How Many Diagonals In A Hexagon
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 4 min read
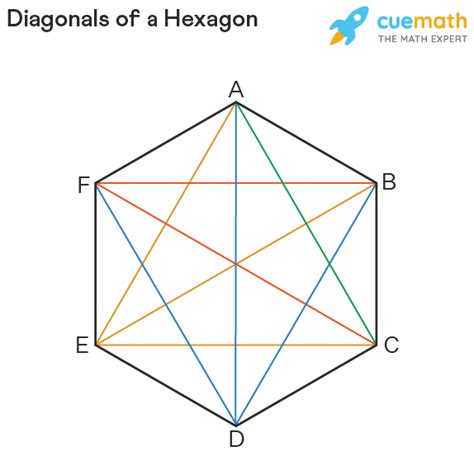
Table of Contents
How Many Diagonals Does a Hexagon Have? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the number of diagonals in a polygon, especially a hexagon, is a fundamental concept in geometry. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "How many diagonals does a hexagon have?" but also equip you with the knowledge to calculate the diagonals of any polygon, regardless of its number of sides. We'll delve into the underlying principles, explore different approaches to solving this problem, and even touch upon the broader mathematical context.
Understanding Polygons and Diagonals
Before we dive into hexagons, let's define some key terms. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure with straight sides. The number of sides determines the type of polygon:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon (or Septagon): 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- and so on...
A diagonal of a polygon is a line segment connecting two non-adjacent vertices (corners) of the polygon. Crucially, it's internal to the polygon; it lies within the shape itself. Sides of the polygon are not considered diagonals.
Calculating Diagonals in a Hexagon: The Formulaic Approach
The most efficient way to determine the number of diagonals in any polygon, including a hexagon, is using a mathematical formula. This formula avoids the tedious process of counting diagonals individually, especially for polygons with many sides.
The formula for the number of diagonals (d) in a polygon with 'n' sides is:
d = n(n - 3) / 2
Where:
- d represents the number of diagonals
- n represents the number of sides of the polygon
Let's apply this formula to a hexagon, which has 6 sides (n = 6):
d = 6(6 - 3) / 2 = 6(3) / 2 = 18 / 2 = 9
Therefore, a hexagon has 9 diagonals.
Calculating Diagonals in a Hexagon: The Combinatorial Approach
Alternatively, we can approach this problem using combinations from combinatorics. A diagonal connects any two vertices of the polygon. However, we must exclude the sides of the polygon, since they are not considered diagonals.
A hexagon has 6 vertices. The number of ways to choose 2 vertices from 6 is given by the combination formula:
⁶C₂ = 6! / (2! * (6-2)!) = 6! / (2! * 4!) = (6 * 5) / (2 * 1) = 15
This represents all possible line segments connecting any two vertices. Since this includes the 6 sides of the hexagon, we must subtract these to get the number of diagonals:
15 (total line segments) - 6 (sides) = 9 diagonals
Visualizing the Diagonals of a Hexagon
It's often helpful to visualize the problem. Draw a hexagon and try to systematically draw all the diagonals. You'll notice that from each vertex, you can draw three diagonals. However, simply multiplying 6 (vertices) * 3 (diagonals per vertex) would be incorrect, as it double counts each diagonal. The formula and combinatorial approach account for this double counting.
Extending the Concept: Diagonals in Other Polygons
The formula d = n(n - 3) / 2 works for any polygon. Let's look at a few examples:
- Triangle (n=3): d = 3(3 - 3) / 2 = 0. Triangles have no diagonals.
- Square (n=4): d = 4(4 - 3) / 2 = 2. Squares have two diagonals.
- Pentagon (n=5): d = 5(5 - 3) / 2 = 5. Pentagons have five diagonals.
- Octagon (n=8): d = 8(8 - 3) / 2 = 20. Octagons have twenty diagonals.
Properties of Diagonals in a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon is a hexagon where all sides and angles are equal. In a regular hexagon, some interesting properties emerge concerning its diagonals:
- Equal Length Diagonals: A regular hexagon has three different lengths of diagonals. The longest diagonals connect vertices that are separated by three other vertices. There are shorter diagonals that connect vertices separated by two other vertices. And there are the medium-length diagonals.
- Intersection Points: The diagonals of a regular hexagon intersect at specific points within the hexagon, forming smaller equilateral triangles and other geometric shapes. These intersection points have interesting properties relating to the symmetry and proportions of the hexagon.
- Symmetry: The diagonals contribute significantly to the six-fold rotational symmetry of a regular hexagon.
Hexagons in the Real World
Hexagons are surprisingly common in nature and design:
- Honeycomb: Bees construct their honeycombs using hexagonal cells, maximizing space and minimizing material usage. This is a testament to the efficiency of hexagonal geometry.
- Crystals: Some crystals form hexagonal structures due to the arrangement of their atoms.
- Architecture and Design: Hexagonal patterns appear in various architectural and design elements, often for their aesthetic appeal and structural properties.
Beyond the Basics: Further Exploration
The concept of diagonals extends beyond simple polygons. In three-dimensional geometry, we encounter similar concepts involving polyhedra (three-dimensional shapes) and their spatial diagonals. The mathematical principles remain consistent, although the complexity increases significantly.
Conclusion: Mastering the Diagonals
Understanding how to calculate the number of diagonals in a polygon, particularly a hexagon, is a valuable skill in geometry. This guide has explored various methods for solving this problem, providing both a formulaic approach and a combinatorial interpretation. Beyond simply answering the question, we've explored the visual representation of diagonals, their properties in regular hexagons, and the broader context of polygons in nature and design. This comprehensive understanding will serve as a strong foundation for tackling more advanced geometric problems. Remember the formula: d = n(n - 3) / 2. Use it wisely, and you'll be well-equipped to conquer any diagonal-related challenge!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Tenths Are In An Inch
Jul 15, 2025
-
Which Word Has The Most Positive Connotation
Jul 15, 2025
-
How Do I Send An Evite Reminder
Jul 15, 2025
-
When Performing A Self Rescue When Should You Swim To Shore
Jul 15, 2025
-
How Many Decaliters Are In A Liter
Jul 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Diagonals In A Hexagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.