Colorless Liquid Hydrocarbon Of Alkane Series
Kalali
Jun 14, 2025 · 3 min read
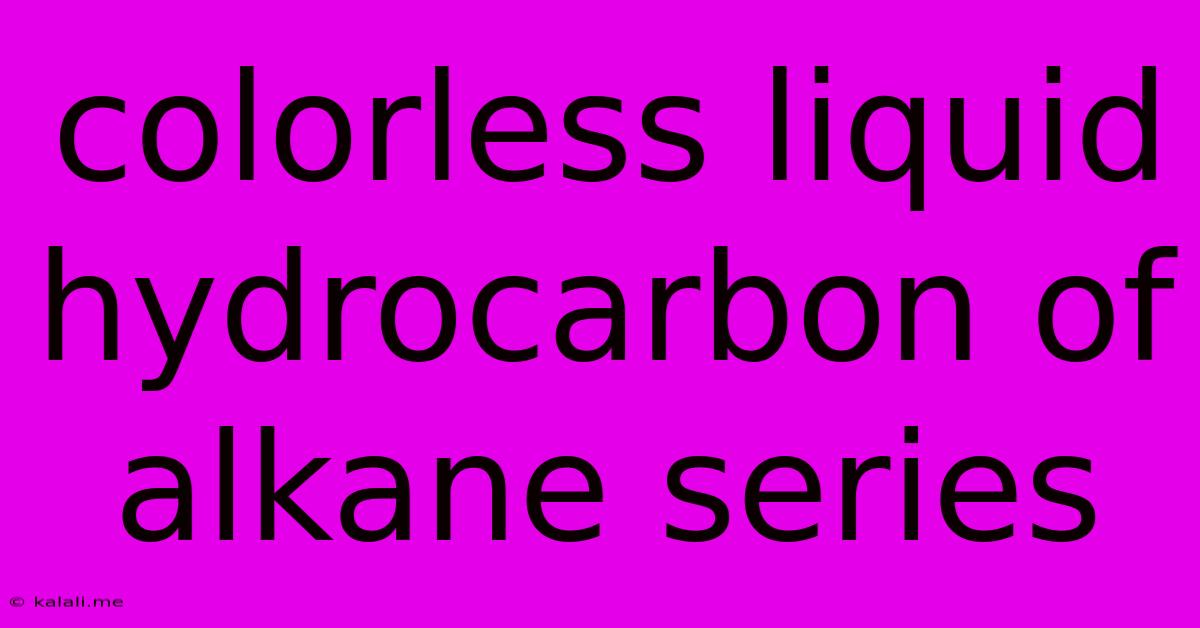
Table of Contents
Understanding Colorless Liquid Hydrocarbons of the Alkane Series
Meta Description: Explore the fascinating world of colorless liquid alkanes – their properties, uses, and importance in various industries. Learn about common examples and the factors influencing their characteristics.
Colorless liquid hydrocarbons belonging to the alkane series are a significant class of organic compounds with widespread applications. These saturated hydrocarbons, characterized by single carbon-carbon bonds (C-C) and carbon-hydrogen bonds (C-H), are crucial in various industries and play a vital role in our daily lives. This article will delve into the properties, uses, and importance of these remarkable compounds.
Properties of Colorless Liquid Alkanes
The physical properties of colorless liquid alkanes are largely determined by their molecular weight and chain length. Generally, they are:
- Non-polar: Their symmetrical structure and non-polar C-H bonds result in weak intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces). This contributes to their low boiling points and volatility.
- Insoluble in water: Due to their non-polar nature, they are immiscible with water but readily dissolve in non-polar solvents like ether and benzene.
- Low reactivity: Alkanes are relatively unreactive compared to other hydrocarbon classes. Their stability stems from the strong C-C and C-H bonds. They primarily undergo combustion reactions, readily burning in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
- Boiling point increases with molecular weight: As the chain length increases, the van der Waals forces become stronger, leading to higher boiling points. This means shorter-chain alkanes are liquids at room temperature, while longer chains are often solids.
Common Examples of Colorless Liquid Alkanes
Several alkanes exist as colorless liquids at room temperature. Some common examples include:
- Butane (C₄H₁₀): Used as a fuel in lighters and camping stoves.
- Pentane (C₅H₁₂): Used as a solvent and in the production of certain polymers.
- Hexane (C₆H₁₄): A common solvent in the laboratory and industry.
- Heptane (C₇H₁₆): Used as a solvent and in the production of gasoline.
- Octane (C₈H₁₈): A major component of gasoline, with its octane rating reflecting its resistance to knocking in internal combustion engines.
Uses and Applications of Colorless Liquid Alkanes
The versatility of colorless liquid alkanes makes them essential in a wide range of applications:
- Fuels: Many alkanes, such as butane, propane, octane and others, serve as vital fuels in various applications, from heating and cooking to powering vehicles.
- Solvents: Alkanes like hexane and heptane are widely used as solvents in various industrial processes, such as cleaning, extraction and chemical synthesis.
- Chemical feedstocks: They serve as essential building blocks in the petrochemical industry, being used in the production of plastics, synthetic fibers, and other important materials.
- Refrigerants: Certain alkanes are used as refrigerants in refrigeration systems.
Factors Influencing the Properties of Colorless Liquid Alkanes
Several factors influence the specific properties of these compounds:
- Chain branching: Branched-chain alkanes have lower boiling points than their straight-chain isomers due to reduced surface area and weaker intermolecular forces.
- Molecular weight: As mentioned earlier, higher molecular weight correlates with higher boiling points and potentially a transition from liquid to solid state at room temperature.
- Conformational isomers: Different conformations of the same alkane molecule can have slightly different properties.
In conclusion, colorless liquid alkanes are a crucial class of hydrocarbons with numerous applications. Their properties, determined by their molecular structure and intermolecular forces, make them valuable in various industries. Understanding their characteristics is key to appreciating their significance in our modern world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
University Of North Carolina Wilmington Sat Scores
Jun 14, 2025
-
Perimeter Of Isosceles Right Angled Triangle
Jun 14, 2025
-
Mosses And Lichens Are Found In
Jun 14, 2025
-
An Organism That Feeds On Dead And Decomposing Matter
Jun 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Characteristic Of Shifting Cultivation
Jun 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Colorless Liquid Hydrocarbon Of Alkane Series . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.