Common Multiples Of 9 And 6
Kalali
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
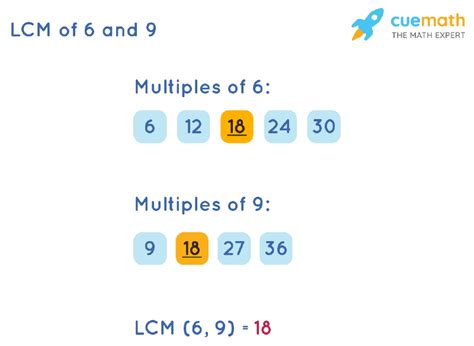
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries of Common Multiples: A Deep Dive into the Multiples of 9 and 6
Finding common multiples might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying principles unlocks a deeper appreciation for number theory and its applications. This article delves into the fascinating world of common multiples, specifically focusing on the common multiples of 9 and 6. We'll explore various methods for identifying these multiples, discuss their significance in mathematics, and even touch upon real-world applications. Prepare to be amazed by the interconnectedness of seemingly simple numbers!
Understanding Multiples
Before we dive into the specifics of 9 and 6, let's establish a solid foundation. A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any whole number (0, 1, 2, 3, and so on). For example:
- Multiples of 6: 0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 66, 72, 78, 84, 90, 96, 102, 108, 114, 120... and so on to infinity.
- Multiples of 9: 0, 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, 99, 108, 117, 126, 135, 144, 153, 162, 171, 180... and so on to infinity.
Notice that both lists extend infinitely. This is true for the multiples of any whole number.
Identifying Common Multiples
A common multiple is a number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. In our case, we're interested in the common multiples of 9 and 6. Looking at the lists above, we can already spot some:
- 18: 18 is both 6 x 3 and 9 x 2.
- 36: 36 is both 6 x 6 and 9 x 4.
- 54: 54 is both 6 x 9 and 9 x 6.
- 72: 72 is both 6 x 12 and 9 x 8.
- 90: 90 is both 6 x 15 and 9 x 10.
- 108: 108 is both 6 x 18 and 9 x 12.
And so on. These are just the first few common multiples. There are infinitely many common multiples of 9 and 6.
Finding Common Multiples: Systematic Approaches
Manually identifying common multiples from lists becomes impractical for larger numbers or a greater number of numbers. Let's explore more efficient methods:
1. Listing Multiples and Comparing
While not ideal for large numbers, this method provides a clear visual understanding. Create lists of multiples for both numbers and identify the overlapping values.
2. Prime Factorization
This is a powerful technique for finding the least common multiple (LCM) and all common multiples. Let's break down 9 and 6 into their prime factors:
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 9 = 3 x 3 = 3²
The LCM is found by taking the highest power of each prime factor present in the numbers: 2¹ x 3² = 18. The LCM (18) is the smallest common multiple. All other common multiples are multiples of the LCM. Therefore, the common multiples of 6 and 9 are: 18, 36, 54, 72, 90, 108, 126, 144, 162, 180...and so on.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
This formula directly calculates the least common multiple (LCM) using the greatest common divisor (GCD).
- Find the GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of 9 and 6: The GCD of 9 and 6 is 3.
- Apply the formula: LCM(9, 6) = (9 x 6) / 3 = 18
Again, we find that the LCM is 18. All multiples of 18 are common multiples of 9 and 6.
Least Common Multiple (LCM) and Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The least common multiple (LCM) is the smallest positive number that is a multiple of both numbers. In our case, the LCM of 9 and 6 is 18. The greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as the highest common factor (HCF), is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. The GCD of 9 and 6 is 3. These concepts are fundamental in various mathematical fields.
Real-World Applications of Common Multiples
The seemingly abstract concept of common multiples has surprising real-world applications:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses arrive at a stop at different intervals. One bus arrives every 6 minutes, and another every 9 minutes. Finding the common multiples helps determine when both buses will arrive at the stop simultaneously. The LCM (18 minutes) tells us the next time both buses will be at the stop together.
-
Tiling and Patterns: When designing tiled floors or creating repeating patterns, understanding common multiples ensures seamless designs. If you have tiles that are 6 units and 9 units wide, using the LCM (18 units) will guarantee a clean, repeating pattern without any gaps or overlaps.
-
Gear Ratios: In mechanical engineering, gear ratios utilize the principles of GCD and LCM to optimize speed and torque. Understanding common multiples helps determine the optimal gear ratios for smooth and efficient operation.
-
Fractions: Finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions. This ensures you have a common denominator to perform the operation correctly. For example, adding 1/6 + 1/9 requires finding the LCM of 6 and 9, which is 18. The fractions become 3/18 + 2/18 = 5/18.
-
Music Theory: Musical intervals and harmonies are often based on relationships between frequencies, which can be analyzed using multiples and common multiples. Understanding the common multiples helps in creating harmonious musical compositions.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
The exploration of common multiples extends beyond the simple examples presented here. Consider these advanced concepts:
-
Common Multiples of More Than Two Numbers: The principles we’ve discussed can be extended to find common multiples of three or more numbers. The process involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then determining the LCM, which will then generate all common multiples.
-
Infinitely Many Common Multiples: It's important to remember that any two (or more) whole numbers will have infinitely many common multiples. The LCM is simply the smallest positive one.
-
Applications in Abstract Algebra: Concepts related to multiples and divisors play a significant role in abstract algebra, a branch of mathematics dealing with algebraic structures.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Common Multiples
Understanding common multiples is more than just a mathematical exercise; it's a key concept with practical applications in various fields. From scheduling and design to engineering and music, the ability to identify and utilize common multiples demonstrates a deeper understanding of numerical relationships. By mastering the techniques discussed in this article, you’ll not only improve your mathematical skills but also gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of numbers and their real-world significance. So, next time you encounter a problem involving multiples, remember the power and elegance hidden within these seemingly simple concepts. Keep exploring, keep learning, and keep discovering the fascinating world of mathematics!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Miles Is 100 Kilometers
Mar 12, 2025
-
What Is The 30 Of 500
Mar 12, 2025
-
50 Milliliters Equals How Many Ounces
Mar 12, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 72 In
Mar 12, 2025
-
What Percent Is 1 Of 8
Mar 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Multiples Of 9 And 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
