Common Multiples Of 7 And 3
Kalali
Mar 11, 2025 · 5 min read
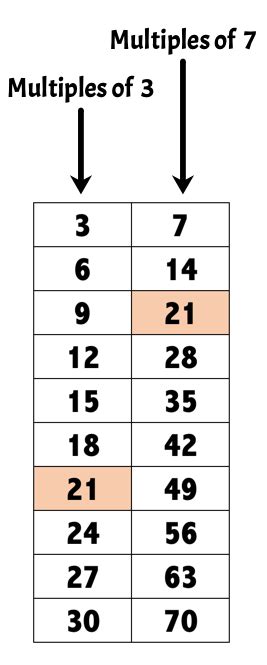
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries of Common Multiples of 7 and 3: A Deep Dive
Finding common multiples, especially for seemingly simple numbers like 7 and 3, might seem straightforward at first glance. However, a deeper exploration reveals fascinating patterns, connections to other mathematical concepts, and practical applications that extend far beyond elementary arithmetic. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of common multiples of 7 and 3, exploring various methods for finding them, uncovering their properties, and highlighting their significance in diverse mathematical contexts.
Understanding Multiples and Common Multiples
Before we embark on our journey into the specific realm of common multiples of 7 and 3, let's establish a clear understanding of the foundational concepts.
What are Multiples?
A multiple of a number is the result of multiplying that number by any whole number (integer). For instance, multiples of 7 include 7 (7 x 1), 14 (7 x 2), 21 (7 x 3), 28 (7 x 4), and so on, extending infinitely in the positive direction. Similarly, multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so forth.
What are Common Multiples?
When two or more numbers share multiples, these shared multiples are called common multiples. In our case, we're interested in the common multiples of 7 and 3. These are numbers that appear in both the list of multiples of 7 and the list of multiples of 3. The smallest of these common multiples is known as the least common multiple (LCM).
Finding Common Multiples of 7 and 3: Methods and Techniques
Several methods can effectively determine the common multiples of 7 and 3. Let's explore some of the most common and practical approaches:
1. Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method involves listing the multiples of each number separately and then identifying the common entries.
Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70, 77, 84, 91, 98, 105...
Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 51, 54, 57, 60, 63, 66, 69, 72, 75, 78, 81, 84, 87, 90, 93, 96, 99, 102, 105...
By comparing the two lists, we can readily identify common multiples: 21, 42, 63, 84, 105, and so on. This method is excellent for smaller numbers but becomes cumbersome as the numbers increase in size.
2. Prime Factorization
Prime factorization provides a more elegant and efficient approach, especially for larger numbers. It involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors.
- Prime Factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
- Prime Factorization of 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
Since 7 and 3 are both prime numbers and have no common factors other than 1, their least common multiple (LCM) is simply their product: 7 x 3 = 21. All other common multiples are multiples of the LCM. Therefore, the common multiples of 7 and 3 are 21, 42, 63, 84, 105, and so on, which are all multiples of 21.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
This formula utilizes the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the two numbers. The GCD of 7 and 3 is 1 (since they share only the common divisor 1).
Therefore, LCM(7, 3) = (7 x 3) / 1 = 21. Again, all common multiples are multiples of the LCM, 21.
Properties and Patterns of Common Multiples of 7 and 3
The common multiples of 7 and 3 exhibit several interesting properties and patterns:
-
Arithmetic Progression: The common multiples form an arithmetic progression with a common difference equal to the LCM (21). This means that each subsequent common multiple is obtained by adding 21 to the previous one.
-
Divisibility: Every common multiple of 7 and 3 is divisible by both 7 and 3. This is a fundamental property of common multiples.
-
Infinite Set: There are infinitely many common multiples of 7 and 3. The set of common multiples is unbounded.
Applications and Significance
While understanding common multiples might seem purely theoretical, it finds applications in various real-world scenarios:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses, one arriving every 7 minutes and another every 3 minutes. Finding the common multiples helps determine when both buses arrive simultaneously at the bus stop. The LCM (21 minutes) represents the shortest time interval when this occurs.
-
Pattern Recognition: In areas like music theory and tiling patterns, understanding common multiples is crucial for identifying recurring patterns and cycles.
-
Fraction Operations: Finding the least common multiple is essential when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. The LCM serves as the common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
-
Modular Arithmetic: In cryptography and computer science, modular arithmetic relies heavily on the concept of multiples and LCM.
-
Geometry: In geometry, common multiples can play a role in determining when certain geometric figures can perfectly tile a plane without overlaps or gaps.
Exploring Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
Let's venture into some more advanced aspects related to common multiples:
Least Common Multiple (LCM) and Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Relationship
The LCM and GCD of two numbers are intimately related. For any two positive integers 'a' and 'b', the product of their LCM and GCD is always equal to the product of the two numbers:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
This relationship is a powerful tool in number theory and simplifies many calculations.
Extended Euclidean Algorithm
The extended Euclidean algorithm is an efficient method for finding both the GCD and LCM of two numbers simultaneously. It's particularly useful for larger numbers where the prime factorization method might be computationally expensive.
Applications in Abstract Algebra
The concepts of LCM and GCD extend beyond basic arithmetic and find their place in abstract algebra, specifically in ring theory and ideal theory.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Common Multiples
The seemingly simple concept of common multiples of 7 and 3, or any two numbers for that matter, unveils a rich tapestry of mathematical connections and practical applications. From basic arithmetic operations to sophisticated algorithms and abstract algebraic structures, the understanding of common multiples permeates various mathematical domains. Mastering these concepts equips individuals with valuable tools for solving problems across diverse fields, from scheduling and pattern recognition to advanced computational and theoretical mathematics. The exploration of common multiples, therefore, is not just an exercise in arithmetic but a journey into the heart of mathematical structure and its real-world relevance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Real World Examples Of Scatter Plots
May 09, 2025
-
How Do You Find A Quotient Of A Fraction
May 09, 2025
-
Whats 16 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit
May 09, 2025
-
How Much Is 90cm In Inches
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 12 In A Fraction
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Multiples Of 7 And 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.