Heat Capacity Of Aluminum In J Kg K
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
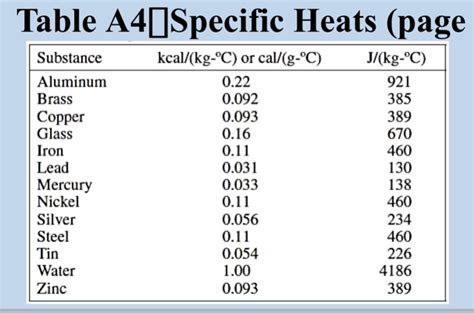
Table of Contents
Heat Capacity of Aluminum: A Deep Dive into J/kg·K
Aluminum, a ubiquitous metal in modern life, possesses a remarkable set of properties, including a relatively high heat capacity. Understanding this heat capacity, specifically expressed in J/kg·K (Joules per kilogram per Kelvin), is crucial for numerous applications, from engineering design to material science research. This article will delve into the specifics of aluminum's heat capacity, exploring its variations, influencing factors, and practical implications.
What is Heat Capacity?
Before we delve into the specifics of aluminum, let's establish a firm understanding of heat capacity itself. Heat capacity, denoted by 'C', is a physical property that quantifies the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by a specific amount. It's expressed as the ratio of the heat transferred (Q) to the resulting temperature change (ΔT):
C = Q / ΔT
The units typically used are J/K (Joules per Kelvin) for molar heat capacity (amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance) and J/kg·K (Joules per kilogram per Kelvin) for specific heat capacity (amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one kilogram of a substance). The latter is the focus of our discussion regarding aluminum.
The specific heat capacity indicates how efficiently a material absorbs and stores thermal energy. Materials with high specific heat capacities require more energy to change their temperature compared to those with lower specific heat capacities.
Aluminum's Specific Heat Capacity: The J/kg·K Value
The specific heat capacity of aluminum is approximately 900 J/kg·K. This value, however, is not entirely constant and can be influenced by several factors, as discussed below. It's important to note that this is an average value, and slight variations can occur depending on the purity of the aluminum and the temperature range considered. More precise values might be found in material property databases for specific aluminum alloys.
The relatively high specific heat capacity of aluminum has several important implications:
Practical Implications of Aluminum's High Heat Capacity
-
Heat Transfer Applications: Aluminum's high heat capacity makes it an excellent material for heat sinks and heat exchangers. It can absorb significant amounts of heat without experiencing a drastic temperature increase, making it ideal for applications like cooling computer components or managing thermal energy in industrial processes.
-
Thermal Management: In various engineering designs, particularly in electronics and automotive industries, the ability of aluminum to absorb and dissipate heat is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Its use in car engines, for example, leverages this property to prevent overheating.
-
Cooking Utensils: Aluminum's high heat capacity contributes to its popularity in cookware. It heats up relatively quickly and distributes heat evenly, leading to consistent cooking.
-
Building Materials: In some construction applications, aluminum's thermal properties are exploited. Its ability to absorb and release heat can contribute to thermal regulation within a building.
Factors Affecting Aluminum's Heat Capacity
While the approximate value of 900 J/kg·K is widely used, it's crucial to understand that several factors can influence the actual heat capacity:
Temperature Dependence
The specific heat capacity of aluminum is not completely temperature-independent. It varies slightly with temperature, generally increasing with higher temperatures. This variation is often relatively small within typical operating temperature ranges, but it becomes more significant at extreme temperatures. Precise data for this temperature dependence can be found in detailed thermodynamic property tables.
Alloying Elements
The presence of alloying elements significantly affects the heat capacity of aluminum. Different alloy compositions will have different specific heat capacities. Adding other metals alters the crystal structure and electron interactions within the material, thus influencing its thermal properties. For instance, aluminum alloys used in aerospace applications might exhibit slightly different heat capacities compared to pure aluminum or common aluminum alloys used in everyday objects.
Phase Transitions
While not directly relevant to typical ambient temperatures, it is worth noting that phase transitions (like melting or boiling) will dramatically impact the heat capacity. During a phase transition, significant energy is absorbed or released without a corresponding temperature change. The heat capacity becomes effectively infinite during these transitions because the added heat energy is used to change the phase rather than increasing the temperature.
Crystal Structure and Defects
The crystalline structure of aluminum and the presence of defects (like dislocations or grain boundaries) can also slightly alter its heat capacity. A perfectly ordered crystal might have a slightly different heat capacity than a material with imperfections. This effect is often smaller compared to temperature and alloying variations.
Measuring Heat Capacity: Experimental Techniques
The specific heat capacity of aluminum, and other materials, can be measured using various experimental techniques. Some common methods include:
Calorimetry
Calorimetry is a widely used method for measuring heat capacity. Different types of calorimeters exist, such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and adiabatic calorimetry. These techniques involve carefully measuring the heat transferred to a sample of aluminum as its temperature changes, allowing for the calculation of its specific heat capacity.
Thermal Analysis Techniques
Techniques such as thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermal analysis (DTA) can also provide information related to heat capacity, particularly in relation to phase transitions and changes in material properties at different temperatures.
Applications and Importance of Understanding Aluminum's Heat Capacity
The precise understanding of aluminum's heat capacity is essential in numerous applications:
Engineering Design
In engineering design, knowing the heat capacity of aluminum allows engineers to accurately predict and manage thermal behavior in various systems. This is crucial for designing effective cooling systems, optimizing thermal performance, and preventing overheating.
Material Science Research
Material scientists use heat capacity measurements to study the fundamental properties of materials and their response to thermal stresses. This research contributes to the development of new materials with improved thermal characteristics.
Industrial Processes
Many industrial processes involve significant heat transfer. Understanding the heat capacity of aluminum helps optimize the efficiency and safety of these processes.
Environmental Considerations
The use of aluminum in various applications has environmental implications. Knowing its thermal properties helps to design systems that minimize energy waste and optimize energy efficiency.
Conclusion
The specific heat capacity of aluminum, commonly approximated as 900 J/kg·K, is a critical parameter for numerous applications. While this value is a useful approximation, it’s vital to remember that it’s influenced by several factors, including temperature, alloying elements, and crystal structure. Understanding these influences is essential for accurate predictions and optimal design in various engineering and scientific fields. Further research and precise measurements using different techniques will continue to refine our understanding of aluminum's thermal properties and expand its practical applications. Accurate characterization of materials like aluminum is paramount for technological advancement and sustainable development.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
147 Cm Is How Many Inches
Mar 19, 2025
-
Common Multiples Of 12 And 30
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is 0 125 As A Percent
Mar 19, 2025
-
Similarity And Altitudes In Right Triangles
Mar 19, 2025
-
1 2 A Pound Is How Many Ounces
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Heat Capacity Of Aluminum In J Kg K . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
