Common Multiples Of 2 And 5
Kalali
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
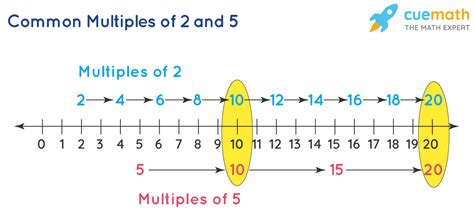
Table of Contents
Common Multiples of 2 and 5: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding common multiples is a fundamental concept in number theory with applications extending far beyond the classroom. Understanding common multiples, especially those of seemingly simple numbers like 2 and 5, unlocks a deeper appreciation for mathematical relationships and provides a strong foundation for more advanced concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of common multiples of 2 and 5, exploring their properties, methods of identification, and practical applications.
Understanding Multiples and Common Multiples
Before we dive into the specifics of 2 and 5, let's establish a clear understanding of the core terms.
What are Multiples?
A multiple of a number is the result of multiplying that number by any integer (whole number). For example:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20... and so on.
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50... and so on.
Notice that multiples extend infinitely in both positive and negative directions. However, we often focus on positive multiples in practical applications.
What are Common Multiples?
A common multiple of two or more numbers is a number that is a multiple of all those numbers. For example, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30...
The common multiples of 2 and 3 are the numbers that appear in both lists: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30... and so on.
Identifying Common Multiples of 2 and 5
Finding the common multiples of 2 and 5 is relatively straightforward due to their prime factorization. Both 2 and 5 are prime numbers; they are only divisible by 1 and themselves. This simplifies the process significantly.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most basic method is to list the multiples of each number and identify the common ones.
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50...
By comparing the two lists, we immediately see that the common multiples are 10, 20, 30, 40, 50... and so on.
Method 2: Using the Least Common Multiple (LCM)
A more efficient method involves finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM). The LCM is the smallest positive common multiple of two or more numbers. Once you find the LCM, all other common multiples are multiples of the LCM.
For 2 and 5, the LCM can be easily determined:
- Prime Factorization: The prime factorization of 2 is simply 2. The prime factorization of 5 is simply 5.
- LCM Calculation: Since 2 and 5 are prime and have no common factors, their LCM is their product: 2 x 5 = 10.
Therefore, the common multiples of 2 and 5 are all multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60... and so on. This method is far more efficient than listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers.
Properties of Common Multiples of 2 and 5
The common multiples of 2 and 5 exhibit several interesting properties:
- All end in 0: A crucial observation is that all common multiples of 2 and 5 end in the digit 0. This is because any multiple of 10 (the LCM) will always be a multiple of both 2 and 5. This property makes them easily identifiable.
- Divisible by 10: As mentioned earlier, all common multiples are divisible by 10. This is a direct consequence of the LCM being 10.
- Even Numbers: Since all common multiples are multiples of 2, they are all even numbers.
- Infinite Number of Common Multiples: Like all pairs of numbers, there are infinitely many common multiples of 2 and 5.
Applications of Common Multiples of 2 and 5
Understanding common multiples, particularly those of 2 and 5, has practical applications in various fields:
Everyday Life:
- Counting Objects: Imagine you're arranging objects in rows and columns. If you want to arrange them in groups of 2 and also in groups of 5, the total number of objects must be a common multiple of 2 and 5 (a multiple of 10).
- Time Measurement: The most common application is in time. Minutes and seconds are inherently connected to multiples of 2 and 5. 60 seconds in a minute (multiples of 2 and 5), 60 minutes in an hour, etc. This structure is based on ancient Babylonian systems employing base-60 which has many factors including 2 and 5.
- Money: Many currencies are structured in base-10 systems which directly relates to common multiples of 2 and 5. This makes financial calculations easier and more intuitive.
Mathematics and Computer Science:
- Modular Arithmetic: Common multiples play a key role in modular arithmetic, which is widely used in cryptography and computer science algorithms.
- Number Theory: Understanding common multiples is foundational to number theory, providing insight into the structure and relationships between integers.
- Algorithm Design: Efficient algorithms for finding LCMs and common multiples are crucial for many computer science tasks.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
While we've focused on the common multiples of 2 and 5, the concepts can be expanded:
Finding Common Multiples of More Than Two Numbers
The process extends to finding common multiples of more than two numbers. For example, to find the common multiples of 2, 3, and 5, one would first find the LCM of these three numbers. The prime factorization method is particularly useful in these cases. The LCM of 2, 3, and 5 is 2 x 3 x 5 = 30. Therefore, all common multiples of 2, 3, and 5 are multiples of 30.
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and LCM Relationship
The GCD (greatest common divisor) and LCM are closely related. For any two integers a and b, the product of their GCD and LCM is always equal to the product of the two numbers (a x b). This relationship provides a powerful tool for calculating either the GCD or the LCM if the other is known.
Applications in Abstract Algebra
The concepts of multiples and common multiples extend into the realm of abstract algebra, where they play a role in understanding the structure of groups and rings.
Conclusion
Understanding common multiples, even for seemingly simple numbers like 2 and 5, reveals a rich mathematical landscape with numerous practical and theoretical applications. From everyday tasks to advanced mathematical concepts, the ability to identify and work with common multiples is an essential skill. The simplicity of finding common multiples of 2 and 5 provides a solid foundation for exploring more complex number theory concepts and their diverse applications across various fields. Mastering these fundamental ideas opens doors to a deeper understanding of the intricate world of mathematics and its influence on our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
7am To 11am Is How Many Hours
Jul 12, 2025
-
If Your 35 What Year Was You Born
Jul 12, 2025
-
How Many Cups Is 1 Pound Of Cheese
Jul 12, 2025
-
30 X 30 Is How Many Square Feet
Jul 12, 2025
-
How Much Does A Half Oz Weigh
Jul 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Multiples Of 2 And 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.