A Temperature Difference Of 5 K Is Equal To
Kalali
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
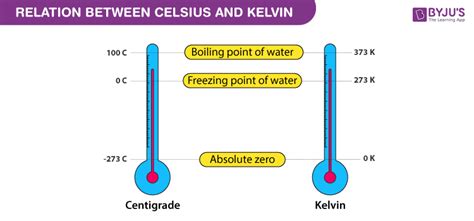
Table of Contents
A Temperature Difference of 5 K is Equal To... A Deep Dive into Kelvin and its Significance
A temperature difference of 5 K (Kelvin) might seem like a small, insignificant number. However, understanding what this difference represents unlocks a deeper appreciation for the Kelvin scale and its crucial role in physics, engineering, and various scientific disciplines. This article will explore the implications of a 5 K temperature difference, explaining the Kelvin scale, its relationship to Celsius and Fahrenheit, and showcasing real-world examples where this seemingly small change can have significant consequences.
Understanding the Kelvin Scale
The Kelvin scale, denoted by K, is the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. Unlike Celsius and Fahrenheit, which use arbitrary reference points (like the freezing and boiling points of water), the Kelvin scale begins at absolute zero – the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. This absolute zero is defined as 0 K, and it's a fundamental concept in thermodynamics.
Key differences from Celsius and Fahrenheit:
- Absolute Zero: The Kelvin scale's starting point, 0 K, represents the absence of all thermal energy. Celsius and Fahrenheit have arbitrary zero points.
- Unit Size: The size of a Kelvin degree is identical to that of a Celsius degree. This means a temperature change of 5 K is exactly equivalent to a temperature change of 5 °C.
- No Negative Temperatures: Since Kelvin starts at absolute zero, there are no negative temperatures on this scale.
5 K Temperature Difference: What Does it Mean?
A 5 K temperature difference signifies a change in thermal energy. This change, though seemingly small, can have significant effects depending on the context. Let's explore several scenarios:
1. Cryogenics and Superconductivity
In cryogenics, the study of extremely low temperatures, a 5 K difference can be substantial. Many materials exhibit fascinating properties at very low temperatures, including superconductivity – the ability to conduct electricity with zero resistance. A 5 K shift might move a material from a superconducting state to a normal resistive state, or vice versa, depending on its critical temperature (Tc). This has huge implications for superconducting magnets used in MRI machines, particle accelerators, and other advanced technologies. A slight temperature fluctuation could severely impact their functionality.
2. Space Exploration and Astrophysics
In the extreme cold of space, even a 5 K difference can matter. Spacecraft components need to withstand immense temperature variations, and precise temperature control is essential for their operation. Instruments designed for sensitive measurements in deep space require exceptionally stable thermal environments, with even small fluctuations potentially affecting the accuracy of observations. Consider the James Webb Space Telescope, which operates at incredibly low temperatures to detect faint infrared signals from distant galaxies. A 5K shift could compromise its operational capabilities.
3. Semiconductor Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry relies on highly precise temperature control during chip manufacturing. Even small temperature variations can significantly affect the properties of semiconductors, impacting their performance and reliability. Etching, doping, and other critical processes in chip fabrication require extremely stable thermal environments. A 5 K difference during a delicate manufacturing step could result in defects, leading to malfunctions or lower yields.
4. Materials Science and Phase Transitions
Many materials undergo phase transitions at specific temperatures. These transitions can involve changes in physical state (e.g., solid to liquid) or crystal structure. A 5 K temperature difference could be enough to trigger or prevent a phase transition, dramatically altering the material's properties. This is critical in materials science research, where precise temperature control is essential for studying and manipulating material behavior.
5. Climate Science and Meteorology
While a 5 K change in ambient temperature may not seem dramatic at first glance, it is significant in climate science, especially when considering global average temperature increases. A global average temperature increase of 5 K would represent a catastrophic climate change scenario, leading to widespread melting of polar ice caps, extreme weather events, and significant disruptions to ecosystems. While a localized 5K change might seem less alarming, it can still point towards a larger regional climate trend that needs attention.
The Practical Applications and Implications of Precise Temperature Control
The examples above highlight the significance of even small temperature differences, particularly in situations demanding precise thermal regulation. Maintaining stable temperatures within a 5 K range (or even tighter tolerances) often requires sophisticated techniques:
- Cryostats: Devices for maintaining extremely low temperatures, frequently used in cryogenic research and applications.
- Thermoelectric Coolers (Peltier devices): These solid-state devices offer precise temperature control without the use of refrigerants.
- High-precision Thermometers: Accurate temperature measurement is crucial, using sensors like resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), thermocouples, or thermistors.
- Thermal Insulation: Minimizing heat transfer is essential for maintaining stable temperatures, often achieved through vacuum insulation, specialized materials, or cryogenic shrouds.
The Relationship between Kelvin, Celsius, and Fahrenheit
To fully appreciate the significance of a 5 K difference, it's vital to understand its relationship to other temperature scales:
- Kelvin to Celsius: K = °C + 273.15
- Celsius to Kelvin: °C = K - 273.15
- Celsius to Fahrenheit: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
- Fahrenheit to Celsius: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Therefore, a 5 K temperature difference is exactly equivalent to a 5 °C temperature difference. However, the equivalent change in Fahrenheit would be 9 °F (5°C x 9/5). This emphasizes the importance of using the appropriate scale for different applications.
Conclusion: The Subtle but Profound Impact of 5 K
A temperature difference of 5 K, while numerically small, carries significant implications across various scientific and technological domains. From the cryogenic world of superconductivity to the vast expanse of space exploration and the intricate processes of semiconductor manufacturing, precise temperature control within this range is often critical for optimal performance, accuracy, and stability. Understanding the Kelvin scale and its relationship to other temperature scales is key to grasping the profound impact that even small temperature changes can have. This highlights the importance of advanced thermal management techniques and precise temperature measurement in a wide array of applications. The seemingly simple 5 K difference unveils a complex world where subtle shifts in temperature can lead to substantial outcomes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Kilos Are 20 Pounds
Mar 19, 2025
-
11 Out Of 30 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 92 Grados Fahrenheit En Centigrados
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Get Magnitude Of Force
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Can You Separate Sugar From Water
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Temperature Difference Of 5 K Is Equal To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
