Another Name For Newton's First Law Of Motion
Kalali
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
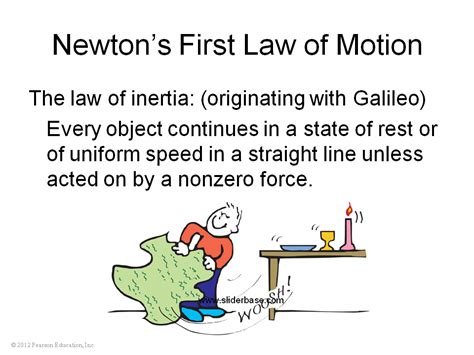
Table of Contents
Another Name for Newton's First Law of Motion: Unpacking the Law of Inertia
Newton's First Law of Motion, a cornerstone of classical mechanics, is famously known as the law of inertia. However, understanding its implications and nuances requires exploring its various interpretations and the reasons behind its different names. This comprehensive article delves deep into Newton's First Law, exploring its multiple names, its profound implications, and its applications across various scientific fields. We'll unpack the core concepts, address common misconceptions, and showcase its enduring relevance in the modern world.
Understanding Newton's First Law: The Foundation of Motion
Before we dive into alternative names, let's solidify our understanding of the law itself. Newton's First Law states: An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
This seemingly simple statement packs a powerful punch. It introduces the concept of inertia, the inherent resistance of an object to changes in its state of motion. This resistance is directly proportional to the object's mass: more massive objects exhibit greater inertia.
Key Components of Newton's First Law:
- Inertia: The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. This is the central concept behind the law.
- Rest: A state of zero velocity. An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an external force.
- Motion: A state of non-zero velocity. An object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity (both speed and direction) unless an external force acts upon it.
- Unbalanced Force: A net force acting on an object. If the forces acting on an object are balanced, the object's state of motion remains unchanged.
Why "Law of Inertia" is the Most Common Name?
The name "Law of Inertia" directly reflects the central concept of the law – inertia. It highlights the object's inherent resistance to changes in its state of motion. This name is concise, descriptive, and effectively captures the essence of the principle. Its widespread adoption makes it the most universally recognized name for Newton's First Law.
Alternative Names and Interpretations: Expanding the Understanding
While "Law of Inertia" is the most prevalent term, several other names and interpretations highlight different aspects of the law:
1. The Law of Conservation of Momentum (in a specific context):
While not a direct synonym, the Law of Conservation of Momentum is deeply related to Newton's First Law. In the absence of external forces, the total momentum of a system remains constant. This conservation of momentum is a direct consequence of inertia. If no external forces act on a system, individual objects within the system will maintain their respective momenta, thus preserving the total momentum of the system. This connection provides a broader perspective on the implications of inertia.
2. The Law of Uniform Motion:
This name emphasizes the crucial aspect of constant velocity. If an object is in motion and no unbalanced force acts upon it, it continues its motion with uniform speed and in a straight line. This name is particularly helpful when discussing the motion of objects in the absence of friction or other resistive forces.
3. The Galilean Principle of Relativity (in a limited sense):
Galileo Galilei, a precursor to Newton, laid groundwork for the understanding of inertia. His observations of projectile motion contributed significantly to the concept. While not an exact equivalent, Newton's First Law can be seen as a refined and formalized version of Galileo's insights into relative motion. In a frame of reference moving with constant velocity, the laws of motion are the same as in a stationary frame. This aspect connects Newton's First Law to the broader principle of relativity.
4. The Principle of Inertia:
This phrasing often appears in textbooks and scientific literature, emphasizing the fundamental principle at the heart of the law. It underscores the importance of inertia as a core concept in understanding motion.
Applications of Newton's First Law Across Disciplines
The implications of Newton's First Law extend far beyond textbook examples. Its applications span a wide range of scientific fields and everyday experiences:
1. Automotive Safety:
Seat belts, airbags, and crumple zones in vehicles are all designed based on the principle of inertia. In a collision, a passenger's body tends to continue moving forward due to inertia. These safety features are designed to counteract this inertia and minimize injury.
2. Sports:
Understanding inertia is crucial in many sports. The follow-through in a golf swing or baseball bat swing utilizes inertia to maximize the impact force. Inertia also plays a vital role in activities like ice skating and skiing.
3. Aerospace Engineering:
Designing rockets and spacecraft requires a deep understanding of inertia. The massive thrust needed to overcome the inertia of a spacecraft is a direct consequence of the law.
4. Robotics:
In robotics, understanding inertia helps engineers to design more efficient and stable robots. The ability to predict and control the inertia of robotic components is critical in their movement and functionality.
5. Everyday Life:
Many everyday experiences illustrate the principle of inertia. The feeling of being pushed back in your seat when a car accelerates or thrown forward during sudden braking is a direct result of inertia. Similarly, the difficulty in starting a heavy object from rest is a manifestation of its inertia.
Misconceptions about Newton's First Law
Several common misconceptions surround Newton's First Law:
-
Objects at rest require no force to remain at rest: This is incorrect. While a balanced force system results in no net force and hence no change in motion, this does not mean no forces are acting on the object. Gravity and normal forces act on an object at rest, creating a balanced system.
-
Friction is ignored in the law: Friction is a force that opposes motion. Newton's First Law describes motion in the absence of unbalanced forces. Friction is a force, and if present, it would create an unbalanced force, leading to a change in motion. The law doesn't ignore friction; it simply states that if there's no unbalanced force, then motion remains constant.
-
Inertia is a force: Inertia is not a force but a property of matter – its resistance to changes in its motion. Forces cause changes in motion; inertia is the object's resistance to those changes.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Newton's First Law
Newton's First Law, irrespective of its name—be it the Law of Inertia, the Law of Uniform Motion, or any other suitable descriptor—remains a fundamental pillar of classical mechanics. Its implications reach far beyond theoretical physics, permeating our daily lives and shaping technological advancements. By understanding its nuances, we can appreciate its profound impact on our understanding of motion and the universe around us. Further exploration into this fundamental law unveils a rich tapestry of concepts that underpin our understanding of physics and engineering. Continual study and application of Newton's First Law are critical for continued advancements in science and technology. Its legacy as a foundational principle ensures its continued relevance for generations to come. The various names reflect different aspects of this powerful law, providing a multifaceted perspective on its importance and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Prehistoric Humans Felt Stress
Apr 03, 2025
-
120 Out Of 150 As A Percentage
Apr 03, 2025
-
Cuanto Son 40 Onzas En Litros
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is 19 Out Of 25
Apr 03, 2025
-
Cuantos Grados Son 64 Fahrenheit En Centigrados
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Another Name For Newton's First Law Of Motion . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
