Explain The Relationship Between Photosynthesis And Respiration
Kalali
Mar 23, 2025 · 7 min read
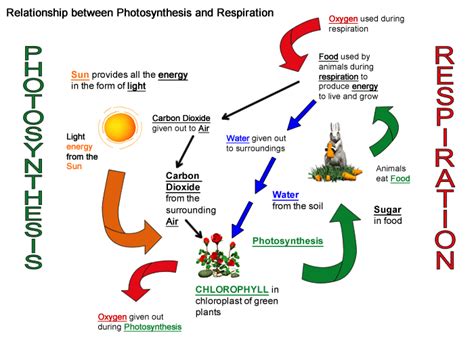
Table of Contents
The Intertwined Dance of Photosynthesis and Respiration: A Deep Dive into Life's Fundamental Processes
Photosynthesis and respiration are two fundamental biological processes that are not only essential for life on Earth but are also intricately linked in a continuous cycle. Understanding their relationship is crucial to grasping the fundamental mechanisms that drive the biosphere and sustain all life forms, from the smallest bacteria to the largest whales. This article will delve into the intricacies of photosynthesis and respiration, exploring their individual mechanisms, their interconnectedness, and the significant impact they have on the global carbon cycle.
Photosynthesis: Capturing the Sun's Energy
Photosynthesis, literally meaning "synthesis using light," is the remarkable process by which green plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. This process forms the basis of most food chains on Earth, providing the energy that fuels almost all ecosystems.
The Process Unveiled: A Step-by-Step Look
Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle).
1. Light-Dependent Reactions: This stage takes place in the thylakoid membranes within chloroplasts. Chlorophyll and other pigments absorb light energy, exciting electrons to a higher energy level. This energy is then used to:
- Split water molecules (photolysis): This process releases electrons, protons (H+), and oxygen (O2), the latter being a byproduct that is crucial for aerobic respiration in many organisms.
- Generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate): This molecule is the primary energy currency of cells.
- Produce NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate): This molecule acts as a reducing agent, carrying high-energy electrons to the next stage.
2. Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): This stage occurs in the stroma, the fluid-filled space surrounding the thylakoids. Here, the energy stored in ATP and NADPH is utilized to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere into glucose (C6H12O6), a simple sugar. This process involves a series of enzymatic reactions, ultimately fixing carbon from an inorganic form into an organic molecule.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Several environmental factors significantly influence the rate of photosynthesis. These include:
- Light intensity: Increased light intensity generally leads to a higher rate of photosynthesis up to a saturation point, beyond which further increases have little effect.
- Carbon dioxide concentration: Similar to light intensity, CO2 concentration impacts the rate of photosynthesis, with higher concentrations generally leading to faster rates.
- Temperature: Photosynthesis is enzyme-driven, and enzyme activity is temperature-sensitive. Optimal temperatures vary depending on the plant species. Extreme temperatures can denature enzymes and reduce photosynthetic efficiency.
- Water availability: Water is a reactant in photosynthesis, and its deficiency can significantly limit the process.
Respiration: Releasing the Stored Energy
Respiration is the process by which organisms break down organic molecules, such as glucose, to release the stored chemical energy. This energy is then used to power various cellular processes, including growth, movement, and reproduction. There are two main types of respiration: aerobic and anaerobic.
Aerobic Respiration: The Oxygen-Dependent Pathway
Aerobic respiration, the most common type, requires oxygen as the final electron acceptor. It occurs in three main stages:
1. Glycolysis: This initial stage takes place in the cytoplasm and involves the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. This process generates a small amount of ATP and NADH.
2. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): This cycle occurs in the mitochondria and involves the further oxidation of pyruvate, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) and generating more ATP, NADH, and FADH2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide).
3. Electron Transport Chain (ETC): This final stage, also located in the mitochondria, involves a series of electron carriers that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2. This electron flow drives the pumping of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient. This gradient is then used by ATP synthase to generate a large amount of ATP through chemiosmosis. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, combining with protons to form water.
Anaerobic Respiration: Life Without Oxygen
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. It is less efficient than aerobic respiration, generating far less ATP. Two common types of anaerobic respiration are:
- Lactic acid fermentation: This process occurs in muscle cells during intense exercise when oxygen supply is limited. Pyruvate is converted to lactic acid, regenerating NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue.
- Alcoholic fermentation: This process is used by yeast and some bacteria. Pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide, also regenerating NAD+.
The Interdependence of Photosynthesis and Respiration: A Symbiotic Relationship
Photosynthesis and respiration are fundamentally interconnected, forming a cyclical relationship that underpins the biosphere's stability and energy flow. The products of one process are the reactants of the other:
- Photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen: Glucose serves as the primary energy source for respiration, and oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration.
- Respiration produces carbon dioxide and water: Carbon dioxide is a crucial reactant in photosynthesis, and water is used in the light-dependent reactions.
This continuous cycle ensures the efficient recycling of essential elements and the flow of energy through ecosystems. Plants, through photosynthesis, capture solar energy and convert it into chemical energy stored in glucose. Animals, and even plants themselves, then utilize this stored energy through respiration to power their life processes. The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is essential for aerobic respiration, and the carbon dioxide released during respiration is crucial for photosynthesis.
The Global Carbon Cycle and its Dependence on Photosynthesis and Respiration
The global carbon cycle involves the continuous exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. Photosynthesis and respiration play pivotal roles in this cycle:
- Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere: Plants absorb CO2 during photosynthesis and incorporate it into organic molecules, effectively removing it from the atmosphere.
- Respiration returns carbon dioxide to the atmosphere: Both plants and animals release CO2 during respiration, completing the cycle.
The balance between photosynthesis and respiration is crucial for maintaining the Earth's atmospheric CO2 levels and regulating global climate. Any disruption to this balance, such as deforestation or increased fossil fuel combustion, can lead to significant changes in atmospheric CO2 concentrations and contribute to climate change.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Nuances
The relationship between photosynthesis and respiration is complex and multifaceted. Several factors influence the interplay between these processes:
- Environmental conditions: Variations in light intensity, temperature, and water availability can impact both photosynthesis and respiration rates, affecting the overall carbon cycle.
- Plant type: Different plant species exhibit variations in photosynthetic and respiratory efficiency, influencing their contribution to the carbon cycle.
- Organism type: The respiratory processes employed by different organisms (aerobic vs. anaerobic) also affect the carbon cycle dynamics.
The Future of Photosynthesis and Respiration Research
Ongoing research continues to unveil new details about the intricacies of photosynthesis and respiration. This includes:
- Engineering more efficient photosynthetic pathways: Scientists are exploring ways to enhance the efficiency of photosynthesis in crops to increase food production and mitigate climate change.
- Understanding the impact of climate change on photosynthesis and respiration: Studies are focusing on how changes in temperature, CO2 levels, and water availability affect the balance between these processes.
- Developing new biofuels based on photosynthetic products: Researchers are investigating ways to utilize photosynthetic products as sustainable sources of energy.
Conclusion: A Harmonious Interplay for Life on Earth
The intertwined relationship between photosynthesis and respiration is a cornerstone of life on Earth. These processes, in their elegant interplay, sustain the flow of energy and the cycling of essential elements, driving the biosphere's complexity and supporting the diversity of life. As we continue to study and understand these fundamental processes, we gain crucial insights into the delicate balance of our planet and the measures we need to take to maintain its health and sustainability. The future of our planet hinges, in part, on the continued health and efficiency of these vital biological processes. Understanding their relationship is not merely an academic exercise; it’s a key to ensuring a sustainable future for all life on Earth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Ten Feet In Meters
May 09, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 5 Out Of 15
May 09, 2025
-
How To Find Molarity From Titration
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 244
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 75
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Explain The Relationship Between Photosynthesis And Respiration . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.