How Do You Find The Diameter Of A Cylinder
Kalali
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
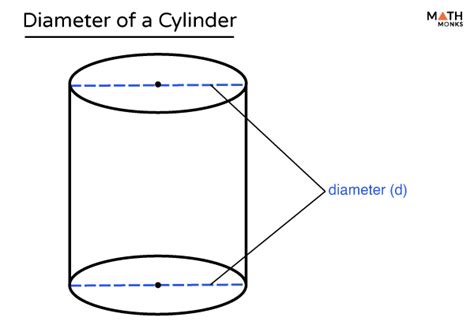
Table of Contents
How Do You Find the Diameter of a Cylinder? A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the diameter of a cylinder might seem straightforward, but the method you use depends heavily on what information you already possess. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various scenarios and techniques, ensuring you can accurately determine the diameter regardless of the available data. We'll cover everything from direct measurement to calculations using other cylindrical dimensions.
Understanding the Cylinder and its Diameter
Before diving into the methods, let's define our terms. A cylinder is a three-dimensional solid with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. The diameter is a straight line passing from side to side through the center of a circle (or, in this case, the circular base of the cylinder). It's twice the length of the radius, which is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on the circumference.
Method 1: Direct Measurement – The Simplest Approach
If you have a physical cylinder and access to basic measuring tools, the most straightforward way to find the diameter is by direct measurement.
Tools Required:
- Caliper: A caliper provides the most accurate measurement, allowing for precise clamping onto the cylinder's base. Digital calipers offer even greater precision.
- Ruler: A ruler is a suitable alternative, though slightly less accurate, particularly for smaller cylinders. Ensure the ruler is placed accurately across the widest part of the cylinder's base.
Steps:
- Position the Tool: Carefully place the caliper jaws or ruler across the widest part of the cylinder's circular base, ensuring the measurement is taken through the center.
- Record the Measurement: Note the measurement displayed on the caliper or read the ruler's markings. This value represents the diameter of the cylinder.
Important Considerations:
- Accuracy: Calipers generally offer superior accuracy compared to rulers, especially for smaller cylinders where even minor errors can significantly affect the result.
- Surface Irregularities: If the cylinder's surface isn't perfectly smooth, multiple measurements at different points might be necessary to obtain a reliable average diameter.
- Unit Consistency: Ensure that all measurements are recorded in the same units (e.g., millimeters, centimeters, inches).
Method 2: Calculating Diameter from the Circumference
If you know the circumference of the cylinder's base, you can easily calculate its diameter using the following formula:
Diameter (d) = Circumference (C) / π
Where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
Example:
Let's say you've measured the circumference of a cylinder's base to be 25 centimeters. To find the diameter:
d = 25 cm / 3.14159 ≈ 7.96 cm
Practical Applications:
This method is particularly useful when direct measurement isn't feasible, such as when dealing with very large cylinders or when only the circumference is readily available (e.g., through indirect measurement techniques).
Method 3: Calculating Diameter from the Radius
If you know the radius of the cylinder's base, determining the diameter is even simpler:
Diameter (d) = 2 * Radius (r)
Example:
If the radius of a cylindrical object is 5 inches, the diameter is:
d = 2 * 5 inches = 10 inches
Applications:
This method is frequently used in geometrical calculations and engineering designs where the radius is a known or readily obtainable parameter.
Method 4: Calculating Diameter from the Area
Knowing the area of the cylinder's base allows for the calculation of its diameter through a slightly more involved process. The area (A) of a circle (and thus the base of a cylinder) is given by:
A = π * r²
We can rearrange this formula to solve for the radius:
r = √(A / π)
Once we have the radius, we can calculate the diameter using the formula from Method 3:
d = 2 * r = 2 * √(A / π)
Example:
Suppose the area of a cylinder's base is 78.5 square meters. To find the diameter:
- Calculate the radius: r = √(78.5 m² / 3.14159) ≈ 5 m
- Calculate the diameter: d = 2 * 5 m = 10 m
When to Use This Method:
This method is applicable when the area of the circular base is known, possibly obtained through measurements or calculations involving other geometrical properties.
Method 5: Using Volume and Height to Infer Diameter
While less direct, if you know the volume (V) and height (h) of the cylinder, you can calculate the diameter. The volume of a cylinder is given by:
V = π * r² * h
Solving for the radius:
r = √(V / (π * h))
Then, calculate the diameter:
d = 2 * r = 2 * √(V / (π * h))
Example:
Let's say a cylinder has a volume of 157 cubic centimeters and a height of 5 centimeters.
- Calculate the radius: r = √(157 cm³ / (3.14159 * 5 cm)) ≈ 3.16 cm
- Calculate the diameter: d = 2 * 3.16 cm ≈ 6.32 cm
Limitations and Considerations:
This method relies on accurate measurements of both volume and height. Any inaccuracies in these measurements will propagate into the calculated diameter. This method is less precise than direct measurement or using circumference or radius.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
Dealing with Irregular Cylinders:
Not all cylinders are perfectly cylindrical. If the cylinder is slightly warped or deformed, taking multiple measurements at different orientations and averaging them will provide a more representative diameter.
Using 3D Scanning:
For highly irregular or complex shapes, 3D scanning technology can provide detailed dimensional data, including the diameter of the cylinder's base.
Statistical Analysis for Multiple Measurements:
If you've taken multiple diameter measurements, calculating the average and standard deviation will provide a measure of the precision and variability in your measurements. This is especially helpful when dealing with imperfect cylinders or less precise measurement tools.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method
The best method for determining the diameter of a cylinder depends entirely on the information available and the desired level of accuracy. Direct measurement with a caliper is generally the most precise, while calculating from other dimensions provides viable alternatives when direct measurement isn't possible. Remember to always consider potential sources of error and select the method best suited to the situation. By understanding these various approaches, you'll be equipped to accurately determine the diameter of any cylinder you encounter.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
9 Out Of 16 As A Percentage
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Are The Common Multiples Of 4 And 5
Mar 14, 2025
-
Cuanto Son 32 Onzas En Litros
Mar 14, 2025
-
Equation Relating Electric Field And Voltage
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 9 12
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Find The Diameter Of A Cylinder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
