How Do You Write 5 As A Decimal
Kalali
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
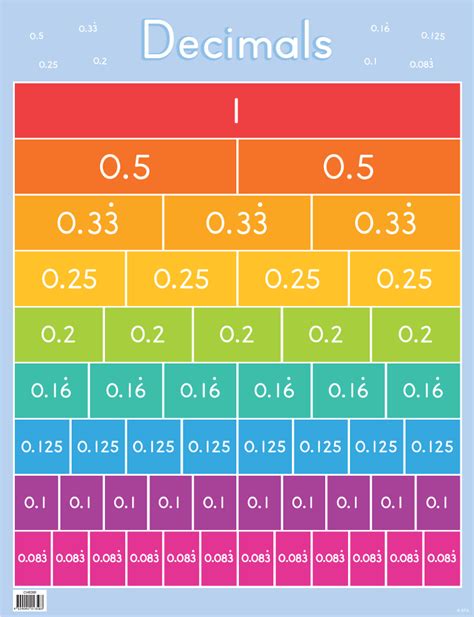
Table of Contents
How Do You Write 5 as a Decimal? A Deep Dive into Decimal Representation
The seemingly simple question, "How do you write 5 as a decimal?" opens the door to a fascinating exploration of the decimal number system, its foundations, and its implications in mathematics and beyond. While the immediate answer might appear trivial – it's simply 5.0 – a deeper understanding reveals the intricacies of place value, the significance of the decimal point, and the relationship between integers and decimal numbers. This article will delve into these aspects, providing a comprehensive and SEO-optimized exploration of the topic.
Understanding the Decimal System
The decimal system, also known as the base-10 system, is the foundation of our everyday numerical representation. It's based on ten digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. The power and elegance of this system lie in its place value system. Each digit's position relative to the decimal point dictates its value. Moving to the left from the decimal point, the place values increase by powers of 10 (ones, tens, hundreds, thousands, and so on). Moving to the right, the place values decrease by powers of 10 (tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on).
Representing Whole Numbers as Decimals
Whole numbers, like 5, are inherently part of the decimal system. They are simply integers, numbers without any fractional part. To represent a whole number as a decimal, we simply add a decimal point followed by a zero (or multiple zeros). Therefore, 5 as a decimal is written as 5.0. This notation explicitly shows that there is no fractional component. The '0' in the tenths place signifies that there are zero tenths. Similarly, we could write it as 5.00, 5.000, and so on, without changing its value. Adding additional zeros after the decimal point doesn't alter the numerical value; it only provides further precision or clarifies its decimal nature.
The Significance of the Decimal Point
The decimal point is the crucial element that separates the whole number part from the fractional part of a number. It acts as a pivotal marker in the place value system, defining the boundary between the integer portion and the decimal portion. Without the decimal point, the representation would be ambiguous; we would lose the information about the absence of a fractional part in the number. The decimal point is essential for unambiguous representation and accurate calculations, especially when dealing with numbers that have both whole and fractional parts.
Expanding the Concept: Decimals with Non-Zero Fractional Parts
While the question focuses specifically on representing 5 as a decimal, understanding how decimals work with non-zero fractional parts provides a more holistic perspective. Consider the number 5.25. Here, the '5' represents 5 ones, the '2' represents 2 tenths (2/10), and the '5' represents 5 hundredths (5/100). The number is thus equal to 5 + 2/10 + 5/100. This illustrates the additive nature of the decimal system: each digit contributes its value according to its position relative to the decimal point.
Practical Applications of Decimal Representation
The ability to write numbers as decimals is crucial in numerous contexts:
- Measurements: Measurements are often expressed in decimal form. For instance, the length of an object might be measured as 5.75 meters, indicating a whole number of meters (5) plus a fraction of a meter (75 hundredths).
- Finance: Financial calculations extensively use decimals. Prices, interest rates, and currency exchanges are commonly represented using decimals. A stock price of $5.50 signifies five whole dollars and fifty cents (50/100 of a dollar).
- Science and Engineering: Scientific and engineering applications frequently use decimals for precision and accuracy in various measurements and calculations. For example, scientific notation leverages decimals to represent very large or very small numbers concisely.
- Computing: Computers internally represent numbers using binary (base-2) systems, but these numbers are often converted to decimal representation for human readability and interaction.
Converting Fractions to Decimals
The decimal system seamlessly integrates with fractions. Any fraction can be converted into a decimal by performing division. For example, the fraction 1/2 can be converted to a decimal by dividing 1 by 2, resulting in 0.5. Similarly, 1/4 becomes 0.25, 1/8 becomes 0.125, and so on. This conversion process highlights the fundamental relationship between fractions and decimals – they represent the same underlying numerical value but in different notations.
Decimal Representation and Place Value: A Detailed Analysis
Let's analyze the place value system in more depth, focusing on the positions to the right of the decimal point.
- Tenths (1/10): This position represents one-tenth of a whole unit. For example, in 5.2, the '2' represents two tenths (2/10).
- Hundredths (1/100): This represents one-hundredth of a whole unit. In 5.25, the second '5' represents five hundredths (5/100).
- Thousandths (1/1000): This position represents one-thousandth of a whole unit, and so on. The pattern continues, with each position representing successively smaller fractions of a whole unit.
Representing 5 as a Decimal in Different Contexts
While 5.0 is the most straightforward way to represent 5 as a decimal, the context can influence the chosen representation. For instance:
- Scientific Notation: For very large or small numbers, scientific notation uses decimals. While 5 is simple, expressing it in scientific notation would be 5 x 10⁰.
- Significant Figures: In scientific measurements, the number of significant figures is crucial. If the measurement of 5 has only one significant figure, it would remain 5; however, if more precision is required, it might be written as 5.00 to indicate the level of accuracy.
- Programming: In programming languages, the representation might be slightly different based on the data type used. However, the underlying numerical value would still be 5.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Some common misconceptions surrounding decimal representation include:
- Infinite Zeros: Adding infinite zeros after the decimal point does not change the value; it's simply a matter of representation. 5.0, 5.00, and 5.000... all represent the same value.
- Terminating vs. Repeating Decimals: The number 5 is a terminating decimal—the decimal representation ends after a finite number of digits. Other numbers, like 1/3 (0.333...), are repeating decimals, with a pattern of digits repeating indefinitely.
- Decimal Precision and Accuracy: The number of digits after the decimal point doesn't necessarily reflect the accuracy of a measurement; it only represents the precision of the measurement.
Conclusion: Mastering Decimal Representation
The question of writing 5 as a decimal, while seemingly simple, opens a pathway to a rich understanding of the decimal number system and its fundamental principles. Mastering decimal representation is essential for successful navigation of various fields that rely on numerical calculations and precision. From understanding place value to performing calculations involving fractions and decimals, a solid grasp of this concept serves as a crucial foundation for further mathematical exploration and practical problem-solving. The seemingly trivial "5.0" actually encapsulates the essence of the decimal system’s elegance and power. Understanding this seemingly simple representation lays the groundwork for more complex numerical concepts and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Bottles Of Water Is 1 Liter
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days In A Million Minutes
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days Is In 11 Weeks
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Grams Are In One Tola Gold
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Oz In A Pound Of Freon
Jul 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Write 5 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.