using urine or blood ketone strips can help you track your ketosis levels and ensure you're staying in the metabolic state. This isn't necessary for everyone, but it can be helpful, especially in the beginning.
-
Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before starting any new diet, especially one as restrictive as keto, it's crucial to consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian. This is particularly important if you have any underlying health conditions.
-
Electrolyte Balance: Pay close attention to your electrolyte intake (sodium, potassium, magnesium). These are often lost during the initial stages of ketosis, contributing to keto flu symptoms.
-
Plan Your Meals: Prepare your meals in advance to avoid impulsive unhealthy food choices.
-
Find Keto-Friendly Recipes: There are countless keto-friendly recipes available online and in cookbooks to help you stay on track.
-
Be Patient and Persistent: It takes time to adapt to the ketogenic diet. Don't get discouraged if you experience some initial challenges.
Foods to Include and Avoid on a Ketogenic Diet
Here's a quick overview of foods to include and avoid on a ketogenic diet:
Foods to Include:
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, nuts, seeds, fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna).
- Proteins: Meat (beef, chicken, pork), poultry, fish, eggs, cheese, Greek yogurt (full-fat).
- Low-Carb Vegetables: Leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce), broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, peppers.
- Healthy Fats: Nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil should be your best friends on a keto diet.
Foods to Avoid or Limit:
- Sugary Drinks: Soda, juice, sweetened beverages.
- Processed Foods: Most packaged foods contain hidden sugars and carbohydrates.
- Grains: Bread, pasta, rice, cereal.
- Starchy Vegetables: Potatoes, corn, peas.
- Fruits (Most): While some berries can be consumed in moderation, most fruits are high in sugar.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils.
Conclusion: Ketogenic Diets and Personalized Approaches
The ketogenic diet is a powerful tool for weight loss and managing certain health conditions, primarily through the severe restriction of carbohydrate intake. However, it's essential to approach it with careful planning, monitoring, and professional guidance. It is vital to remember that what works for one person may not work for another. Individual needs and preferences should always be considered, and consulting a healthcare professional is paramount before embarking on a ketogenic diet or any significant dietary change. The information presented here is for educational purposes and should not be considered medical advice. Remember to always prioritize your health and well-being and work with professionals to tailor a plan that suits your specific needs and goals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Fraction Is Equivalent To 1 2
Jul 13, 2025
-
What Is The Average Iq For A 9 Year Old
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Long Does It Take For Brandy Melville To Ship
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Many Times Does 3 Go Into 30
Jul 13, 2025
-
In What Episode Of Bleach Does Ichigo Ask Orihime Out
Jul 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Ketogenic Diet Limits The Intake Of Which Macronutrient . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.