Are Liver Cells Haploid Or Diploid
Kalali
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
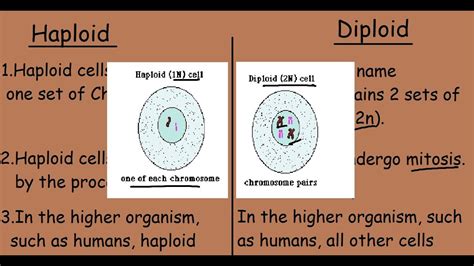
Table of Contents
Are Liver Cells Haploid or Diploid? Understanding Ploidy in Somatic Cells
The question of whether liver cells are haploid or diploid is fundamental to understanding cell biology and genetics. The answer, simply put, is diploid. However, a deeper dive reveals a nuanced understanding of ploidy and its implications for liver cell function, health, and disease. This comprehensive article will explore the concept of ploidy, the specific ploidy of liver cells (hepatocytes), and delve into situations where deviations from typical diploid status can occur.
Understanding Ploidy: Haploid vs. Diploid
Before we examine liver cells specifically, let's establish a clear understanding of ploidy. Ploidy refers to the number of complete sets of chromosomes found in a biological cell. Chromosomes, the structures carrying genetic information (DNA), exist in pairs in most organisms.
-
Haploid (n): A cell containing only one complete set of chromosomes. In humans, this means 23 chromosomes. Gametes, or sex cells (sperm and egg), are prime examples of haploid cells. Their role in sexual reproduction requires a halving of the chromosome number to maintain the species' characteristic diploid number after fertilization.
-
Diploid (2n): A cell containing two complete sets of chromosomes. In humans, this means 46 chromosomes (23 pairs). The vast majority of cells in the human body, known as somatic cells, are diploid. These include liver cells, skin cells, muscle cells, and nerve cells, among others.
Liver Cells (Hepatocytes): A Diploid Workforce
Liver cells, also known as hepatocytes, are the primary functional cells of the liver. They perform a multitude of vital functions, including:
- Metabolism: Processing nutrients, synthesizing proteins, and breaking down toxins.
- Detoxification: Filtering harmful substances from the bloodstream.
- Bile Production: Producing bile, crucial for fat digestion and absorption.
- Storage: Storing essential nutrients like glucose and vitamins.
These complex functions necessitate a complete set of genetic instructions, which is precisely what a diploid cell provides. The two sets of chromosomes allow for redundancy and the potential for gene expression regulation, essential for the liver's intricate metabolic activities. Therefore, the standard and functional state of liver cells is diploid. This diploid nature ensures the proper functioning of the liver and its crucial contributions to overall body homeostasis.
Exceptions and Deviations from Diploid Status in Liver Cells
While the diploid state is the norm, there are exceptions and situations where deviations from the typical diploid number of chromosomes can occur in liver cells. These deviations are often associated with pathological conditions.
Polyploidy in Liver Cells
Polyploidy refers to the presence of more than two complete sets of chromosomes in a cell. Polyploidy in liver cells is relatively common, particularly in adult livers. This means some liver cells may be triploid (3n), tetraploid (4n), or even higher ploidy levels. The exact causes and consequences of polyploidy in liver cells are still being actively researched, but several factors are implicated:
- Endoreduplication: A process where DNA replicates without subsequent cell division, leading to increased chromosome number within a single cell.
- Cell Fusion: The merging of two or more cells, combining their chromosomal content.
- Mitotic Errors: Errors during cell division can result in the unequal distribution of chromosomes, leading to cells with abnormal ploidy levels.
The significance of polyploidy in liver cells remains an area of active investigation. While it's often associated with aging and some liver diseases, it doesn't automatically imply impaired function. In some cases, polyploidy might even provide a functional advantage, potentially increasing protein synthesis or enhancing metabolic capacity. However, excessive polyploidy or its association with specific pathological conditions may contribute to liver dysfunction.
Aneuploidy in Liver Cells
Aneuploidy refers to an abnormal number of chromosomes, which is not a whole multiple of the haploid number (n). This differs from polyploidy, where the chromosome number is a whole multiple of n. Aneuploidy in liver cells is less frequent than polyploidy but can be associated with various liver diseases, including:
- Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma): Aneuploidy is a hallmark of many cancerous cells, including those in hepatocellular carcinoma. The chromosomal instability associated with aneuploidy contributes to the uncontrolled growth and malignant transformation of liver cells.
- Chronic Liver Diseases: Conditions like cirrhosis and hepatitis can lead to increased chromosomal instability and aneuploidy in liver cells, contributing to the progression of liver damage.
Aneuploidy is often indicative of genomic instability, a characteristic of many diseases. The presence of aneuploid liver cells reflects a disruption in the precise control of cell division and chromosomal segregation, which is associated with a higher risk of malignant transformation.
Detecting Ploidy in Liver Cells: Techniques and Methods
Determining the ploidy of liver cells requires specialized techniques. Several methods are employed, each with its strengths and limitations:
- Flow Cytometry: This technique uses fluorescent dyes to label DNA, enabling the measurement of DNA content in individual cells. This provides a rapid assessment of ploidy levels in a large population of liver cells.
- Microscopy: Microscopic examination of liver cell nuclei can reveal variations in size, which may reflect different ploidy levels. However, this method is less precise than flow cytometry.
- Chromosome Analysis (Karyotyping): This technique involves staining and visualizing individual chromosomes, allowing for a detailed examination of chromosome number and structure. It's more labor-intensive than flow cytometry but provides a more comprehensive analysis of chromosomal abnormalities.
These techniques are often used in research settings and in clinical diagnostics to assess liver health and diagnose diseases.
The Importance of Understanding Liver Cell Ploidy
Understanding the ploidy of liver cells, both the typical diploid state and deviations from it, is crucial for several reasons:
- Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis: Changes in ploidy can serve as biomarkers for liver diseases, particularly liver cancer. Assessing ploidy levels can assist in diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment decisions.
- Drug Development: Knowledge of ploidy and its impact on cellular function can inform the development of targeted therapies for liver diseases.
- Basic Research: Investigating the mechanisms underlying changes in liver cell ploidy provides insights into fundamental cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation, DNA replication, and genomic stability.
Conclusion: Ploidy – A Key Indicator of Liver Health
In conclusion, while the typical and functional state of liver cells is diploid, deviations in ploidy, particularly polyploidy and aneuploidy, are observed in various circumstances. These deviations are often linked to aging, liver disease, and liver cancer. Advances in techniques for detecting ploidy have significantly improved our understanding of liver cell biology and pathology. Further research into the causes and consequences of ploidy changes in liver cells will be vital for developing improved diagnostic tools and therapies for liver-related diseases. The study of ploidy in liver cells highlights the intricate and dynamic nature of cellular processes and their importance in maintaining health and preventing disease.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
18 Out Of 25 As A Percentage
Mar 24, 2025
-
4 Out Of 6 Is What Percent
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 155 Cm
Mar 24, 2025
-
5 Cups Is How Many Fluid Ounces
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Renewable Resource
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Are Liver Cells Haploid Or Diploid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
