How Long Does It Take For Water To Boil
Kalali
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
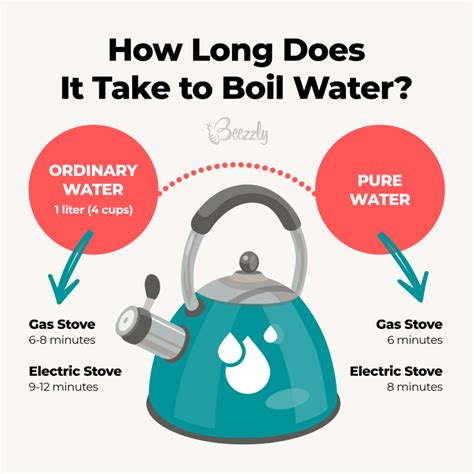
Table of Contents
How Long Does It Take for Water to Boil? A Comprehensive Guide
Boiling water, a seemingly simple task, actually involves a complex interplay of factors that determine the precise time it takes. This isn't just a matter of flipping a switch and waiting; understanding the science behind boiling allows for better control and efficiency in the kitchen and beyond. This comprehensive guide delves into the various elements influencing water's boiling time, offering practical tips and insights for optimizing the process.
The Science of Boiling: Heat Transfer and Phase Change
Before we dive into the specifics of timing, let's understand the fundamental principles. Boiling is a phase transition, where liquid water transforms into gaseous water vapor (steam). This transition requires energy, specifically latent heat of vaporization. The rate at which this energy is supplied dictates how quickly the water boils.
Heat Sources and Their Efficiency:
The primary factor influencing boiling time is the heat source. Different sources transfer heat at varying rates:
-
Stovetops (Gas, Electric, Induction): Gas stoves often provide faster heating due to direct flame contact, while electric coils and induction cooktops offer controlled heating with varying efficiency depending on the wattage and design. Induction cooktops are generally considered the most efficient.
-
Microwaves: Microwaves heat water directly through molecular excitation, often leading to quicker boiling times, particularly for smaller volumes. However, uneven heating can occur in larger quantities.
-
Electric Kettles: Designed specifically for boiling water, electric kettles offer rapid heating due to their optimized design and powerful heating elements. They are arguably the most efficient for simple boiling tasks.
The Role of Water Volume and Starting Temperature:
The amount of water directly impacts boiling time. A larger volume requires more energy to raise its temperature to the boiling point and then convert it to steam. Similarly, colder water takes longer to boil than warmer water, as it must first overcome a larger temperature difference.
Atmospheric Pressure:
Atmospheric pressure significantly impacts the boiling point of water. At higher altitudes, where atmospheric pressure is lower, water boils at a lower temperature (less than 100°C or 212°F). Conversely, at higher pressures, the boiling point increases. This explains why pressure cookers cook food faster – the elevated pressure raises the boiling point, allowing for higher temperatures.
Container Material and Design:
The type of container influences heat transfer. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper and aluminum, transfer heat more efficiently than materials like glass or stainless steel, resulting in faster boiling times. The shape and size of the container also play a role. A wider, shallower pan exposes a larger surface area to the heat source, potentially speeding up the process.
Water Purity:
Impurities in water can slightly alter its boiling point. Minerals and dissolved solids can increase the boiling point marginally, though this effect is often negligible in everyday scenarios. However, significant amounts of impurities can impact the boiling point more noticeably.
Factors Affecting Boiling Time: A Deeper Dive
Let's explore the individual factors in greater detail to provide a more nuanced understanding:
1. Heat Source Power:
The wattage (power) of your heat source directly influences boiling time. A higher wattage means more energy is transferred per unit of time, resulting in faster boiling. This is particularly noticeable when comparing different stovetops or electric kettles. Check the wattage rating of your appliance to get a better understanding of its heating capacity.
2. Water Volume:
A simple rule of thumb is that doubling the water volume roughly doubles the boiling time (assuming all other factors remain constant). This is because you need twice the energy to heat twice the amount of water. However, this is an approximation, and the exact relationship is more complex, influenced by other factors.
3. Initial Water Temperature:
Cold water requires substantially more time to reach boiling point compared to lukewarm or warm water. Starting with warmer water can significantly reduce boiling time, particularly noticeable in large volumes. Using pre-heated water, perhaps from a hot water tap (being mindful of scalding!), is a smart time-saving technique.
4. Altitude:
The altitude at which you are boiling water affects its boiling point. The lower the atmospheric pressure, the lower the boiling point. At high altitudes, water boils at a lower temperature, meaning it boils faster, but it also takes longer to cook food because of the lower temperature. If you live at a high altitude, adjust your cooking times accordingly.
5. Container Material:
Metals like copper and aluminum are excellent heat conductors. They transfer heat efficiently from the heat source to the water, leading to faster boiling. Stainless steel is a good conductor but generally slower than copper or aluminum. Glass is a poor conductor of heat, resulting in considerably longer boiling times.
6. Lid Use:
Using a lid traps heat within the container, leading to faster boiling. The lid prevents heat from escaping as steam, thus accelerating the heating process. This simple technique can significantly reduce boiling time.
7. Stirring:
Stirring the water helps to distribute heat evenly throughout the pot, which prevents the formation of localized hot spots and ensures uniform heating. While the effect on boiling time might be marginal, it contributes to more efficient and consistent boiling.
8. Impurities:
Dissolved solids in water raise the boiling point slightly. While this effect is typically minor for most tap water, significantly impure water might show a noticeable increase in boiling time. Distilled water, being highly pure, boils slightly faster.
How to Minimize Boiling Time: Practical Tips
Here are some actionable strategies to reduce the time it takes to boil water:
-
Use a high-wattage heat source: Choose a stovetop burner or electric kettle with a high wattage rating.
-
Start with warmer water: If practical, use warm or lukewarm water instead of cold water.
-
Use a pot with a tight-fitting lid: Trapping steam speeds up the boiling process.
-
Use a pot made from a highly conductive material: Copper or aluminum pots heat faster than glass or stainless steel pots.
-
Choose the right pot size: Select a pot whose size is appropriate for the amount of water you need to boil; avoid using oversized pots for small volumes of water.
-
Stir the water occasionally: This promotes even heating.
-
Consider an electric kettle: Electric kettles are typically designed for rapid and efficient boiling.
Beyond the Kitchen: Boiling Water in Other Contexts
The principles discussed here apply beyond the kitchen. Understanding boiling time is crucial in various applications:
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes rely on precise boiling times for efficiency and quality control.
-
Scientific Experiments: Boiling time is a critical parameter in various scientific experiments requiring accurate temperature control.
-
Emergency Situations: Quickly boiling water for sanitation or hydration in emergency situations demands an understanding of factors affecting boiling time.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Boiling Water
Boiling water might seem trivial, but the underlying science reveals a surprisingly complex process. By understanding the interplay of heat sources, water volume, starting temperature, atmospheric pressure, container materials, and other factors, we can optimize boiling time for greater efficiency and control. This knowledge not only improves our cooking but extends to various applications, highlighting the importance of understanding the fundamentals of heat transfer and phase transitions. Through careful consideration of these elements, you can master the art of boiling water and enhance your efficiency in the kitchen and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Did The Cow Want A Divorce
Jul 14, 2025
-
Lowest Common Denominator For 3 4 5
Jul 14, 2025
-
Can You Be A Professor With A Masters
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Bottles Of Water Is 1 Liter
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days In A Million Minutes
Jul 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Long Does It Take For Water To Boil . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.