Does Plasma Have A Difinite Volume
Kalali
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
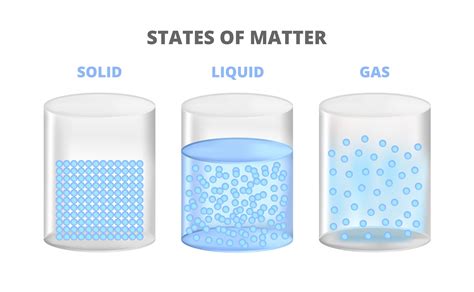
Table of Contents
Does Plasma Have a Definite Volume? Exploring the Nature of the Fourth State of Matter
Plasma, often called the fourth state of matter, is a fascinating and complex substance. Unlike solids, liquids, and gases, its behavior is governed by unique properties, leading to questions about its fundamental characteristics, such as volume. The simple answer is no, plasma does not have a definite volume. However, understanding why requires a deeper dive into the nature of plasma itself.
Understanding the Nature of Plasma
To grasp why plasma lacks a definite volume, we first need a solid understanding of what it is. Plasma is an ionized gas, meaning its atoms have been stripped of some or all of their electrons, resulting in a collection of positively charged ions and negatively charged electrons. This ionization process is typically achieved through high temperatures, strong electromagnetic fields, or intense radiation.
This fundamental difference from gases is key. While gases have relatively weak intermolecular forces, allowing them to expand to fill their container, plasma is governed by powerful electromagnetic forces. These forces, originating from the charged particles, significantly influence the plasma's behavior and its ability to maintain a fixed volume.
The Role of Electromagnetic Forces
The charged particles in plasma interact through long-range Coulomb forces. These forces are significantly stronger than the weak van der Waals forces found in gases. The attraction and repulsion between ions and electrons create a complex interplay that dictates the plasma's overall properties. This means plasma isn't just a collection of independently moving particles; it's a dynamic, interconnected system where the behavior of each particle directly influences the others.
This interaction prevents plasma from behaving like an ideal gas. Ideal gases follow predictable relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature, as described by the ideal gas law (PV = nRT). However, the strong electromagnetic interactions in plasma introduce complexities that invalidate this simple model.
Plasma Confinement: A Key Factor Affecting Apparent Volume
Due to the lack of definite volume, plasma confinement is a major challenge and a significant area of research. Scientists employ various methods to contain and manipulate plasma, including:
-
Magnetic Confinement: This technique uses strong magnetic fields to constrain the charged particles, preventing them from dispersing. This is the approach used in many fusion experiments, where the goal is to create and sustain a controlled plasma reaction.
-
Inertial Confinement: This involves rapidly compressing a small pellet of fuel using powerful lasers, creating high temperatures and densities that lead to plasma formation. The inertia of the compressed fuel helps to temporarily contain the plasma.
-
Electrostatic Confinement: This method utilizes electric fields to confine the plasma, but it's generally less effective for large-scale applications.
These confinement methods define an apparent volume for the plasma, but this volume is not inherent to the plasma itself. If the confining fields were removed, the plasma would rapidly expand and disperse.
Factors Influencing Plasma Volume
While plasma doesn't possess a fixed volume in the same way a solid or liquid does, several factors influence its apparent size and shape. These include:
-
Temperature: Higher temperatures generally lead to increased kinetic energy of the particles, causing the plasma to expand. The increased thermal motion overcomes the electromagnetic forces to a greater extent.
-
Pressure: External pressure can compress the plasma, reducing its apparent volume. However, the compressibility of plasma is significantly different from that of gases, influenced heavily by the electromagnetic interactions.
-
Magnetic Field Strength: Stronger magnetic fields can effectively confine the plasma, limiting its expansion and reducing its apparent volume. The magnetic field acts like a "container" for the charged particles.
-
Density: The number of particles per unit volume affects the electromagnetic interactions within the plasma. Higher densities generally lead to stronger interactions and a more cohesive plasma, which may exhibit a more defined (although not truly definite) shape.
-
Plasma Type: The specific type of plasma (e.g., cold plasma, hot plasma, weakly ionized plasma, fully ionized plasma) influences its properties and its response to external factors. This impacts the apparent volume as well.
Comparing Plasma to Other States of Matter
The lack of a definite volume is a crucial difference between plasma and the other states of matter.
-
Solids: Solids have a definite volume and shape due to the strong intermolecular forces holding their atoms or molecules in a fixed structure.
-
Liquids: Liquids have a definite volume but an indefinite shape; they adapt to the shape of their container. Intermolecular forces are still relatively strong but allow for some movement.
-
Gases: Gases have neither a definite volume nor a definite shape; they expand to fill their container. Intermolecular forces are weak compared to solids and liquids.
Plasma's behavior, dictated by electromagnetic interactions, sets it apart from these three states. While it can be contained and appear to have a defined volume under specific conditions, this volume is imposed by external forces and is not an intrinsic property of the plasma itself.
Applications of Plasma and the Importance of Volume Control
The understanding and control of plasma volume are critical to many applications. Examples include:
-
Fusion Energy Research: Containing and manipulating plasma at extremely high temperatures and densities is essential for achieving controlled nuclear fusion. The efficiency of fusion reactions directly relates to plasma confinement, which implies careful volume control.
-
Plasma Processing in Semiconductor Manufacturing: Plasma etching and deposition are crucial steps in the manufacturing of microchips. Precise control of the plasma's shape and volume is vital for creating intricate patterns on the chip surface.
-
Plasma Displays: Plasma displays use the light emitted by excited plasma in small cells to create images. The precise control of plasma volume in each cell influences the brightness and clarity of the display.
-
Space Physics: Understanding plasma behavior in space is vital for various applications, including satellite design and communication systems. The interaction of solar wind plasma with Earth's magnetic field significantly affects our planet's environment. The volume, or rather the spatial distribution, of this plasma greatly influences this interaction.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Uncontained State
In conclusion, plasma does not possess a definite volume in the conventional sense. Its behavior is determined by the interplay of strong electromagnetic forces between charged particles, making it drastically different from solids, liquids, and gases. While various techniques exist to confine and seemingly define the volume of plasma, this volume is imposed externally and is not an inherent property. The ability to control and manipulate plasma, including its apparent volume, is key to advancing many scientific and technological applications. The understanding of plasma's dynamic and expansive nature is therefore essential for continued breakthroughs in various fields. The ongoing research into plasma physics continually unveils new insights into its complex behavior and its potential applications, solidifying its position as one of the most intriguing and versatile states of matter.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Words That Start With Y In Science
Jul 12, 2025
-
Prevent An Expressway Emergency By Merging Without
Jul 12, 2025
-
How Many Grams Of Sugar In A Pound
Jul 12, 2025
-
7am To 11am Is How Many Hours
Jul 12, 2025
-
If Your 35 What Year Was You Born
Jul 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Does Plasma Have A Difinite Volume . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.