How Does The Hydrosphere Affect The Biosphere
Kalali
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
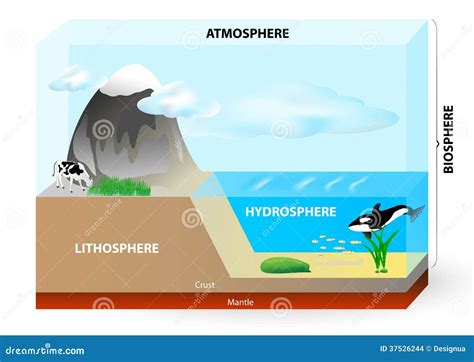
Table of Contents
How Does the Hydrosphere Affect the Biosphere? A Deep Dive into the Interconnectedness of Water and Life
The Earth's biosphere, the zone of life, is intricately interwoven with its hydrosphere, the sphere encompassing all water on the planet. This relationship is not merely a coexistence; it’s a fundamental interdependence where the hydrosphere profoundly shapes the biosphere's structure, function, and distribution. Understanding this dynamic interplay is crucial to comprehending the complexities of our planet and the challenges of environmental sustainability. This article explores the multifaceted ways the hydrosphere affects the biosphere, examining various aspects of their interconnectedness.
The Hydrosphere: The Foundation of Life
Water, the defining element of the hydrosphere, is the very elixir of life. Its unique properties – high specific heat capacity, excellent solvent capabilities, and its role in biochemical reactions – make it indispensable for all known life forms. The distribution and characteristics of water within the hydrosphere – oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater, glaciers, and atmospheric water vapor – directly influence the biosphere in numerous ways.
1. Habitat Provision and Biodiversity
The hydrosphere provides habitats for a vast array of species. Oceans, with their diverse ecosystems like coral reefs, kelp forests, and deep-sea hydrothermal vents, support an unparalleled level of biodiversity. Freshwater ecosystems, including rivers, lakes, and wetlands, are equally significant, harboring unique plant and animal communities adapted to specific water conditions. The sheer volume and variety of aquatic habitats showcase the crucial role of the hydrosphere in maintaining global biodiversity.
The influence of water availability and quality: The quantity and quality of available water are critical factors determining species richness and distribution. Water scarcity limits the size and distribution of populations, while water pollution can have devastating consequences on aquatic ecosystems and those that rely on them. For instance, nutrient pollution leading to eutrophication can cause harmful algal blooms, depleting oxygen levels and killing fish and other aquatic organisms.
2. Climate Regulation and Biome Distribution
The hydrosphere plays a pivotal role in regulating Earth's climate. Oceans, acting as massive heat reservoirs, absorb and release heat energy, influencing global temperature patterns and weather systems. Ocean currents redistribute heat around the globe, moderating temperatures in coastal regions and impacting climate patterns across continents. Evaporation from water bodies contributes to atmospheric moisture, influencing rainfall patterns and supporting terrestrial ecosystems.
The impact on biomes: Climate regulation by the hydrosphere significantly impacts the distribution and characteristics of terrestrial biomes. Rainfall patterns, determined by evaporation and atmospheric circulation influenced by ocean currents and temperatures, dictate the types of vegetation and animal communities that can thrive in a particular region. For instance, the Amazon rainforest's immense biodiversity is directly linked to the high levels of rainfall generated by the Amazon River basin and its interactions with atmospheric moisture.
The Hydrosphere's Influence on Biogeochemical Cycles
The hydrosphere is inextricably linked to various biogeochemical cycles, the processes that cycle essential elements through the biosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere. Water acts as a vital transport medium, influencing the flow and availability of nutrients that sustain life.
1. The Water Cycle: The Driving Force
The water cycle, the continuous movement of water through the Earth's system, is the most fundamental biogeochemical cycle influenced by the hydrosphere. Evaporation, precipitation, transpiration, and runoff constantly redistribute water, influencing the availability of freshwater resources for terrestrial and aquatic life. Changes in the water cycle, driven by climate change or human activities, directly impact biodiversity and ecosystem functions.
Impact of altered water cycles: Increased evaporation due to rising temperatures can lead to water scarcity in some regions, impacting agriculture, and affecting the survival of both plants and animals. Altered precipitation patterns, leading to more intense rainfall or prolonged droughts, can disrupt ecosystems and cause widespread ecological damage.
2. Nutrient Cycling: A Vital Connection
The hydrosphere plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling, facilitating the movement of essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon. Rivers transport nutrients from terrestrial ecosystems to aquatic environments, supporting aquatic food webs. Ocean currents redistribute nutrients globally, influencing the productivity of marine ecosystems. Furthermore, water is involved in the breakdown of organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the environment.
Nutrient pollution and its effects: Human activities, such as agricultural runoff and sewage discharge, can significantly alter nutrient cycles. Excess nitrogen and phosphorus can lead to eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems, resulting in oxygen depletion and harmful algal blooms, severely impacting aquatic biodiversity.
The Hydrosphere and Human Impacts
Human activities have significantly altered the hydrosphere, impacting its ability to support the biosphere. These impacts underscore the urgent need for sustainable water management practices.
1. Water Pollution: A Growing Threat
Pollution of the hydrosphere, through industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste, poses a major threat to aquatic ecosystems and human health. Pollutants contaminate water sources, harming aquatic organisms and disrupting food webs. Waterborne diseases, linked to contaminated water, remain a significant global health concern.
Addressing water pollution: Effective strategies for addressing water pollution involve reducing pollutant discharges from various sources, implementing stricter environmental regulations, and promoting sustainable water management practices, including wastewater treatment and responsible waste disposal.
2. Climate Change and Water Resources
Climate change is exacerbating existing water challenges, altering precipitation patterns, increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, and contributing to sea-level rise. These changes disrupt water availability, affecting agriculture, human settlements, and ecosystems. Glacial melt and changes in snowpack contribute to altered river flows, impacting downstream ecosystems.
Mitigation and adaptation strategies: Addressing the impact of climate change on water resources requires a multi-faceted approach including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, implementing climate change adaptation strategies to enhance water security, and fostering sustainable water management practices to build resilience to future climate impacts.
Conclusion: A Symbiotic Relationship Requiring Stewardship
The hydrosphere and the biosphere are inextricably linked, forming a symbiotic relationship where the health of one is intrinsically tied to the health of the other. The hydrosphere provides habitats, regulates climate, and facilitates biogeochemical cycles, fundamentally shaping the structure and function of the biosphere. However, human activities have significantly altered the hydrosphere, causing widespread pollution, and exacerbating water scarcity. To ensure the continued health and resilience of both the hydrosphere and the biosphere, it is imperative to adopt sustainable water management practices, mitigate climate change, and reduce pollution. Protecting this vital resource is not just an environmental imperative, but a cornerstone of ensuring the well-being of both present and future generations. Only through a comprehensive understanding of this interconnectedness and the implementation of responsible stewardship can we ensure the health of our planet and the life it sustains.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
12 Out Of 20 As Percentage
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Meters In 2 Km
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 50 Is 30
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Liters Is 8 Gallons
Apr 03, 2025
-
64 Oz Is How Many Cups
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does The Hydrosphere Affect The Biosphere . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
