Explain How The Biosphere Interacts With The Atmosphere
Kalali
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
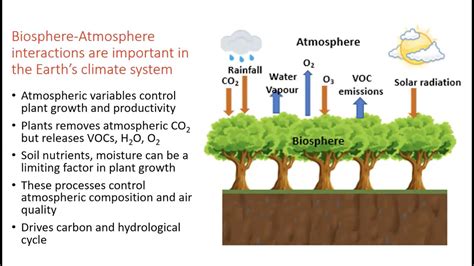
Table of Contents
The Intertwined Dance of Biosphere and Atmosphere: A Complex Relationship
The Earth's biosphere and atmosphere are locked in a continuous, intricate dance, a relationship so profound that the existence of one is entirely dependent on the other. Understanding this complex interplay is crucial to comprehending the planet's past, present, and future, particularly in the face of climate change. This article delves into the multifaceted interactions between the biosphere and atmosphere, exploring the processes that shape our world and the delicate balance that sustains life.
The Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket and a Reactive Medium
The atmosphere, a gaseous envelope surrounding the Earth, plays a vital role in regulating the planet's temperature, shielding it from harmful solar radiation, and facilitating the water cycle. Composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen, with smaller proportions of other gases like carbon dioxide, argon, and water vapor, it acts as a dynamic, reactive medium. Its composition and structure are constantly being influenced by the biosphere and, in turn, influence the biosphere's functioning.
The Role of Atmospheric Gases in Biospheric Processes:
-
Oxygen (O₂): Essential for aerobic respiration in most organisms, oxygen is a byproduct of photosynthesis, a process primarily driven by plants and other photosynthetic organisms within the biosphere. The levels of atmospheric oxygen have dramatically fluctuated throughout Earth's history, largely determined by the evolution and activity of life.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): A crucial greenhouse gas, CO₂ plays a vital role in regulating global temperature. It's also the primary carbon source for photosynthesis. The balance of atmospheric CO₂ is directly impacted by the biosphere through photosynthesis and respiration, as well as by the decomposition of organic matter. Human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly disrupted this balance, leading to increased atmospheric CO₂ and contributing to climate change.
-
Water Vapor (H₂O): A powerful greenhouse gas, water vapor contributes significantly to the Earth's temperature and the hydrological cycle. The biosphere significantly influences the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere through transpiration (water released by plants) and evaporation from water bodies.
-
Nitrogen (N₂): Although largely inert in the atmosphere, nitrogen is an essential nutrient for life. Nitrogen fixation, primarily by bacteria in the soil and water, converts atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants. This process is integral to the biogeochemical cycles that support life within the biosphere.
The Biosphere: A Dynamic System Driving Atmospheric Change
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms on Earth and their interactions with the physical environment. This vast and complex system plays a dominant role in shaping the composition and dynamics of the atmosphere.
Biospheric Processes Affecting the Atmosphere:
-
Photosynthesis: This fundamental process converts sunlight, water, and CO₂ into glucose (energy) and oxygen. Photosynthetic organisms, mainly plants and algae, are primary producers, forming the base of most food chains. Through photosynthesis, the biosphere significantly reduces atmospheric CO₂ and replenishes oxygen.
-
Respiration: The opposite of photosynthesis, respiration releases CO₂ and water vapor as organisms utilize glucose for energy. The combined respiration of all living organisms contributes significantly to the atmospheric CO₂ levels. The balance between photosynthesis and respiration largely dictates the net flux of CO₂ into or out of the atmosphere.
-
Decomposition: The breakdown of dead organic matter by decomposers (bacteria and fungi) releases nutrients back into the ecosystem, but also releases CO₂ and other gases into the atmosphere. The rate of decomposition is influenced by factors like temperature, moisture, and the types of organisms involved.
-
Volcanic Activity (Indirect Biospheric Influence): While not directly a biospheric process, volcanic eruptions release gases, including CO₂ and sulfur dioxide, into the atmosphere. The biosphere, however, plays a role in mitigating the effects of these eruptions through processes like carbon sequestration and the absorption of sulfur dioxide by plants.
-
Evapotranspiration: The combined effect of evaporation from water bodies and transpiration from plants, evapotranspiration, plays a critical role in the water cycle and the formation of clouds and precipitation. It significantly contributes to atmospheric moisture content and influences weather patterns.
Feedback Loops: A Delicate Balance
The interactions between the biosphere and atmosphere aren't unidirectional; they involve complex feedback loops that can either stabilize or destabilize the system.
Positive Feedback Loops: Amplifying Changes
Positive feedback loops amplify initial changes, leading to potentially dramatic effects. For example:
-
Arctic Ice Melt: As Arctic ice melts due to rising temperatures (driven partly by increased atmospheric CO₂), it exposes darker ocean surfaces that absorb more solar radiation, leading to further warming and more ice melt. This is a positive feedback loop that accelerates climate change.
-
Deforestation and CO₂ Levels: Deforestation reduces the capacity of the biosphere to absorb CO₂, contributing to increased atmospheric CO₂ and further warming, which can lead to more deforestation. This again forms a positive feedback loop exacerbating the issue.
Negative Feedback Loops: Dampening Changes
Negative feedback loops, in contrast, act to dampen changes and maintain stability. For instance:
-
CO₂ Fertilization Effect: Increased atmospheric CO₂ can stimulate plant growth, leading to greater CO₂ absorption. However, this effect is complex and has limitations, with other factors influencing plant productivity.
-
Cloud Formation: Increased water vapor in the atmosphere can lead to increased cloud cover, which can reflect solar radiation back into space, thereby cooling the planet. This is a negative feedback mechanism that helps regulate temperature.
Human Impacts: Disrupting the Delicate Balance
Human activities have significantly altered the delicate balance between the biosphere and atmosphere. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial emissions, and agricultural practices have profoundly impacted atmospheric composition, leading to:
-
Climate Change: Increased greenhouse gas concentrations, particularly CO₂, methane, and nitrous oxide, trap more heat, leading to global warming, sea-level rise, and altered weather patterns. This has significant impacts on biospheric processes and ecosystems globally.
-
Ocean Acidification: Increased atmospheric CO₂ dissolves in the oceans, leading to ocean acidification, harming marine life and ecosystems.
-
Air Pollution: Emissions from industries and vehicles release pollutants into the atmosphere, harming human health and the environment, impacting plant growth and overall ecosystem health.
-
Ozone Depletion: The release of certain chemicals has depleted the ozone layer, increasing the amount of harmful ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth's surface, impacting both living organisms and biogeochemical cycles.
The Future of the Biosphere-Atmosphere Interaction
Understanding the complex interactions between the biosphere and atmosphere is crucial for predicting and mitigating the impacts of climate change and other environmental challenges. Future research should focus on:
-
Improving climate models: Incorporating more detailed representations of biospheric processes in climate models is essential for more accurate predictions.
-
Developing sustainable practices: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, protecting and restoring forests, and adopting sustainable agricultural practices are crucial for maintaining a healthy biosphere and atmosphere.
-
Monitoring atmospheric and biospheric changes: Continuous monitoring of atmospheric composition and biospheric health is essential for tracking changes and evaluating the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
The intricate dance between the biosphere and atmosphere is a testament to the interconnectedness of Earth's systems. Maintaining the delicate balance of this relationship is paramount for the continued health of our planet and the survival of all life on Earth. Understanding the processes involved and implementing sustainable practices are critical for ensuring a future where this vital interaction continues to support life as we know it.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Bottles Of Water Is 1 Liter
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days In A Million Minutes
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days Is In 11 Weeks
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Grams Are In One Tola Gold
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Oz In A Pound Of Freon
Jul 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Explain How The Biosphere Interacts With The Atmosphere . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.