How Does A Veterinarian Use Comparative Anatomy To Treat Animals
Kalali
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
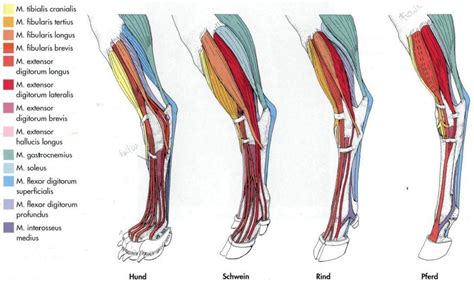
Table of Contents
How Veterinarians Use Comparative Anatomy to Treat Animals
Veterinary medicine is a fascinating field that relies heavily on a deep understanding of animal biology. While each species presents unique challenges, the principles of comparative anatomy form a cornerstone of successful veterinary practice. Comparative anatomy, the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species, allows veterinarians to apply knowledge gained from one animal to another, leading to more effective diagnoses and treatments. This article delves into the crucial role comparative anatomy plays in various aspects of veterinary care.
Understanding the Foundation: Similarities and Differences
At its core, comparative anatomy highlights the evolutionary relationships between species. While animals may look drastically different on the surface, their underlying anatomical structures often share surprising similarities. This is particularly true for mammals, showcasing the evolutionary branching from common ancestors. These shared structures, known as homologous structures, often perform similar functions, even if adapted to different environments. For instance, the basic skeletal structure of a human hand, a bat's wing, and a whale's flipper are remarkably similar, demonstrating their shared evolutionary origins.
However, understanding the differences is equally, if not more, crucial for veterinarians. Species-specific variations in anatomy can significantly impact diagnosis and treatment. A treatment that works wonders for a dog might be ineffective or even harmful for a cat, simply due to differences in their digestive systems, cardiovascular systems, or metabolic rates. Comparative anatomy helps veterinarians anticipate these variations and tailor their approaches accordingly.
Examples of Homologous Structures in Veterinary Practice:
- Skeletal System: The basic skeletal structure of mammals, birds, and reptiles provides a framework for understanding bone fractures, dislocations, and arthritic conditions. While the size and shape of bones differ, the underlying principles of fracture repair and joint mechanics remain relatively consistent.
- Cardiovascular System: The four-chambered heart is a common feature among mammals and birds, allowing veterinarians to apply principles of cardiology learned in one species to another. However, subtle differences in heart rate, blood pressure, and cardiac output necessitate species-specific adjustments in treatment protocols.
- Nervous System: While the overall organization of the nervous system is similar across many vertebrates, variations in brain structure and function can influence anesthetic protocols, pain management strategies, and the diagnosis of neurological disorders.
Comparative Anatomy in Diagnosis
Comparative anatomy is instrumental in diagnosing animal illnesses. By understanding the typical anatomy of a species, a veterinarian can quickly identify deviations from the norm. For example:
-
Radiology and Imaging: Veterinarians use X-rays, ultrasounds, and CT scans to visualize internal structures. A veterinarian's understanding of comparative anatomy allows them to interpret these images accurately, identifying abnormalities such as bone fractures, organ displacements, or tumors. They can compare the images to their knowledge of the species’ normal anatomical structures to pinpoint the problem area.
-
Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination relies heavily on comparative anatomy. By feeling the animal's abdomen, listening to its heart and lungs, and examining its posture and gait, the veterinarian assesses the animal's anatomy. Any deviation from the expected anatomical landmarks or function can signal a problem. For example, an unusual swelling in a specific location could indicate an abscess, tumor, or other pathological condition.
-
Pathology: When examining tissue samples, a veterinarian's understanding of comparative anatomy is essential. They can identify abnormalities in tissue structure and cellular composition and recognize pathological changes relative to the normal anatomy of the specific species.
Comparative Anatomy in Treatment
The application of comparative anatomy extends beyond diagnosis and into the realm of treatment planning and execution.
Surgery:
-
Surgical Techniques: Many surgical techniques are adapted across species, but anatomical differences dictate modifications. The precise location of organs, the size and shape of blood vessels, and the thickness of tissues all influence surgical approaches. A veterinarian experienced in comparative anatomy can perform surgery on a variety of species with appropriate modifications.
-
Anesthesia and Analgesia: Dosage and type of anesthetic agents and pain relievers vary greatly across species due to differences in metabolism and physiology. Comparative anatomy informs veterinarians' decisions on the most appropriate and safest anesthetic protocol.
Pharmacology:
- Drug Dosage and Administration: Drug dosages are adjusted based on species, size, and metabolic rate. Understanding species-specific anatomical differences influences the choice of drug administration routes (e.g., intravenous, intramuscular, oral). Comparative anatomy helps predict how a drug will be processed and metabolized in the body, ensuring optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects.
Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy:
- Targeted Exercises and Therapies: Understanding the musculoskeletal system's anatomy across species is essential for designing effective rehabilitation programs for animals recovering from injuries or surgeries. Rehabilitation protocols are tailored to the species' specific anatomy and capabilities.
Specific Examples of Comparative Anatomy in Veterinary Practice:
-
Cardiology: Veterinarians use their knowledge of comparative cardiology to diagnose and treat heart conditions in various animals. While the basic principles of cardiac function are conserved, differences in heart rate, rhythm, and anatomical structures require species-specific treatment strategies.
-
Orthopedics: Comparative anatomy is crucial in orthopedics. Veterinarians need to understand the skeletal structure, joint mechanics, and muscle attachments of different animals to diagnose and treat musculoskeletal injuries. Surgical techniques and rehabilitation plans are tailored to these differences.
-
Neurology: The nervous system presents significant variations across species. Veterinarians use their knowledge of comparative neuroanatomy to diagnose and treat neurological conditions. Differences in brain structure and function affect the choice of diagnostic tools and therapeutic approaches.
-
Gastroenterology: Digestive systems vary widely. Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores have distinct anatomical adaptations affecting their digestive processes. Veterinarians use comparative anatomy to understand species-specific digestive issues and to design effective treatments.
The Future of Comparative Anatomy in Veterinary Medicine:
With advancements in imaging techniques and genetic analysis, comparative anatomy's role in veterinary medicine continues to evolve. The integration of genomic data with anatomical information allows veterinarians to personalize treatment approaches based on an animal's genetic predisposition to certain diseases. Furthermore, 3D modeling and simulation techniques are improving surgical planning and training, leading to more precise and effective surgical interventions.
Conclusion:
Comparative anatomy is not merely a theoretical subject for veterinarians; it's a practical, indispensable tool. From diagnosis to treatment and rehabilitation, understanding the similarities and differences in animal anatomy underpins successful veterinary practice. By continuously expanding their knowledge of comparative anatomy, veterinarians enhance their ability to provide effective, compassionate, and species-appropriate care for the diverse animal population they serve. The integration of comparative anatomy with other advancements in veterinary science promises further progress in animal health and welfare.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 19 20 As A Percent
Apr 02, 2025
-
2 Is What Percent Of 9
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Limit Involving The Cosine Function
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Much Is 36 Inches In Feet
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is A 5 Out Of 7
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does A Veterinarian Use Comparative Anatomy To Treat Animals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
