How Long It Takes To Boil Water
Kalali
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
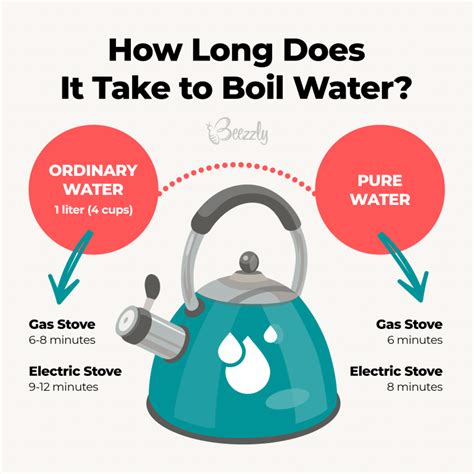
Table of Contents
- How Long It Takes To Boil Water
- Table of Contents
- How Long Does It Take to Boil Water? A Comprehensive Guide
- The Science Behind Boiling: More Than Just Heat
- Factors Influencing Boiling Time
- Practical Applications & Time Estimations
- Boiling Small Amounts of Water (e.g., a cup):
- Boiling Larger Amounts of Water (e.g., a pot for pasta):
- Optimizing Your Boiling Time: Tips and Tricks
- Beyond Boiling: Understanding Heat Transfer
- Conclusion: A Variable Process, Yet Manageable
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Long Does It Take to Boil Water? A Comprehensive Guide
Boiling water, a seemingly simple task, actually involves a complex interplay of factors that significantly influence the time it takes. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone from a seasoned chef meticulously crafting a perfect pasta dish to a camper needing a quick cup of tea in the wilderness. This comprehensive guide delves into the science behind boiling water and provides you with the knowledge to accurately estimate and optimize your boiling times.
The Science Behind Boiling: More Than Just Heat
Before diving into the specifics of time, let's establish the fundamental principles. Boiling water is the process of transitioning water from its liquid state to its gaseous state (steam) at its boiling point – 212°F (100°C) at standard atmospheric pressure. This transition requires a specific amount of energy, known as the latent heat of vaporization. This means that once the water reaches 100°C, it doesn't get hotter until all the water has turned to steam. The heat input is solely dedicated to changing the state of matter.
Factors Influencing Boiling Time
Numerous factors influence the time it takes to boil water. Let's break them down:
-
Initial Water Temperature: Colder water takes longer to boil than warmer water. Starting with room-temperature water will require significantly more time compared to using already-warm water from a hot water tap.
-
Volume of Water: More water means more heat energy is required to raise its temperature to boiling point. A larger volume directly translates to a longer boiling time. A kettle full of water will boil much slower than a small cup.
-
Heat Source: The intensity of your heat source dramatically affects boiling time. A high-powered stove burner will boil water much faster than a low-powered camping stove. Electric kettles, designed specifically for boiling water, typically offer the quickest boiling times. Microwave ovens provide a different type of heating and the time can vary significantly based on wattage and the shape of the container.
-
Altitude: Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude. At higher altitudes, water boils at a lower temperature. This means it takes less energy to reach the boiling point, but the process of boiling itself might take slightly longer because the lower temperature means less vigorous bubbling.
-
Pot Material & Design: The material of your pot impacts heat transfer efficiency. Thicker-bottomed pots, especially those made of materials like copper or stainless steel with a thick base, distribute heat more evenly and efficiently, leading to faster boiling times. A pot with a narrow base will heat slower than one with a wide base because the heat source needs to cover more surface area. The shape of the pot also influences heat convection currents, which are natural movements of water within the pot that enhance heat transfer and mixing. A taller, narrow pot might show less obvious convection currents than a wider, shallower pot.
-
Type of Pot: The material of your pot will impact boiling time. Metal pots generally boil water faster than glass or ceramic pots, because metal is a better conductor of heat. However, even within metal pots, different metals offer varying levels of heat conductivity. Copper is superior in heat conductivity, followed by aluminum, stainless steel, and then iron. Therefore, a copper pot will generally boil water the fastest.
-
Lid: Using a lid significantly reduces boiling time. A lid traps heat within the pot, preventing heat loss to the surrounding environment. This allows the water to reach its boiling point much faster.
-
Water Purity: While the effect is minimal, impurities in the water can slightly alter the boiling point and hence the time it takes to boil. Extremely mineral-rich water may have a slightly higher boiling point.
Practical Applications & Time Estimations
Let's move beyond the theoretical and apply this knowledge to real-world scenarios. While precise estimations are difficult without specific equipment details, we can provide general guidelines:
Boiling Small Amounts of Water (e.g., a cup):
- Stovetop (high heat): 2-5 minutes (highly dependent on burner power and pot type).
- Microwave (high power): 1-3 minutes (dependent on microwave power and volume).
- Electric Kettle: 1-2 minutes.
Boiling Larger Amounts of Water (e.g., a pot for pasta):
- Stovetop (high heat): 10-20 minutes (highly dependent on burner power, pot size, and lid usage).
- Large Electric Kettle: 5-10 minutes (dependent on kettle capacity and wattage).
Note: These are rough estimations. The actual boiling time can vary significantly based on the factors discussed earlier.
Optimizing Your Boiling Time: Tips and Tricks
Following these tips can help you minimize boiling time:
- Use a lid: A lid significantly reduces boiling time by trapping heat inside the pot.
- Choose the right pot: Opt for a pot with a thick, even base made of a highly conductive material like copper or stainless steel.
- Use a high-heat burner: A powerful burner will significantly reduce boiling time.
- Start with warm water: If possible, use warm water instead of cold water to reduce the time it takes.
- Don't overcrowd the pot: Overfilling the pot will reduce the efficiency of heat transfer and increase boiling time.
Beyond Boiling: Understanding Heat Transfer
The process of boiling isn't solely about reaching 100°C. It’s also about how efficiently heat is transferred from the heat source to the water. This involves three primary methods:
- Conduction: The direct transfer of heat through the pot's material from the heat source to the water at the bottom of the pot. A better conductor means faster heat transfer.
- Convection: The movement of heated water upwards, creating currents that distribute heat more evenly throughout the pot. This process is enhanced by using a wider pot, stirring the water, or letting the water gently simmer.
- Radiation: While less significant than conduction and convection in boiling water, radiation plays a small role, especially with exposed heat sources. The infrared radiation from the burner will slightly contribute to the heating of the water.
Understanding these heat transfer mechanisms is crucial for optimizing your boiling process. Choosing the right pot, using a lid effectively, and employing techniques like stirring will all enhance these processes, leading to quicker and more efficient boiling times.
Conclusion: A Variable Process, Yet Manageable
Boiling water, while seemingly simple, reveals a fascinating interplay of physical and chemical processes. Numerous variables influence the boiling time, making precise predictions challenging. However, understanding these factors allows for informed estimations and effective optimization of your boiling processes. By considering factors such as water volume, heat source, pot material, and lid usage, you can significantly improve your efficiency in the kitchen or even in the outdoors. Experiment, observe, and refine your technique based on your specific circumstances. With practice and knowledge, you'll become a master of boiling water in no time!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 25 Percent Of 60
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Meters In 36 Feet
Apr 02, 2025
-
Convert 200 Degrees Fahrenheit To Celsius
Apr 02, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 3 4 De Taza En Onzas
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is 60 Milliliters
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Long It Takes To Boil Water . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
