Formula Of Circumference Of A Cylinder
Kalali
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
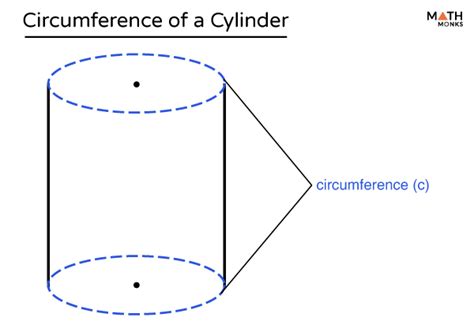
Table of Contents
Decoding the Cylinder: A Comprehensive Guide to its Circumference Formula
Understanding the circumference of a cylinder is fundamental to various fields, from engineering and architecture to packaging design and even baking. While the concept seems straightforward, a deeper dive reveals nuances and applications that extend beyond simple calculations. This comprehensive guide will explore the formula for the circumference of a cylinder, its derivations, practical applications, and common misconceptions. We'll also touch upon related concepts like surface area and volume to provide a holistic understanding of cylindrical geometry.
Understanding Cylindrical Geometry: Basics and Definitions
Before diving into the formula, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a cylinder. A cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved lateral surface. Key elements include:
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of a circular base to any point on its circumference.
- Diameter (d): The distance across the circle through its center; twice the radius (d = 2r).
- Height (h): The perpendicular distance between the two circular bases.
- Circumference (C): The distance around the circular base.
The Formula for the Circumference of a Cylinder
The circumference of a cylinder is simply the circumference of its circular base. Since the base is a circle, the formula is identical to that of a circle's circumference:
C = 2πr
Where:
- C represents the circumference.
- π (pi): A mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. It represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
- r represents the radius of the circular base.
Alternatively, using the diameter (d):
C = πd
Derivation of the Circumference Formula
The formula's derivation stems from the definition of π. Imagine taking a string and wrapping it around a circular object. The length of the string required to encircle the object exactly once is its circumference. If you then measure the diameter and divide the circumference by the diameter, you will always arrive at the same constant value, π. This fundamental relationship forms the basis of the circumference formula.
Practical Applications of the Circumference Formula
The circumference formula finds extensive application across diverse fields:
1. Engineering and Manufacturing:
- Pipe and Tube Sizing: Calculating the circumference is crucial for determining the appropriate size of pipes, tubes, and other cylindrical components in various engineering systems. This is critical for fluid flow calculations and material selection.
- Gear Design: In mechanical engineering, the circumference of gears dictates their rotational speed and meshing characteristics. Accurate circumference calculations are vital for designing efficient and reliable gear systems.
- Shaft Design: Designing rotating shafts requires considering their circumference to ensure appropriate strength and prevent failure under stress.
2. Architecture and Construction:
- Column Design: Architectural columns are often cylindrical, and understanding their circumference is essential for material estimation and structural integrity.
- Pipe Layout: In building construction, accurate circumference calculations are crucial for laying out plumbing and other pipe systems effectively.
- Dome Construction: Many domes have a cylindrical base, necessitating the calculation of the circumference for accurate material estimates and structural planning.
3. Packaging and Design:
- Label Design: Designing labels for cylindrical containers requires knowledge of the circumference to ensure proper fit and coverage.
- Container Production: Manufacturers need precise circumference calculations to produce cylindrical containers of the correct size and dimensions.
4. Other Applications:
- Calculating the speed of a rotating object: Knowing the circumference allows you to determine the distance traveled per revolution.
- Determining the amount of material required for wrapping or covering a cylinder: The circumference is essential for calculating the amount of material needed to wrap a cylindrical object.
- In fields like astronomy: The circumference of celestial bodies is used in calculations related to their rotation and orbital mechanics.
Common Misconceptions and Mistakes
While the formula seems simple, common errors can arise:
- Confusing Radius and Diameter: Incorrectly using the diameter instead of the radius, or vice versa, is a frequent mistake leading to incorrect circumference calculations. Always double-check your units and ensure you are using the correct value.
- Incorrect Use of Pi: Using an inaccurate value for π can lead to significant errors, especially in precision-critical applications. Using a sufficiently precise value of π (at least 3.14159) is highly recommended.
- Ignoring Units: Failing to include units (e.g., centimeters, meters, inches) in your calculations and final answer is a critical error. Always maintain consistency in units throughout your calculations.
Expanding the Scope: Surface Area and Volume
While this article focuses on circumference, it's helpful to understand its relationship to other key cylindrical properties:
- Lateral Surface Area: This is the area of the curved surface connecting the two bases. The formula is: A<sub>lateral</sub> = 2πrh.
- Total Surface Area: This includes the lateral surface area and the area of both circular bases. The formula is: A<sub>total</sub> = 2πrh + 2πr².
- Volume: The space enclosed within the cylinder. The formula is: V = πr²h.
These formulas, alongside the circumference formula, provide a comprehensive set of tools for working with cylinders in various applications.
Advanced Considerations: Non-Circular Cylinders
While we've primarily focused on cylinders with circular bases, it's important to note that cylinders can also have elliptical or other shaped bases. The circumference calculation for such cylinders is more complex and involves integral calculus, going beyond the scope of this introductory guide.
Conclusion: Mastering the Circumference of a Cylinder
Understanding and applying the circumference formula is a fundamental skill with far-reaching implications across numerous disciplines. By grasping the formula, its derivation, and its various applications, you equip yourself with a powerful tool for solving real-world problems and tackling intricate geometric challenges. Remember to avoid common pitfalls like confusing radius and diameter, using an appropriate value for π, and always including units in your calculations. With practice and attention to detail, you can master the art of calculating the circumference of a cylinder and unlock its many practical uses.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 26 Out Of 30 As A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 26 In
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 6 Out Of 20 As A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is Melting Point Of Glass
Mar 17, 2025
-
Cuanto Es El 30 Por Ciento De 500
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Formula Of Circumference Of A Cylinder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
