Does A Stretched Bow And Arrow Have Energy
Kalali
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
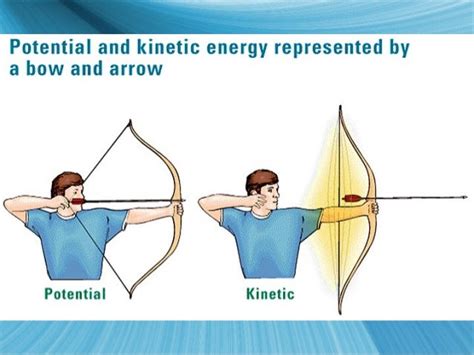
Table of Contents
Does a Stretched Bow and Arrow Have Energy? Understanding Potential and Kinetic Energy
The simple answer is a resounding yes, a stretched bow and arrow possesses energy. However, the type of energy and how it's manifested are crucial to understanding the physics involved. This article will delve into the intricacies of potential and kinetic energy as they relate to a drawn bow and arrow, exploring the concepts in detail and clarifying common misconceptions. We'll also touch upon factors influencing the stored energy and its subsequent release.
Understanding Potential Energy
Before we dive into the specifics of a bow and arrow, let's define potential energy. Potential energy is stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or configuration. It's the energy waiting to be released and converted into other forms of energy, like kinetic energy (energy of motion). Think of it as energy in a dormant state, ready to be unleashed.
Several types of potential energy exist, but in the case of a drawn bow, we're primarily concerned with elastic potential energy. This type of potential energy is stored within an elastic material when it's deformed, such as stretching a rubber band or, in this case, bending a bow. The more the bow is stretched (the greater the deformation), the more elastic potential energy it stores.
The Bow as an Elastic System
A bow, unlike a rigid object, is designed to flex and store energy. The limbs of the bow, often made from materials like wood, fiberglass, or carbon fiber, are elastic. When you pull back the bowstring, you're essentially stretching these limbs, deforming them from their natural, relaxed state. This deformation is what stores the elastic potential energy.
Factors Affecting Potential Energy in a Stretched Bow
The amount of potential energy stored in a stretched bow depends on several factors:
-
Draw Weight: This is the force required to hold the bow at full draw. A higher draw weight means more force was applied to stretch the bow, resulting in greater stored energy. This is a crucial specification for archers and is often measured in pounds or kilograms.
-
Draw Length: This is the distance the bowstring is pulled back from its resting position. A longer draw length generally means more stretching of the bow limbs and therefore, more stored energy.
-
Bow Material: Different materials have different elastic properties. Some materials, like carbon fiber, can store more energy for a given amount of deformation than others, like wood. This influences the overall energy storage capacity of the bow.
-
Bow Design: The design of the bow significantly affects how energy is stored and released. Different bow types (e.g., recurve, longbow, compound bow) have distinct designs impacting their efficiency in storing and transferring energy.
The Transformation to Kinetic Energy
When the archer releases the bowstring, the stored elastic potential energy is rapidly converted into kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. This transformation happens almost instantaneously. The released bowstring transfers its energy to the arrow, propelling it forward.
The arrow, now possessing considerable kinetic energy, flies through the air. The amount of kinetic energy the arrow possesses directly correlates to the initial potential energy stored in the drawn bow. A more powerfully drawn bow will launch an arrow with greater kinetic energy, resulting in a faster and farther shot.
Factors Affecting Kinetic Energy Transfer
Several factors influence the efficiency of the energy transfer from the bow to the arrow:
-
Arrow Weight: A heavier arrow will require more energy to accelerate to a given speed, resulting in a less efficient transfer. Lighter arrows generally achieve higher velocities with the same amount of stored potential energy.
-
Bow Efficiency: Different bow designs have varying efficiencies in converting potential energy to kinetic energy. Compound bows, for example, are designed for high efficiency, minimizing energy loss during the transfer.
-
Arrow Release Technique: The archer's technique plays a vital role. A clean, consistent release ensures a smooth transfer of energy. A poor release can cause energy loss, reducing the arrow's velocity.
Beyond Potential and Kinetic Energy: Other Energy Considerations
While potential and kinetic energy are the dominant forms of energy at play, other minor energy considerations exist:
-
Heat: Some energy is lost as heat due to friction within the bow limbs and between the bowstring and other components. This loss is relatively small, but it's a factor influencing overall efficiency.
-
Sound: The release of the bow produces a characteristic sound, representing a tiny amount of energy converted into sound waves.
-
Vibrations: The bow and arrow vibrate slightly after the release, dissipating a small amount of energy.
Misconceptions about Energy in a Stretched Bow
Several misconceptions surround the energy stored in a stretched bow:
-
Myth 1: Energy is stored in the string: While the string plays a crucial role in transferring energy, the primary energy storage is in the bent limbs of the bow. The string is the mechanism for storing and releasing the energy, but it doesn't hold the energy itself.
-
Myth 2: All the stored energy is transferred to the arrow: This is incorrect. Some energy is lost to heat, sound, and vibrations, as mentioned earlier. The efficiency of energy transfer is never 100%.
-
Myth 3: A heavier bow always means a more powerful shot: While a heavier draw weight generally indicates more stored potential energy, other factors like bow design, arrow weight, and shooting technique significantly impact the final arrow velocity and power.
Conclusion: A Symphony of Energy Conversion
A stretched bow and arrow is a fascinating example of potential energy converted to kinetic energy. The amount of energy stored is influenced by several factors, from draw weight and draw length to bow design and arrow weight. Understanding these factors is crucial for archers seeking to maximize their shot's power and accuracy. While some energy is lost during the conversion process, the principle of storing and releasing elastic potential energy remains the fundamental mechanism behind the power and precision of archery. This intricate interplay of potential and kinetic energy underscores the elegant physics at the heart of this ancient and enduring sport. By mastering these principles, archers can consistently achieve impressive results, demonstrating a keen understanding of the energy dynamics at play.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percentage Is 25 Of 75
Apr 03, 2025
-
72 Inches Is How Many Cm
Apr 03, 2025
-
17 Out Of 18 As A Percentage
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Does Erosion Change The Surface Of The Earth
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Type Of Symmetry Do Mollusks Have
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Does A Stretched Bow And Arrow Have Energy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
