Diagonal Cross Section Of A Pyramid Example
Kalali
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
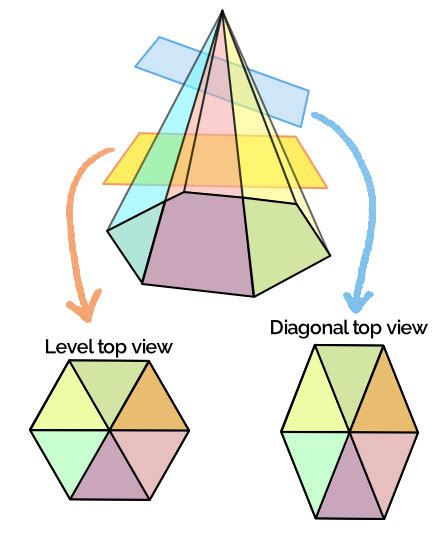
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries: A Deep Dive into Diagonal Cross-Sections of Pyramids
Understanding the geometry of pyramids, particularly their cross-sections, is crucial in various fields, from architecture and engineering to computer graphics and game development. While understanding perpendicular cross-sections (slices parallel to the base or through the apex) is relatively straightforward, diagonal cross-sections present a fascinating and more complex challenge. This article delves into the intricacies of diagonal cross-sections of pyramids, exploring their properties, methods of calculation, and practical applications.
What is a Diagonal Cross-Section?
A cross-section, in general, is the shape obtained when a three-dimensional object is sliced by a plane. A diagonal cross-section of a pyramid is a plane that intersects the pyramid in a way that it's not parallel to any of the pyramid's faces and doesn't pass through the apex. Crucially, it intersects at least two non-adjacent edges of the pyramid's base. This creates a polygon within the pyramid that is neither a triangle similar to the pyramid's lateral faces, nor simply a scaled-down version of the base. The shape and properties of this cross-section depend heavily on the shape of the pyramid's base and the angle of the intersecting plane.
Exploring Different Pyramid Types and their Diagonal Cross-Sections
Let's examine how diagonal cross-sections manifest in various pyramid types:
1. Square Pyramids: A Common Case Study
Square pyramids, possessing a square base and four triangular lateral faces, offer a fertile ground for exploring diagonal cross-sections. Consider a square pyramid with a base ABCD and apex P. A diagonal cross-section might intersect edges AB, BC, and possibly CP and DP, resulting in a quadrilateral cross-section. The exact shape of this quadrilateral (parallelogram, trapezoid, etc.) depends on the orientation of the cutting plane. This case necessitates a deeper look at the geometric relationships between the intersecting plane and the pyramid's vertices and edges.
Analyzing the Quadrilateral Cross-Section
The properties of the quadrilateral cross-section can be analyzed using various geometric principles:
- Parallelism: If the intersecting plane is parallel to a particular edge (e.g., AD), then the corresponding sides of the cross-section will be parallel.
- Similarity: Although the quadrilateral cross-section is generally not similar to the base, relationships between angles and ratios of side lengths might still exist. Careful application of similar triangle theorems can be vital here.
- Trigonometry: Utilizing trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) along with the Pythagorean theorem becomes crucial for calculating side lengths and angles within the quadrilateral.
2. Triangular Pyramids (Tetrahedrons): A Simpler Case
Triangular pyramids, also known as tetrahedrons, have four triangular faces. Diagonal cross-sections here are somewhat simpler. A plane intersecting at least two non-adjacent edges will always produce a triangular cross-section. While the orientation will affect the precise dimensions, the resulting shape remains consistent.
3. Pentagonal and Higher-Order Pyramids: Increasing Complexity
As we move beyond square and triangular pyramids to pentagonal, hexagonal, and other higher-order pyramids (those with a polygonal base having more than four sides), the complexity of diagonal cross-sections significantly increases. The resulting cross-sections become polygons with more sides, requiring more intricate geometric calculations. The number of possible intersections dramatically increases, yielding a much broader range of cross-sectional shapes. Advanced techniques, possibly involving vector geometry or 3D coordinate systems, might become necessary for precise analysis.
Methods for Determining the Properties of Diagonal Cross-Sections
Calculating the properties (lengths of sides, angles, area) of a diagonal cross-section typically involves a combination of the following methods:
1. Analytical Geometry (Coordinate Systems)
By assigning coordinates to the vertices of the pyramid in a 3D coordinate system, one can define the intersecting plane using its equation (typically in the form Ax + By + Cz + D = 0). The points of intersection between the plane and the edges of the pyramid can then be calculated by solving the system of equations. Once the coordinates of the vertices of the cross-section are known, their distances (side lengths) and angles can be calculated using the distance formula and the dot product formula, respectively.
2. Vector Geometry
Vector geometry provides a powerful and elegant alternative. Vectors can represent the edges of the pyramid and the direction of the intersecting plane. Using vector operations (dot product, cross product), one can calculate the points of intersection and subsequent properties of the cross-section.
3. Similar Triangles and Proportions
In certain configurations, similar triangle theorems provide a straightforward approach. Identifying similar triangles formed by the intersecting plane and the pyramid's faces can lead to proportional relationships, allowing the calculation of unknown side lengths or angles. However, this method is not always applicable for all diagonal cross-sections.
4. Trigonometry
Trigonometry plays a vital role in calculating angles and side lengths, especially when dealing with inclined planes and three-dimensional projections.
Practical Applications of Understanding Diagonal Cross-Sections
The understanding of diagonal cross-sections isn't merely an academic exercise; it has practical implications in several areas:
- Architecture and Engineering: In designing structures like roofs, bridges, or supporting elements within pyramids, knowledge of internal stresses and forces necessitates understanding the internal structure, including diagonal cross-sections.
- Civil Engineering: Analyzing the stability and strength of earth structures, such as embankments and dams, often involves considering different cross-sections, including diagonal ones, particularly when analyzing load distribution.
- Mining and Geology: In analyzing rock formations and extracting minerals from layered deposits, understanding cross-sections helps in determining the location and properties of the ore bodies.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: Creating realistic 3D models of pyramids and other complex shapes requires a deep understanding of their cross-sections for accurate rendering and texture mapping. Diagonal cross-sections are particularly important for capturing detail and avoiding artifacts.
- Material Science: Studying the microstructure of materials sometimes involves analyzing cross-sections at various angles, including diagonal cuts, to reveal internal features and grain orientations.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of Geometry
Diagonal cross-sections of pyramids, while initially appearing complex, can be understood and analyzed using a combination of powerful geometric methods. The ability to calculate their properties is valuable in numerous fields, emphasizing the enduring importance of geometry and its applications in both theoretical and practical contexts. This deep dive provides a foundation for further explorations into this fascinating aspect of pyramid geometry, and its practical consequences in our world. Further research into specific scenarios and the application of more advanced mathematical tools will undoubtedly lead to a richer understanding of these intricate shapes. Remember that the specific approach used to analyze a diagonal cross-section depends entirely on the context and the information available, necessitating flexibility and a robust understanding of multiple geometric techniques.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Inches Is A Meter Stick
Jul 10, 2025
-
Soundtrack To Step Up 2 The Streets
Jul 10, 2025
-
Keebler Club And Cheddar Crackers Expiration Date
Jul 10, 2025
-
In Many States Trailers With A Gvwr Of 1500
Jul 10, 2025
-
How Many Tablespoons Are In A Hidden Valley Ranch Packet
Jul 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Diagonal Cross Section Of A Pyramid Example . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.