A Kilobyte Is Equal To Approximately One ________ Bytes.
Kalali
Jun 13, 2025 · 2 min read
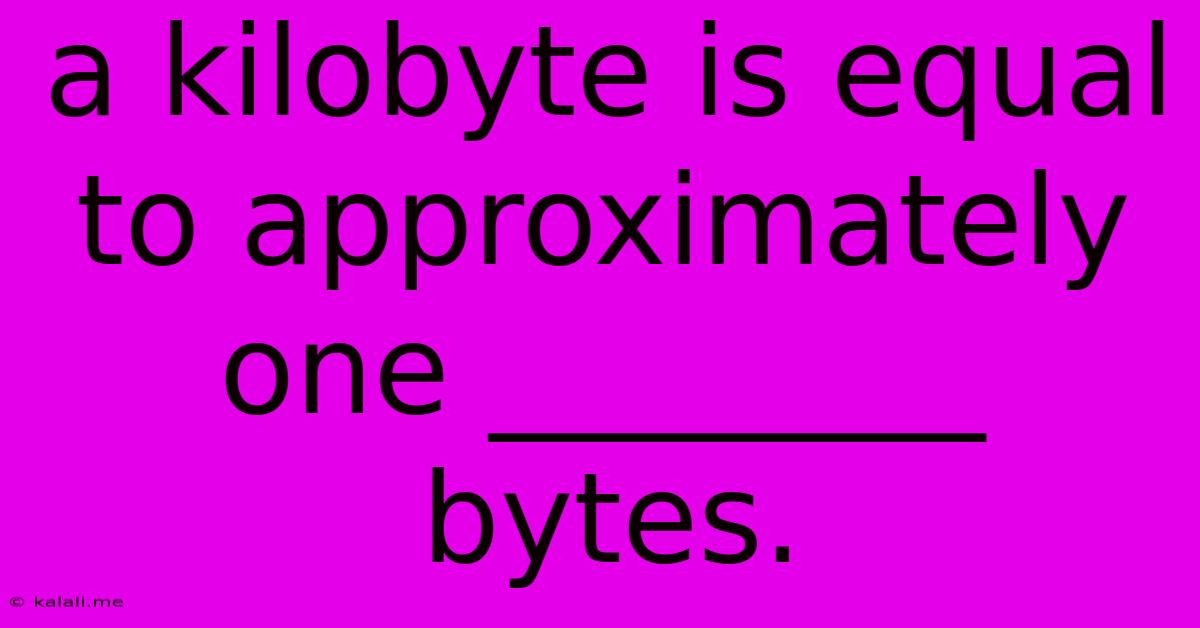
Table of Contents
A Kilobyte is Equal to Approximately One Thousand Bytes
A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of digital information storage. The question "A kilobyte is equal to approximately one ________ bytes?" has a simple answer: one thousand. However, it's crucial to understand that while this is the generally understood definition, the actual value can sometimes differ slightly depending on the context. This article will delve into the nuances of kilobytes and their relationship to bytes, clarifying the common misconception and exploring the related concepts of binary and decimal systems.
This article will cover:
- The fundamental relationship between kilobytes and bytes.
- The difference between decimal and binary kilobytes.
- Practical applications and everyday usage of kilobytes.
- Why understanding this distinction is important for computer users.
Understanding Kilobytes and Bytes
At its core, a byte is the fundamental unit of digital information. It's typically represented by 8 bits. A kilobyte (KB), as you've probably guessed, is a multiple of a byte. The prefix "kilo" means thousand, so a kilobyte is approximately 1,000 bytes. This is the common understanding and the answer to the question posed in the title.
The Decimal vs. Binary Debate: Kibibytes (KiB)
The slight complication arises from the difference between the decimal and binary systems. While the decimal system (base 10) uses powers of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.), computers use the binary system (base 2), which uses powers of 2 (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, etc.).
Therefore, in the binary system, a kilobyte is actually 1024 bytes (2<sup>10</sup> bytes). To avoid confusion, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) introduced the term kibibyte (KiB) to represent 1024 bytes. This distinction helps clarify the difference between the approximate decimal kilobyte (1000 bytes) and the precise binary kibibyte (1024 bytes).
Practical Applications and Everyday Usage
You encounter kilobytes frequently in daily computing:
- File sizes: Small text files, images, or documents are often measured in kilobytes.
- Memory: While less common now, older devices might have specifications expressed in kilobytes.
- Data transfer rates: Though megabytes and gigabytes are more prevalent, you might still see kilobytes used in slower data transfer situations.
Why Understanding This Distinction Matters
Knowing the difference between a kilobyte (approximately 1000 bytes) and a kibibyte (1024 bytes) is important for precise data measurement and understanding technical specifications. While the difference is small for individual kilobytes, it becomes significant when dealing with larger amounts of data. This knowledge can prevent confusion and misunderstandings when interpreting file sizes, memory capacity, and data transfer speeds. Understanding these units helps you become a more informed and knowledgeable computer user.
In conclusion, while a kilobyte is approximately one thousand bytes, the binary system used in computers defines a kilobyte as 1024 bytes (or more precisely, a kibibyte). Understanding this nuance is essential for comprehending digital data storage and processing accurately.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True Of Glycolysis
Jun 14, 2025
-
Diagram Difference Between Frog And Toad
Jun 14, 2025
-
Heat Energy Is Measured In Units Of
Jun 14, 2025
-
Difference Between A Magazine And A Newspaper
Jun 14, 2025
-
Good Words To Describe Your Mother
Jun 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Kilobyte Is Equal To Approximately One ________ Bytes. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.