Distance From Equator To North Pole
Kalali
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
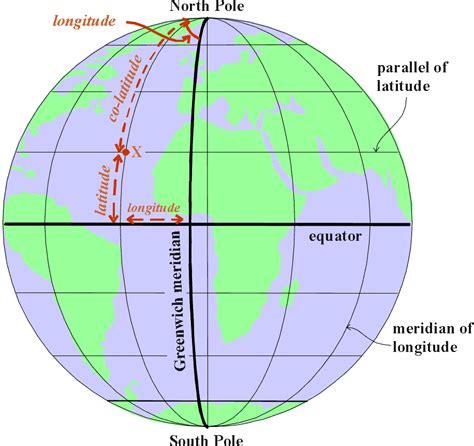
Table of Contents
The Distance from the Equator to the North Pole: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude
The Earth, our vibrant and diverse planet, is a sphere (more accurately, an oblate spheroid) teeming with life and geographical wonders. One fundamental aspect of understanding our planet's geography is grasping the concept of distance, particularly the distance from the equator to the North Pole. This seemingly simple question opens doors to exploring latitude, longitude, the Earth's dimensions, and the fascinating implications of our planet's spherical nature.
Understanding Latitude and Longitude: The Grid System of the Earth
Before delving into the specific distance, let's establish a foundational understanding of latitude and longitude. These two coordinate systems form an invisible grid across the Earth's surface, allowing us to pinpoint any location precisely.
Latitude: Measuring North and South
Latitude measures a location's distance north or south of the equator. The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth midway between the North and South Poles, is assigned a latitude of 0°. As you move north, the latitude increases, reaching 90° North at the North Pole. Similarly, moving south, the latitude increases, reaching 90° South at the South Pole. Lines of latitude are known as parallels because they run parallel to the equator.
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude, on the other hand, measures a location's distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. The Prime Meridian, an arbitrary line running through Greenwich, England, is assigned a longitude of 0°. Longitude lines run from the North Pole to the South Pole and are called meridians. Longitude values range from 0° to 180° east and 0° to 180° west.
Calculating the Distance: More Than Just a Straight Line
Calculating the distance from the equator to the North Pole isn't as straightforward as simply multiplying a degree of latitude by a constant value. The Earth is not a perfect sphere; it's slightly flattened at the poles and bulges at the equator (an oblate spheroid). This means the distance between lines of latitude varies slightly depending on the location.
To accurately calculate the distance, we need to consider the Earth's curvature and its slightly irregular shape. A simplified calculation using the Earth's average radius provides a reasonable approximation, but for high-precision measurements, more complex geodetic models are required.
The Earth's Radius and Circumference: Key Factors
The Earth's radius is crucial in calculating the distance. There are several ways to define the Earth's radius, such as the equatorial radius (the distance from the center to the equator) and the polar radius (the distance from the center to the North or South Pole). The equatorial radius is slightly larger than the polar radius due to the Earth's oblateness.
The Earth's circumference, which is related to its radius, is also relevant. Knowing the circumference allows us to calculate the distance covered by one degree of latitude. However, due to the Earth's shape, this distance is not uniform across all latitudes.
Approximating the Distance: Using the Average Radius
Using the Earth's average radius, approximately 6,371 kilometers (3,959 miles), we can estimate the distance. Since the distance from the equator to the North Pole covers 90 degrees of latitude, a simplified calculation would be:
- Distance ≈ 90° × (Earth's circumference / 360°)
However, this approach neglects the Earth's oblateness. A more accurate calculation would involve integrating along a meridian considering the Earth's actual shape, using geodetic formulas.
The Role of Geodesy and Geodetic Models
Geodesy is the science of measuring the Earth's shape and size. Geodesy employs sophisticated mathematical models and advanced surveying techniques to create highly accurate representations of the Earth's surface. These models account for the irregularities in the Earth's shape, gravity variations, and other factors affecting precise distance calculations.
Modern geodetic models, such as the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84), are widely used for GPS, mapping, and other applications requiring precise location data. Using these models, the distance from the equator to the North Pole can be calculated with a high degree of accuracy.
The Impact of the Earth's Oblateness
The Earth's oblateness significantly influences the distance calculation. Because the Earth bulges at the equator, the distance along a meridian from the equator to the pole is not precisely one-quarter of the Earth's circumference. This means the distance varies slightly depending on the longitude.
While the average distance provides a good approximation, considering the Earth's oblateness leads to a more accurate result. Specialized software and geodetic calculations are required to account for these subtle variations.
Beyond the Numbers: Exploring the Significance
The distance from the equator to the North Pole is more than just a numerical value; it's a fundamental aspect of our planet's geography, impacting various aspects of our lives:
- Climate: Latitude significantly influences climate. Locations closer to the equator experience warmer temperatures due to the higher angle of the sun's rays. The distance from the equator to the North Pole reflects the dramatic climatic changes as one moves toward the poles.
- Navigation: Accurate knowledge of latitude and longitude is crucial for navigation, particularly for seafaring and aviation. Understanding the distance between the equator and the poles is essential for calculating distances and plotting courses across the globe.
- Mapping and Surveying: Accurate mapping and surveying rely on precise geodetic measurements, including the accurate determination of the distance between the equator and the poles.
- Scientific Research: Scientists use precise measurements of latitude and longitude, coupled with the understanding of the distance from the equator to the poles, for various research purposes, including studying climate change, tectonic plate movements, and other geophysical phenomena.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery
The distance from the equator to the North Pole, while seemingly a simple question, unveils a rich tapestry of geographical knowledge. Understanding latitude and longitude, the Earth's shape, and the intricacies of geodetic calculations allows for a deeper appreciation of our planet. This distance represents not merely a linear measurement but a journey across climatic zones, navigational routes, and scientific understanding, highlighting the complex interplay between mathematics, geography, and our world. The journey from the equator to the North Pole is not only a geographical one but also a journey of discovery into the very nature of our planet. It underscores the importance of precise measurement and the continuous evolution of our understanding of Earth's form and dimensions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Get Magnitude Of Force
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Can You Separate Sugar From Water
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are The Common Multiples Of 9 And 10
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is 2 Out Of 16 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Much Is 7 Oz Of Water
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Distance From Equator To North Pole . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
