Cómo Se Escribe El Número 0 En Romano
Kalali
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
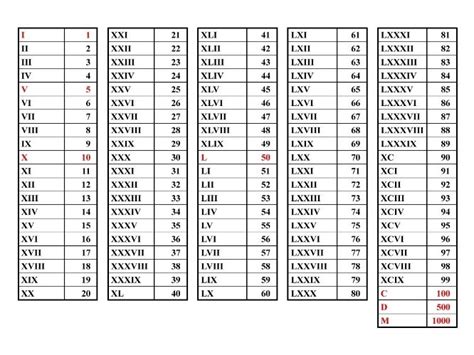
Table of Contents
How to Write the Number 0 in Roman Numerals: A Comprehensive Guide
The Roman numeral system, a numerical notation system originating in ancient Rome, is still used today for various purposes – from clock faces and chapter numbering to copyright dates and outlining. However, a common question arises: how do you write the number 0 in Roman numerals? The short answer is: you don't. The Roman numeral system, in its original form, didn't include a symbol for zero. This is a crucial point to understand and forms the basis of this comprehensive guide.
The Absence of Zero: A Historical Perspective
Unlike the positional decimal system we use today (which relies heavily on the concept of zero as a placeholder), the Roman numeral system was additive and subtractive. Numbers were represented by combinations of letters: I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000). The absence of a zero symbol stems from the system's development and its primary use in practical applications, such as record-keeping and commerce. There wasn't a pressing need for a symbol representing nothingness in the same way that zero functions in our modern numerical system.
Zero, as a concept, evolved later in mathematical history, particularly in the context of the Indian numeral system, which then spread to the Middle East and eventually Europe. Its incorporation revolutionized mathematics, enabling the development of more sophisticated arithmetic operations and algorithms.
Understanding Roman Numeral System Mechanics
Before diving deeper into the implications of the lack of a zero, let's review the fundamental rules of Roman numerals:
-
Additive Principle: Numbers are formed by adding the values of individual symbols. For example, VI (6) = V (5) + I (1).
-
Subtractive Principle: A smaller numeral placed before a larger numeral subtracts its value from the larger numeral. For example, IV (4) = V (5) - I (1), and IX (9) = X (10) - I (1). This subtractive principle is used only for I, X, and C preceding a numeral of a larger denomination.
-
Limitations: There are no direct representations for numbers greater than 3999 (MMMCMXCIX) within the standard Roman numeral system. Different systems of vinculum (overline) notation were developed to handle larger numbers.
Why the Absence of Zero Doesn't Impair Functionality (Historically)
The absence of zero didn't significantly hinder the practical application of the Roman numeral system for everyday calculations of the time. Their practical use focused on counting, representation, and identification, not on complex mathematical operations like those demanding zero as a placeholder.
For instance, consider recording a quantity of goods: using Roman numerals, you could effectively represent the number of items without needing a zero to fill a place value. The lack of zero didn't impede their functionality within those practical contexts.
Modern Interpretations and Workarounds
While there isn't an official Roman numeral for zero, modern interpretations sometimes employ various workarounds when a zero placeholder is needed:
-
Leaving a Blank Space: In contexts where a placeholder is needed, particularly in tabular formats or for dating systems spanning the year zero, a blank space may be left to indicate the absence of value. This is a practical workaround, though not strictly part of the classical Roman numeral system.
-
Using the Letter "N": Occasionally, the letter "N" is used informally as a placeholder for zero. However, this is not a standard convention and can lead to confusion. It’s vital to avoid this, as it's not officially accepted and might be misinterpreted.
-
Contextual Clarity: Often, the meaning is clear from the context. If dealing with years before the Common Era, then simply having the BC label is usually sufficiently clear without needing to represent zero.
The Impact of Zero in the Decimal System
The introduction of zero significantly impacted the development of mathematics. The decimal system, unlike the Roman numeral system, is a positional system, meaning the value of a digit depends on its position within the number. Zero plays a crucial role as a placeholder, allowing us to represent numbers with different orders of magnitude efficiently. This capability enables the swift and accurate calculation of more complex equations and greatly extends the capabilities of arithmetic.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
-
Zero is not the same as "nothing": While zero represents the absence of quantity, it is a number in its own right, enabling essential mathematical operations. The Roman numeral system's lack of a zero symbol shouldn't be interpreted as the ancients not understanding the concept of nothing; it rather reflects the constraints and applications of their chosen numerical system.
-
"Nulla" is not a Roman Numeral for Zero: Sometimes, the Latin word "nulla" (meaning "none" or "nothing") is proposed as a Roman numeral representation of zero. However, "nulla" is not part of the classical Roman numeral system; it's a Latin word, not a symbol within the numeral system.
Conclusion: Embracing the Historical Context
The absence of a zero in the original Roman numeral system is not a deficiency but a characteristic reflecting its historical development and practical uses. Understanding this historical context is essential when exploring this ancient number system. While workarounds exist for modern applications, it's important to remember that no official Roman numeral exists for the number zero. The Roman numeral system, with its strengths and limitations, stands as a testament to the ingenuity and practicality of ancient mathematical thought. The focus should be on understanding the system's rules and its historical context, rather than attempting to force modern mathematical concepts onto an ancient system not designed for them. Learning and appreciating the Roman numeral system for what it was—a functional system for its time—is crucial in understanding its role in mathematical history. The development of zero in subsequent mathematical systems underscores the continuous evolution and improvement of numerical representation throughout history.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 9 8 As A Percent
Mar 15, 2025
-
Convert 2 1 2 To A Decimal
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Much Is 3 4 In Ounces
Mar 15, 2025
-
Como Se Escribe El Cero En Numeros Romanos
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is The Liver Cell Haploid Or Diploid
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cómo Se Escribe El Número 0 En Romano . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
