Common Multiples Of 4 5 6
Kalali
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
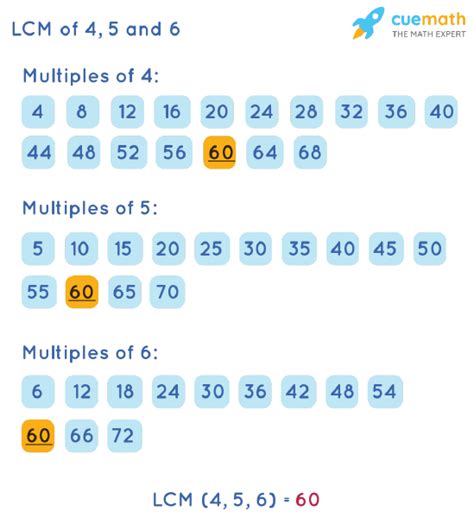
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of Common Multiples: A Deep Dive into 4, 5, and 6
Finding the common multiples of 4, 5, and 6 might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, but it opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, with applications far beyond the classroom. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to find these common multiples but also explore the underlying concepts, practical applications, and even delve into more advanced mathematical ideas related to this seemingly basic problem.
Understanding Multiples and Common Multiples
Before we dive into the specifics of 4, 5, and 6, let's establish a firm understanding of the core concepts.
What is a multiple? A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any other integer (whole number). For example, multiples of 4 are: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, and so on. Each of these numbers is the result of multiplying 4 by an integer (4 x 1, 4 x 2, 4 x 3, etc.).
What is a common multiple? A common multiple is a number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. For instance, consider the numbers 4 and 6. Some multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20... Some multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30... Notice that 12 and 24 appear in both lists. These are common multiples of 4 and 6.
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)? The least common multiple (LCM) is the smallest positive common multiple of two or more numbers. In our example of 4 and 6, the LCM is 12.
Finding the Common Multiples of 4, 5, and 6
Now, let's tackle the task at hand: finding the common multiples of 4, 5, and 6. There are several methods to achieve this.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is a straightforward approach, particularly useful for smaller numbers. Let's list the multiples of each number:
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 50, 52, 56, 60, ...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, ...
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, ...
By comparing the lists, we can identify the common multiples: 60, 120, 180, and so on. The Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 4, 5, and 6 is 60.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 4: 2 x 2 = 2²
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ = 5
Multiply these together: 4 x 3 x 5 = 60. Therefore, the LCM of 4, 5, and 6 is 60.
Method 3: Using the Formula (for two numbers only)
While this formula directly applies only to finding the LCM of two numbers, it can be used iteratively. The formula is:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where GCD is the Greatest Common Divisor. Let's find the LCM of 4 and 5 first. The GCD of 4 and 5 is 1.
LCM(4, 5) = (4 x 5) / 1 = 20
Now, let's find the LCM of 20 and 6. The GCD of 20 and 6 is 2.
LCM(20, 6) = (20 x 6) / 2 = 60
Therefore, the LCM of 4, 5, and 6 is 60. This method is less efficient for more than two numbers.
Real-World Applications of Finding the LCM
Understanding and finding common multiples, especially the LCM, has numerous practical applications in various fields:
Scheduling and Timing
Imagine you have three different machines that operate on cycles: machine A every 4 hours, machine B every 5 hours, and machine C every 6 hours. To find when all three machines will be down for maintenance simultaneously, you need to find the LCM of 4, 5, and 6, which is 60. Therefore, all three machines will be down for maintenance together after 60 hours.
Measurement and Conversion
When dealing with different units of measurement, the LCM can be vital for simplifying calculations. For example, in converting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM helps in finding the least common denominator (LCD).
Project Management and Teamwork
In project management, where multiple tasks with different durations are involved, finding the LCM can help determine the earliest time when all tasks can be completed synchronously.
Music and Rhythm
In music theory, the LCM helps in understanding rhythmic patterns and finding the least common denominator for notes and beats.
Geometry and Tessellations
When dealing with geometric shapes, the LCM is utilized to arrange patterns and create tessellations, ensuring seamless arrangements.
Exploring Further: Advanced Concepts
The seemingly simple problem of finding the common multiples of 4, 5, and 6 opens the door to deeper mathematical concepts:
-
Modular Arithmetic: The concept of common multiples is deeply intertwined with modular arithmetic, which deals with remainders after division. This has significant applications in cryptography and computer science.
-
Number Theory: The study of prime factorization and the properties of numbers, such as the greatest common divisor and least common multiple, are fundamental aspects of number theory. This branch of mathematics has implications far beyond simple arithmetic.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concepts of LCM and GCD extend into abstract algebra, where they are generalized and studied in a broader context of algebraic structures.
-
Algorithms and Computational Complexity: Efficient algorithms for calculating the LCM and GCD are important in computer science, particularly when dealing with very large numbers.
Conclusion
Finding the common multiples of 4, 5, and 6, while seemingly basic, reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts with wide-ranging applications. Understanding these principles not only enhances mathematical proficiency but also equips one with problem-solving skills valuable in diverse fields. This exploration demonstrates the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and their practical relevance in the real world. From scheduling maintenance to understanding rhythmic patterns, the LCM provides a fundamental tool for navigating various complexities. The journey from simple arithmetic to the deeper concepts of number theory and abstract algebra showcases the beauty and power of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Bottles Of Water Is 1 Liter
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days In A Million Minutes
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days Is In 11 Weeks
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Grams Are In One Tola Gold
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Oz In A Pound Of Freon
Jul 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Multiples Of 4 5 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.