Gravitational Force Of Sun On Earth
Kalali
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
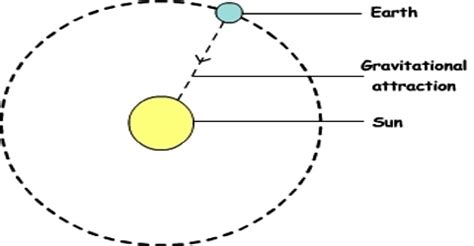
Table of Contents
The Sun's Gravitational Grip: How Our Star Shapes Earth's Orbit and More
The Sun, our nearest star, is a fiery giant dominating our solar system. Its immense mass exerts a powerful gravitational force that dictates the Earth's orbit, influences our tides, and plays a crucial role in the stability of our planet. Understanding this gravitational influence is fundamental to comprehending the dynamics of our solar system and the very existence of life on Earth.
The Fundamental Force: Gravity Explained
Before diving into the specifics of the Sun's gravitational pull on Earth, let's briefly revisit the concept of gravity itself. Gravity, as described by Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, is a fundamental force of attraction between any two objects with mass. The strength of this attraction is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This means that the more massive the objects and the closer they are, the stronger the gravitational force between them.
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation, expressed mathematically:
F = G * (m1 * m2) / r²
Where:
- F represents the force of gravity
- G is the gravitational constant (a fundamental constant in physics)
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects
This seemingly simple equation underpins the complex interactions of celestial bodies, including the Sun's influence on Earth.
The Sun's Dominating Gravitational Influence
The Sun, with its colossal mass (approximately 333,000 times the mass of Earth), exerts an overwhelmingly powerful gravitational force on our planet. This force is the primary reason Earth remains in its stable orbit, preventing it from drifting off into the vast emptiness of space. Without the Sun's gravity, Earth would travel in a straight line, rather than its elliptical path around the Sun.
Orbital Mechanics: A Delicate Dance
Earth's orbit isn't a perfect circle; it's slightly elliptical. This elliptical path is a direct consequence of the balance between the Sun's gravitational pull and Earth's inertia (its tendency to continue moving in a straight line). At its closest point to the Sun (perihelion), Earth experiences a stronger gravitational pull, increasing its orbital speed. Conversely, at its farthest point (aphelion), the gravitational force is weaker, causing a decrease in orbital speed. This continuous interplay between gravity and inertia maintains Earth's orbit.
The Importance of Orbital Stability
The stability of Earth's orbit is crucial for life as we know it. A significantly different orbit could drastically alter Earth's climate, making it too hot or too cold for life to thrive. Slight variations in Earth's orbit over long periods contribute to cyclical climate changes, as explored in the Milankovitch cycles, which influence the timing and severity of ice ages.
Beyond Orbital Stability: Other Effects of Solar Gravity
The Sun's gravity isn't limited to just maintaining Earth's orbit. Its influence extends to various other aspects of our planet's environment:
Tides: A Gravitational Tug-of-War
While the Moon plays a more significant role in Earth's tides, the Sun's gravity also contributes. The Sun's gravitational pull on Earth's oceans creates tidal bulges, although these are less pronounced than those caused by the Moon. When the Sun, Earth, and Moon align (during new and full moons), their combined gravitational forces produce exceptionally high tides known as spring tides. Conversely, when the Sun and Moon are at right angles to each other (during first and third quarter moons), their gravitational forces partially cancel each other out, resulting in lower tides called neap tides.
Solar Wind and its Interaction with Earth's Magnetosphere
Although not directly related to the static gravitational force, the Sun's influence extends to its dynamic solar wind. This continuous stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun interacts with Earth's magnetosphere, a protective shield generated by Earth's magnetic field. This interaction can cause geomagnetic storms, potentially disrupting satellite communication and power grids. While the solar wind is primarily electromagnetic in nature, the overall structure and configuration of the heliosphere (the Sun's influence zone) is ultimately governed by the Sun's gravity.
Shaping the Solar System: A Cosmic Architect
The Sun's gravity isn't only influential on Earth; it governs the entire solar system. It keeps the planets in their orbits, controls the movements of asteroids and comets, and plays a role in the formation and evolution of planetary systems. The Sun's gravitational dominance prevents our planets from colliding or being ejected from the solar system. Its influence is the architect of the solar system's structure and stability.
Exploring the Limits of Newtonian Gravity: Einstein's Intervention
While Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation provides a remarkably accurate description of the Sun's gravitational influence on Earth for most practical purposes, it has its limitations. Einstein's theory of General Relativity provides a more comprehensive understanding of gravity, particularly in situations involving extremely strong gravitational fields or very high speeds.
General Relativity describes gravity not as a force but as a curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy. The Sun's immense mass warps the spacetime around it, causing Earth and other planets to follow curved paths—their orbits. This subtle difference between Newton's and Einstein's descriptions becomes increasingly significant in situations involving very strong gravitational fields. While the difference is negligible for most calculations concerning the Sun's influence on Earth, it's crucial for understanding phenomena like the slight precession of Mercury's orbit.
The Future of Earth's Orbit: Long-Term Stability and Potential Perturbations
While Earth's orbit is remarkably stable over relatively short timescales (thousands of years), subtle influences from other planets can cause slight variations over millions of years. These gravitational perturbations, although small, can cumulatively alter Earth's orbit over geological time.
The long-term stability of Earth's orbit is a complex issue involving intricate calculations and simulations. While significant disruptions are unlikely in the near future, understanding these subtle long-term effects is crucial for comprehending Earth's climate history and predicting potential future changes.
Furthermore, the eventual fate of the Sun, as it evolves into a red giant, will dramatically alter its gravitational influence on Earth. While the precise outcome is still a subject of ongoing research, it’s clear that the Sun’s expanding outer layers will eventually have significant effects on the Earth's orbit, posing a potential threat to the planet's habitability.
Conclusion: An Enduring Gravitational Dance
The Sun's gravitational force is a fundamental element shaping the Earth's existence. From maintaining our stable orbit to influencing our tides, its influence is profound and far-reaching. Understanding this powerful force, both through the lens of Newtonian gravity and the more nuanced perspective of General Relativity, allows us to appreciate the intricate dance between our planet and its star, a dance that has sustained life on Earth for billions of years and will continue to shape its future. Further research into the subtleties of this gravitational interaction will undoubtedly continue to refine our understanding of our place in the cosmos and the long-term stability of our planet's environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Say The Bread In Spanish
Jul 04, 2025
-
How Long Does It Take To Walk 2 5 Miles
Jul 04, 2025
-
How Far Is 600 Miles In Hours
Jul 04, 2025
-
What Do You Get When You Phone A Bee
Jul 04, 2025
-
Was Jennifer Aniston In Sex And The City
Jul 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Gravitational Force Of Sun On Earth . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.