Common Multiples Of 6 And 9
Kalali
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
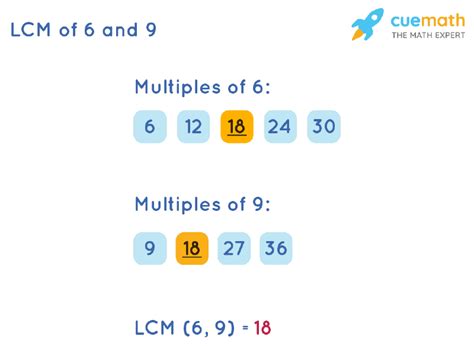
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of Common Multiples: A Deep Dive into the World of 6 and 9
Finding common multiples, especially for seemingly simple numbers like 6 and 9, might seem like a straightforward task. However, a deeper exploration reveals fascinating patterns and connections that extend far beyond basic arithmetic. This comprehensive guide will dissect the concept of common multiples, specifically focusing on 6 and 9, unveiling the underlying mathematical principles and demonstrating practical applications. We'll move beyond simple calculations to explore the deeper mathematical structures at play and reveal how this seemingly simple concept connects to broader areas of mathematics.
Understanding Multiples and Common Multiples
Before diving into the specifics of 6 and 9, let's establish a firm understanding of fundamental concepts. A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any integer (whole number). For instance, multiples of 6 include 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and so on. Similarly, multiples of 9 include 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, and so forth.
A common multiple is a number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. In the case of 6 and 9, a common multiple is a number that appears in both the lists of multiples for 6 and 9. Identifying these common multiples is the core of our exploration.
Finding Common Multiples of 6 and 9: A Step-by-Step Approach
There are several ways to find the common multiples of 6 and 9. Let's explore the most common methods:
1. Listing Multiples
The simplest method involves listing the multiples of each number until we find common values.
Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 66, 72, 78, 84, 90...
Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, 99...
By comparing the two lists, we quickly identify some common multiples: 18, 36, 54, 72, and 90. This method is effective for smaller numbers but becomes cumbersome for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization
A more sophisticated and efficient method utilizes prime factorization. This involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
To find the least common multiple (LCM), we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization: 2¹ x 3² = 2 x 9 = 18. The LCM is the smallest common multiple. All other common multiples are multiples of the LCM. Therefore, common multiples of 6 and 9 are multiples of 18: 18, 36, 54, 72, 90, and so on.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
This method employs the greatest common divisor (GCD). The GCD of two numbers is the largest number that divides both without leaving a remainder. For 6 and 9, the GCD is 3. The formula then becomes:
LCM(6, 9) = (6 x 9) / GCD(6, 9) = 54 / 3 = 18
Again, we find that the LCM is 18, and all other common multiples are multiples of 18.
Exploring the Significance of the Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The LCM, as we've seen, plays a crucial role in understanding common multiples. It's the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both numbers. The significance of the LCM extends to various mathematical applications:
-
Fraction Operations: Finding the LCM is essential when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. By converting fractions to equivalent fractions with a common denominator (the LCM), we can perform these operations seamlessly.
-
Cyclic Events: Imagine two events that occur cyclically. For example, one event repeats every 6 days, and another every 9 days. The LCM (18) tells us when both events will coincide again.
-
Modular Arithmetic: The LCM is fundamental in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with applications in cryptography and computer science.
Beyond the Basics: Patterns and Relationships
Let's delve deeper into the patterns and relationships inherent in the common multiples of 6 and 9:
-
Infinite Set: The set of common multiples of 6 and 9 is infinite. We can always find a larger common multiple by multiplying the LCM (18) by any positive integer.
-
Arithmetic Progression: The common multiples of 6 and 9 form an arithmetic progression with a common difference of 18. This means that each subsequent multiple is obtained by adding 18 to the previous one.
-
Visual Representation: These relationships can be visually represented using number lines or diagrams, providing a clearer understanding of the pattern and spacing between common multiples.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The concept of common multiples transcends theoretical mathematics and finds practical applications in numerous real-world scenarios:
-
Scheduling and Planning: Imagine scheduling meetings or events that need to align with different recurring intervals. Finding the LCM helps determine the earliest time when all events can occur simultaneously.
-
Construction and Engineering: In construction, the LCM is used to determine the optimal length of materials or the spacing between elements in a structure to ensure uniformity and efficiency.
-
Music Theory: Musical intervals and harmonies are often related to common multiples. Understanding these relationships helps composers create pleasing and coherent musical pieces.
-
Data Analysis: In data analysis and programming, common multiples can be used to synchronize data streams or identify recurring patterns in datasets.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those seeking a deeper mathematical understanding, exploring the following concepts can significantly enhance your knowledge:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): Understanding the GCD is essential to comprehending the relationship between the LCM and the GCD. Algorithms like the Euclidean algorithm provide efficient ways to calculate the GCD.
-
Number Theory: The study of common multiples and LCMs is firmly rooted in number theory, a branch of mathematics that explores the properties of integers.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concepts of multiples and divisors extend to more abstract algebraic structures, providing a framework for understanding similar relationships in more complex mathematical systems.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Common Multiples
The seemingly simple task of finding common multiples of 6 and 9 unlocks a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From fundamental arithmetic to advanced number theory, the exploration of common multiples demonstrates the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and their relevance to various fields. This comprehensive guide has aimed to not only provide a clear understanding of the methods for finding common multiples but also to highlight their significance in solving real-world problems and fostering a deeper appreciation for the beauty and elegance of mathematics. By understanding the principles discussed here, you are well-equipped to tackle similar problems and appreciate the underlying mathematical structures at play. The journey of understanding common multiples is far from over; it's a stepping stone to a wider world of mathematical discovery.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Are 40 Inches
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is 18 C In Fahrenheit
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Cups Are In 7 Ounces
Mar 16, 2025
-
6 Gallons Is How Many Liters
Mar 16, 2025
-
Convert 35 Degrees Celsius To Fahrenheit
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Multiples Of 6 And 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
