How Are Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Related
Kalali
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
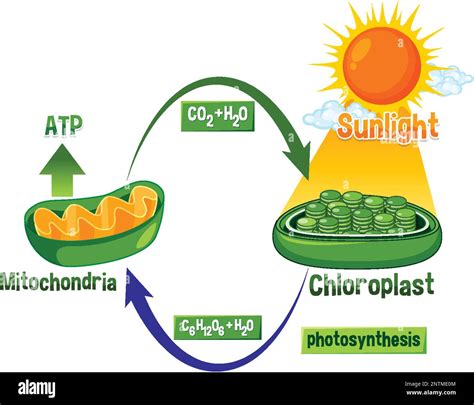
Table of Contents
How Are Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Related? A Deep Dive into the Interconnectedness of Life's Essential Processes
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental processes that underpin the existence of almost all life on Earth. While seemingly disparate, they are intricately linked, forming a cyclical relationship that sustains the biosphere's delicate balance. Understanding their connection is key to grasping the fundamental principles of biology and ecology. This comprehensive article will delve into the details of both processes, highlighting their interdependencies and the crucial role they play in maintaining life as we know it.
Photosynthesis: Capturing the Sun's Energy
Photosynthesis, the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll, is the foundation of most food chains. It's a remarkable feat of biological engineering, converting light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process occurs within chloroplasts, specialized organelles found within plant cells.
The Two Stages of Photosynthesis:
Photosynthesis is broadly divided into two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle).
1. Light-Dependent Reactions: This stage occurs in the thylakoid membranes within the chloroplast. Sunlight excites chlorophyll molecules, initiating a chain of electron transfers. This electron transport chain generates ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's primary energy currency, and NADPH, a reducing agent crucial for the next stage. Water is split (photolysis) during this process, releasing oxygen as a byproduct – the oxygen we breathe.
2. Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): This stage takes place in the stroma, the fluid-filled space surrounding the thylakoids. The ATP and NADPH generated during the light-dependent reactions are utilized to fix atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic molecules, primarily glucose. This process is called carbon fixation and involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The glucose produced serves as the plant's primary energy source and building block for other organic molecules.
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy from Glucose
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other organic molecules to release the stored energy. This energy is then used to power various cellular activities, including growth, repair, and movement. This process occurs in the mitochondria, another specialized organelle found in most eukaryotic cells.
The Stages of Cellular Respiration:
Cellular respiration is a multi-step process, encompassing several interconnected stages:
1. Glycolysis: This initial stage occurs in the cytoplasm and doesn't require oxygen. Glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, yielding a small amount of ATP and NADH.
2. Pyruvate Oxidation: Pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria, where it is converted into acetyl-CoA, releasing carbon dioxide. This step also produces NADH.
3. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): This cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, undergoing a series of reactions that release carbon dioxide, generate ATP, and produce more NADH and FADH2 (another electron carrier).
4. Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation: This final stage takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The NADH and FADH2 generated in the previous steps donate electrons to the electron transport chain. As electrons move down the chain, energy is released and used to pump protons (H+) across the membrane, creating a proton gradient. This gradient drives ATP synthesis through a process called chemiosmosis. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, combining with protons to form water. This stage generates the vast majority of ATP produced during cellular respiration.
The Intertwined Dance: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is best described as a cyclical exchange of energy and matter. They are essentially reverse processes, with the products of one serving as the reactants of the other.
-
Oxygen Production and Consumption: Photosynthesis releases oxygen as a byproduct, which is then utilized by organisms (including plants themselves) during cellular respiration as the final electron acceptor.
-
Carbon Dioxide Exchange: Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. This CO2 is then absorbed by plants during photosynthesis, restarting the cycle.
-
Energy Transformation: Photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. Cellular respiration then releases this chemical energy in the form of ATP, the readily usable energy currency of the cell.
The Symbiotic Relationship in Ecosystems:
This interconnectedness is crucial for maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Photosynthetic organisms, like plants and algae, are primary producers, forming the base of most food chains. They capture solar energy and convert it into organic matter, providing the energy source for all other organisms in the ecosystem. These consumers, in turn, utilize cellular respiration to break down the organic matter, releasing the energy they need and producing carbon dioxide, which is then recycled by photosynthetic organisms.
Exceptions and Variations:
While the typical model describes a clear interplay between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, it's important to acknowledge variations. Some organisms, such as anaerobic bacteria, rely on anaerobic respiration or fermentation, processes that don't require oxygen. These processes are less efficient in terms of ATP production compared to aerobic cellular respiration. Additionally, some plants utilize specialized forms of photosynthesis adapted to specific environmental conditions, such as CAM photosynthesis (common in desert plants) or C4 photosynthesis (common in grasses).
The Impact of Climate Change: A Disrupted Balance
The delicate balance between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is increasingly threatened by climate change. Rising atmospheric CO2 levels, while initially providing more substrate for photosynthesis, can also lead to various negative impacts, including ocean acidification, changes in plant growth patterns, and disruptions in ecosystem dynamics. Increased temperatures can also reduce photosynthetic efficiency and alter the rates of cellular respiration. Understanding the intricate interplay between these two fundamental processes is critical for developing strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change and preserve the Earth's biodiversity.
Conclusion: A Cycle of Life
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two sides of the same coin, representing the fundamental processes that drive the flow of energy and matter through the biosphere. Their intimate relationship forms the basis of life on Earth, highlighting the beautiful interconnectedness of all living things. By understanding their intricate workings and interdependence, we gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance of ecosystems and the importance of conserving this vital cycle for future generations. Continued research into these processes is crucial for addressing environmental challenges and ensuring the long-term sustainability of our planet. The study of these processes continues to be a dynamic field, with ongoing discoveries providing a deeper understanding of the complexities of life itself. Further exploration into the specific enzymatic reactions, regulatory mechanisms, and environmental influences on these processes will undoubtedly reveal even more insights into the fundamental workings of life on Earth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups Is A Liter
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is 20 Percent Of 30
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are 72 Inches
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Many Quarts In 2 5 Gallons
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is The Average Height For A 14 Year Old
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Related . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
