Como Es El Cero En Numeros Romanos
Kalali
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
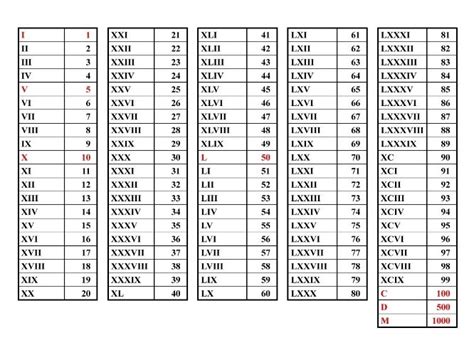
Table of Contents
How is Zero Represented in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive
The Roman numeral system, a fascinating glimpse into ancient Roman civilization, continues to intrigue and challenge us today. While its elegance in representing numbers from 1 to a million is undeniable, one question frequently arises: how is zero represented in Roman numerals? The straightforward answer is that zero doesn't have a direct representation in the classical Roman numeral system. This absence is a key difference between Roman numerals and modern positional number systems like the Arabic system we use daily. Let's delve deeper into this intriguing numerical enigma.
The Absence of Zero: A Historical Perspective
The Roman numeral system developed organically over centuries, primarily for practical purposes like recording dates, quantities, and measurements. It wasn't designed as a sophisticated mathematical tool for complex calculations or abstract concepts like the mathematical concept of zero. The ancient Romans lacked the abstract understanding of zero as a placeholder or a number in its own right, a concept that developed much later in other cultures, particularly in India.
Understanding the Roman System's Limitations
The Roman system relies on a combination of seven basic symbols: I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000). These symbols are added or subtracted depending on their position. For example, VI represents 6 (5 + 1), while IV represents 4 (5 - 1). The system works efficiently for representing whole numbers within a reasonable range, but it lacks the capacity to express fractions or decimals effectively. It also doesn't readily handle operations like multiplication and division as elegantly as the modern positional system.
The absence of a zero symbol directly contributed to the limitations of the system. Without a placeholder, the Romans had no simple way to represent the absence of a value in a given place or to deal with the concept of nothingness as a numerical entity. This omission profoundly impacted their ability to perform complex arithmetic and explore advanced mathematical concepts.
Zero in Other Number Systems: A Comparative Look
Before we further dissect the lack of zero in Roman numerals, let's consider its crucial role in other ancient number systems:
The Babylonian System: A Glimpse of Early Zero Representation
The Babylonian numeral system, dating back to ancient Mesopotamia, employed a sexagesimal (base-60) system. While they didn't use a symbol explicitly representing zero in their early stages, they eventually adopted a placeholder symbol to distinguish between different numerical values. This placeholder, though not a true zero in the modern sense, marked a significant step towards the concept's development.
The Mayan System: A Sophisticated Approach to Zero
The Mayan civilization, renowned for its mathematical and astronomical achievements, possessed a fully developed concept of zero, represented by a shell-like symbol. Their vigesimal (base-20) system incorporated zero not only as a placeholder but as a number that participated in mathematical operations. This advanced understanding greatly enhanced their capabilities in various calculations.
The Indian System: The Birth of Modern Zero
The Indian numeral system is credited with the invention of the modern zero as we know it. This revolutionary concept, along with the positional system's invention, provided a powerful foundation for arithmetic. This system was later adopted and spread by the Arabs and subsequently throughout the world, leading to the number system we use globally today.
Attempts to Incorporate Zero into Roman Numerals
Despite its absence in the classical system, several attempts have been made over the centuries to modify the Roman numeral system to include a representation of zero. These attempts, however, haven't gained widespread acceptance and remain primarily historical footnotes.
The Use of a Dot or an "N"
Some medieval texts used a dot or the letter "N" (from nulla, Latin for "nothing") to signify the absence of a value. However, these notations were inconsistent and never became standardized. They lack the mathematical properties of a true zero, serving merely as placeholders without changing the system's core structure.
Modern Adaptations: Convenience over Authenticity
Today, some modern adaptations might use 0 or include a separate symbol to indicate zero, especially in contexts where it's needed to prevent ambiguity. However, it's crucial to remember that these are modifications, not faithful representations of the classical Roman numeral system.
Why the Absence of Zero? The Significance of Context
The absence of a zero in the classical Roman numeral system wasn't a deficiency in the same way that a modern mathematical system might be incomplete without it. The system served its purpose well within its historical context, prioritizing practical applications rather than abstract mathematical concepts. The Romans didn't require zero for their everyday needs.
The Practicality of Roman Numerals
Roman numerals were primarily used for inscription, not for extensive calculations. Adding and subtracting numbers was possible, though multiplication and division were much more complex. The absence of zero did not hinder everyday activities like recording the year or inventory.
The Evolution of Mathematical Thought
The evolution of the concept of zero itself took considerable time. It was a gradual process, starting with the use of placeholders in earlier number systems before finally developing into the fully fledged mathematical concept we understand today. The Roman numeral system existed long before this conceptual breakthrough.
Conclusion: Zero and the Roman System's Legacy
While the classical Roman numeral system lacks a formal representation of zero, this absence does not diminish its historical significance. Understanding the system's limitations in relation to the development of the zero concept provides valuable insights into the evolution of mathematics and the different ways cultures have approached numerical representation. The Roman numerals' enduring presence in certain contexts, from clock faces to chapter numbering, serves as a testament to their lasting legacy, even without the inclusion of a numerical symbol for zero. Understanding the historical reasons for its absence is key to appreciating both the system and the profound impact the concept of zero has had on mathematics. The absence of zero highlights not a failing, but rather a characteristic reflective of its time and purpose.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
40 Is What Percent Of 16
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Much Inches Is 18 Cm
Apr 07, 2025
-
Cuantos Pies Cuadrados Tiene Un Metro
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Is 90 Degrees In Celsius
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Much Is 150cm In Inches
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Como Es El Cero En Numeros Romanos . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.