How Does Biosphere Interact With Atmosphere
Kalali
Mar 12, 2025 · 7 min read
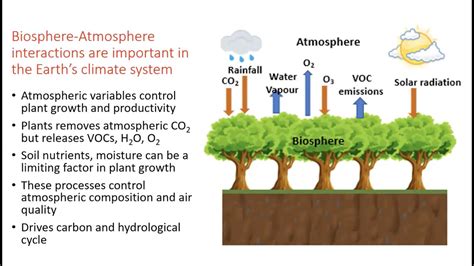
Table of Contents
How Does the Biosphere Interact with the Atmosphere? A Complex Interplay
The Earth's biosphere and atmosphere are inextricably linked in a dynamic dance of exchange and influence. Understanding this interaction is crucial for comprehending the planet's climate, biodiversity, and overall health. This intricate relationship involves a constant flow of energy, gases, and water, shaping both the living world and the gaseous envelope surrounding it. This article delves deep into the multifaceted ways the biosphere and atmosphere interact, exploring the key processes involved and the profound implications of this connection.
The Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket and a Dynamic System
The atmosphere, a mixture of gases predominantly composed of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide, acts as a protective shield against harmful solar radiation. It also plays a critical role in regulating the Earth's temperature through the greenhouse effect. This effect, while essential for maintaining habitable temperatures, is significantly influenced by the biosphere.
Composition and Dynamics:
The atmospheric composition isn't static; it's constantly changing due to both natural processes and human activities. Volcanic eruptions, for example, release significant amounts of gases, including sulfur dioxide and water vapor, affecting atmospheric chemistry and climate. Similarly, the biosphere itself contributes substantially to atmospheric composition, as detailed in the following sections. The dynamics of atmospheric circulation – wind patterns, weather systems, and the movement of air masses – further influence how the biosphere and atmosphere interact. These movements distribute gases, pollutants, and even biological materials (pollen, spores) across vast distances, impacting ecosystems far removed from their origin.
The Biosphere: A Living, Breathing System
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms on Earth and their interactions with the physical environment. From microscopic bacteria in the soil to towering redwood trees, all life forms contribute to, and are influenced by, the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis: The Cornerstone of Atmospheric Interaction
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, forms the bedrock of the biosphere-atmosphere interaction. During photosynthesis, these organisms absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and release oxygen (O2). This process is fundamental to regulating atmospheric CO2 levels and providing the oxygen that sustains most life on Earth. The vast scale of photosynthetic activity across the planet's forests, oceans, and other ecosystems makes it a major driver of atmospheric change.
Respiration: The Counterbalance
Respiration, the process by which organisms obtain energy from organic molecules, serves as a counterbalance to photosynthesis. During respiration, organisms consume oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The balance between photosynthesis and respiration influences the net exchange of carbon dioxide between the biosphere and the atmosphere. While photosynthesis generally leads to a net uptake of CO2, respiration contributes to its release, creating a continuous cycle.
Key Interactions: A Detailed Look
The interactions between the biosphere and atmosphere are multifaceted and involve several key processes:
1. Carbon Cycle: A Critical Exchange
The carbon cycle involves the movement of carbon atoms between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. The biosphere plays a crucial role in this cycle, acting as both a carbon sink (absorbing carbon) and a carbon source (releasing carbon). Forests, for example, store vast amounts of carbon in their biomass (trees, leaves, roots), acting as significant carbon sinks. When forests are cleared or burned, however, they release stored carbon back into the atmosphere, contributing to increased CO2 levels and climate change.
The Role of Soil: Soil organisms, like bacteria and fungi, play a vital role in the carbon cycle by decomposing organic matter and releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Healthy soils act as significant carbon reservoirs, and their degradation can dramatically affect atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
Oceanic Influence: The oceans also play a crucial part in the carbon cycle, absorbing a significant portion of atmospheric CO2. Marine organisms, such as phytoplankton, utilize CO2 during photosynthesis, further influencing atmospheric concentrations. Ocean acidification, caused by increased absorption of CO2, is a major concern as it impacts marine ecosystems and their ability to act as a carbon sink.
2. Water Cycle: A Constant Flow
The water cycle involves the continuous movement of water between the atmosphere, land, and oceans. The biosphere plays a significant role in this cycle through evapotranspiration, the combined process of evaporation from the land surface and transpiration from plants. Plants release water vapor into the atmosphere through their leaves, contributing to humidity and influencing weather patterns. The extent of evapotranspiration varies depending on factors such as vegetation type, temperature, and rainfall, significantly influencing regional and global climate.
Influence on Precipitation: The water released through evapotranspiration influences the formation of clouds and precipitation. Forests, for instance, can significantly increase local rainfall, while deforestation can lead to decreased precipitation and drier conditions.
3. Nutrient Cycles: Atmospheric Deposition
The biosphere relies on various nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, for growth and development. The atmosphere plays a role in nutrient cycling through atmospheric deposition, the process by which nutrients are transferred from the atmosphere to the land and oceans. This can occur through rainfall (wet deposition) or dry deposition of particles and gases. While natural processes contribute to atmospheric deposition, human activities, such as industrial emissions and agricultural practices, significantly alter the amount and composition of deposited nutrients, impacting ecosystem health.
4. Air Pollution: A Human Impact
Human activities release various pollutants into the atmosphere, including particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and greenhouse gases. These pollutants have significant impacts on the biosphere, leading to problems such as acid rain, smog, and respiratory illnesses. Air pollution can damage plants, affect water quality, and harm wildlife, disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems.
The Consequences of Disruption: Climate Change and Beyond
The intricate interaction between the biosphere and atmosphere is crucial for maintaining a stable and habitable planet. However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, have disrupted this delicate balance, leading to significant consequences, primarily climate change. Increased greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere trap heat, causing global warming and a cascade of impacts on the biosphere. These include:
- Changes in precipitation patterns: leading to droughts in some regions and floods in others.
- Sea-level rise: threatening coastal ecosystems and communities.
- Ocean acidification: harming marine life and disrupting marine ecosystems.
- Species extinctions: as organisms struggle to adapt to rapidly changing environmental conditions.
- Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events: such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and wildfires.
Protecting the Interplay: Conservation and Sustainability
Protecting the health of both the biosphere and atmosphere is crucial for the well-being of the planet and future generations. This requires a multi-pronged approach focused on:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: through transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable land management practices.
- Protecting and restoring forests: Forests act as vital carbon sinks and play a crucial role in the water cycle. Protecting existing forests and restoring degraded forests can significantly help mitigate climate change.
- Promoting sustainable agriculture: Agriculture can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and nutrient pollution. Sustainable agricultural practices can minimize these impacts and enhance biodiversity.
- Conserving biodiversity: Biodiversity is essential for ecosystem resilience and the functioning of the biosphere. Protecting and restoring biodiversity can enhance the ability of ecosystems to adapt to environmental changes.
- Monitoring atmospheric conditions: Continuous monitoring of atmospheric composition and climate parameters is essential for understanding changes and developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Conclusion: A Symbiotic Relationship
The intricate interplay between the biosphere and atmosphere is a fundamental aspect of Earth's functioning. Understanding this complex relationship is crucial for addressing environmental challenges, particularly climate change. By embracing sustainable practices and prioritizing conservation efforts, we can strive to maintain the health and balance of this critical symbiotic relationship, ensuring a habitable planet for generations to come. The continuous cycle of exchange between these two vital systems highlights the interconnectedness of all life on Earth and the urgent need for collective action to protect our planet. Further research and monitoring are essential to refine our understanding of this dynamic interaction and develop more effective strategies for environmental stewardship.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A 56 Out Of 60
Aug 03, 2025
-
How Long Does Brandy Melville Take To Ship
Aug 03, 2025
-
Which Element Is More Likely To Become A Anion
Aug 03, 2025
-
What Do Parables And Fables Have In Common
Aug 03, 2025
-
Her Tears Like Diamonds On The Floor Lyrics
Aug 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does Biosphere Interact With Atmosphere . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.