How Do Machines Make Work Easier
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
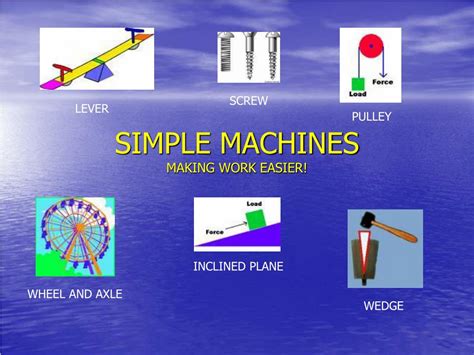
Table of Contents
How Do Machines Make Work Easier? A Deep Dive into Mechanical Advantage
Machines are ubiquitous in modern life, silently transforming how we work and live. From the simplest lever to complex automated systems, they dramatically reduce the effort needed to accomplish tasks. But how exactly do they achieve this? This article delves into the fascinating world of machines, exploring the fundamental principles behind their efficiency and showcasing their diverse applications across various industries.
Understanding Mechanical Advantage: The Core Principle
At the heart of every machine's ability to simplify work lies the concept of mechanical advantage. This is the ratio of the output force (the force the machine exerts) to the input force (the force you apply). A higher mechanical advantage means you can achieve the same amount of work with less effort. This doesn't mean the machine creates energy; it simply redistributes it, making the work easier to perform.
The Six Simple Machines: Building Blocks of Complexity
Many complex machines are built upon six fundamental simple machines:
-
Lever: A rigid bar that pivots around a fixed point (fulcrum). Levers amplify force, allowing you to move heavy objects with less effort. Examples include crowbars, seesaws, and even your forearm. The location of the fulcrum relative to the load and effort determines the mechanical advantage.
-
Wheel and Axle: A wheel attached to a smaller cylinder (axle). This combination allows for easier rotation and movement of objects. Examples include doorknobs, steering wheels, and gears. The ratio of the wheel's radius to the axle's radius determines the mechanical advantage.
-
Pulley: A wheel with a groove around its circumference, used with a rope or cable. Pulleys change the direction of force and can increase mechanical advantage, allowing you to lift heavy objects with less force. Multiple pulleys working together (block and tackle systems) significantly enhance lifting capacity.
-
Inclined Plane: A flat surface tilted at an angle. It reduces the force required to lift an object by increasing the distance over which the force is applied. Ramps, stairs, and even sloping roads are examples of inclined planes.
-
Wedge: A triangular-shaped tool that uses inclined planes to split or separate materials. Examples include knives, axes, and chisels. The sharper the wedge, the greater the force concentration and mechanical advantage.
-
Screw: An inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. Screws convert rotational motion into linear motion, enabling the fastening of objects or lifting heavy loads. The pitch (distance between threads) determines the mechanical advantage.
Machines in Action: Transforming Industries
The impact of machines spans across diverse sectors, revolutionizing productivity and efficiency. Let's explore some key examples:
1. Agriculture: From Manual Labor to Mechanized Efficiency
Historically, agriculture was heavily reliant on manual labor. Machines have dramatically changed this landscape. Tractors, harvesters, and planting machines have replaced human effort, leading to increased yields and reduced labor costs. Automated irrigation systems optimize water usage, while precision farming techniques utilizing GPS and sensors enhance efficiency and minimize waste.
Specific Examples:
- Tractors: These powerful machines provide the horsepower needed for plowing, tilling, and other heavy fieldwork, significantly reducing the physical strain on farmers.
- Harvesters: These automated systems efficiently harvest crops like wheat, corn, and soybeans, increasing yield and speed while minimizing losses.
- Automated Irrigation: Smart irrigation systems monitor soil moisture and weather conditions to deliver precise amounts of water, conserving resources and maximizing crop growth.
2. Manufacturing: Mass Production and Precision Engineering
Machines are the backbone of modern manufacturing. Assembly lines, robotic arms, and CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have enabled mass production of goods with unprecedented speed and precision. This has led to lower costs, higher quality, and increased availability of products.
Specific Examples:
- Assembly Lines: These systems move parts along a conveyor belt, with workers performing specialized tasks at each station. This division of labor optimizes productivity and reduces production time.
- Robotic Arms: These versatile machines perform repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy, improving efficiency and reducing human error in manufacturing processes.
- CNC Machines: These computer-controlled machines can perform intricate machining operations with high precision, leading to the production of complex and highly accurate components.
3. Construction: Building Bigger and Better with Less Effort
The construction industry heavily relies on machinery to manage heavy lifting, excavation, and material handling. Cranes, excavators, bulldozers, and concrete mixers are essential tools that have enabled the construction of large-scale infrastructure projects and buildings.
Specific Examples:
- Cranes: These machines lift and move heavy materials, significantly speeding up construction projects and reducing the risk of injuries associated with manual handling.
- Excavators: These powerful machines are used for excavation, grading, and other earthmoving tasks, dramatically increasing efficiency compared to manual methods.
- Concrete Mixers: These machines automate the mixing of concrete, ensuring consistent quality and significantly speeding up the construction process.
4. Transportation: Moving Goods and People Efficiently
Machines have revolutionized transportation, making it faster, more efficient, and safer. Cars, trains, airplanes, and ships rely on complex mechanical systems to operate, allowing for the movement of goods and people across vast distances.
Specific Examples:
- Cars and Trucks: Internal combustion engines and advanced transmission systems have made personal and commercial transportation significantly faster and more efficient.
- Trains: Rail networks enable the efficient transportation of large volumes of goods and passengers over long distances.
- Airplanes: Air travel has dramatically reduced travel times, connecting distant locations and facilitating global trade.
Beyond Simple Machines: The Rise of Automation and AI
The integration of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) represents a significant advancement in the application of machines to simplify work. These technologies are capable of performing complex tasks with minimal human intervention, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Examples of Advanced Machine Applications:
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): These self-navigating robots transport materials and goods within factories and warehouses, eliminating manual handling and optimizing logistics.
- AI-powered Robotics: Robots equipped with AI can adapt to changing environments and perform complex tasks such as assembly, inspection, and quality control with greater speed and accuracy than human workers.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze data from sensors on machinery to predict potential failures, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
The Future of Machines and Work
The ongoing advancements in machine technology promise to further revolutionize how we work. Automation and AI will continue to streamline processes, increasing productivity and efficiency across various industries. However, it's crucial to acknowledge the potential impact on the workforce. Reskilling and upskilling initiatives will be essential to prepare workers for the changing job market and harness the benefits of technological advancements while mitigating potential negative consequences. The future of work will likely involve a greater collaboration between humans and machines, leveraging the strengths of both to create a more efficient and productive society. The focus will shift towards higher-level tasks requiring creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, complementing the capabilities of increasingly sophisticated machines.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Machines
Machines have undeniably transformed our world, significantly simplifying work and improving our quality of life. By understanding the fundamental principles of mechanical advantage and the diverse applications of machines across various industries, we can appreciate their profound impact on our society. The future promises even more sophisticated machines, further enhancing our ability to accomplish tasks with greater efficiency and ease. Adapting to this evolving landscape, fostering innovation, and embracing ethical considerations will be crucial to harness the full potential of machines while ensuring a prosperous and inclusive future for all.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Mistletoe And Spruce Tree Symbiotic Relationship
Mar 19, 2025
-
177 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 19, 2025
-
Derivative Of The Area Of A Triangle
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Do You Write 10 As A Decimal
Mar 19, 2025
-
6 To The Power Of 5
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do Machines Make Work Easier . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
