How Many Light Years Is Earth From The Sun
Kalali
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
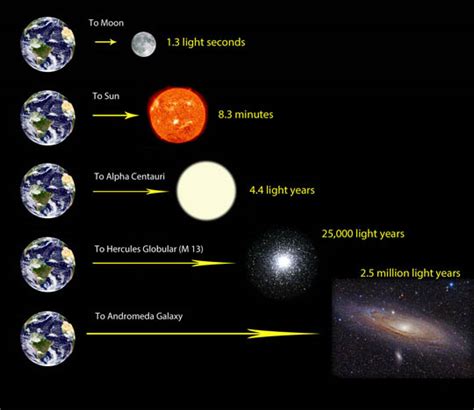
Table of Contents
How Many Light-Years is Earth From the Sun? A Deep Dive into Astronomical Distances
The question, "How many light-years is Earth from the Sun?" might seem deceptively simple. After all, we all learn in school that Earth orbits the Sun. However, understanding the distance and the very concept of a light-year requires delving into the vastness of space and the scales used to measure it. The answer isn't just a number; it's an exploration of astronomical units, light-years, and our place within the solar system and beyond.
Understanding Astronomical Units (AU)
Before we tackle light-years, let's grasp the fundamental unit used to measure distances within our solar system: the Astronomical Unit (AU). One AU is defined as the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. This isn't a constant distance because Earth's orbit is slightly elliptical, meaning its distance from the Sun varies throughout the year.
The average distance is approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). Using AU simplifies calculations within our solar system. For example, Mars is roughly 1.5 AU from the Sun, while Jupiter is about 5.2 AU. This makes comparing planetary distances much more manageable than using kilometers or miles directly.
Why Not Light-Years for Solar System Distances?
While light-years are a common unit for measuring interstellar distances, they're less practical for measuring distances within our solar system. A light-year is an incredibly vast distance, representing the distance light travels in one year. Given the speed of light (approximately 299,792 kilometers per second), a light-year is roughly 9.461 × 10<sup>12</sup> kilometers (5.878 × 10<sup>12</sup> miles).
Using light-years to describe the Earth-Sun distance would result in an incredibly small, almost insignificant number. The Earth-Sun distance in light-years is approximately 0.0000158 light-years. This tiny fraction makes AU a far more convenient and intuitive unit for solar system measurements.
Light-Years: Measuring Interstellar Distances
Light-years become essential when we consider distances between stars and other celestial objects outside our solar system. The nearest star to our Sun, Proxima Centauri, is approximately 4.24 light-years away. This means that the light we see from Proxima Centauri today left the star 4.24 years ago. We are essentially looking back in time when we observe distant stars.
The vastness of interstellar distances becomes truly apparent when considering other stars and galaxies. The Andromeda Galaxy, our nearest large galactic neighbor, is approximately 2.537 million light-years away. This highlights the immense scale of the universe and the limitations of human comprehension when dealing with such enormous distances.
The Significance of the Earth-Sun Distance
The average distance of 1 AU (149.6 million kilometers) between the Earth and the Sun is crucial for life on Earth. This specific distance allows for a habitable temperature range, crucial for liquid water to exist – a fundamental requirement for life as we know it. If Earth were significantly closer, the intense heat would boil away our oceans, while if it were farther away, the planet would freeze over. The Goldilocks zone, often referred to as the habitable zone, is a region around a star where the temperature is just right for liquid water to exist on a planet's surface. Earth's position within the Sun's habitable zone is a defining factor in its suitability for life.
Variations in Earth-Sun Distance: Perihelion and Aphelion
As mentioned earlier, Earth's orbit isn't perfectly circular; it's slightly elliptical. This means the distance between Earth and the Sun varies throughout the year. At its closest point, called perihelion, Earth is approximately 147.1 million kilometers (91.4 million miles) from the Sun. This occurs around January 3rd each year.
At its farthest point, called aphelion, Earth is about 152.1 million kilometers (94.5 million miles) away from the Sun. This happens around July 4th each year. This difference of about 5 million kilometers (3 million miles) is relatively small compared to the average distance, but it's a significant factor in calculations involving Earth's orbital mechanics and seasonal variations.
Calculating Distances in Astronomy: Parallax and Other Methods
Determining the distance to celestial objects, especially those beyond our solar system, requires sophisticated techniques. One common method is parallax, which utilizes the apparent shift in an object's position when viewed from two different points. By measuring this small angular shift and knowing the baseline distance between the observation points (often the Earth's diameter across its orbit), astronomers can calculate the distance to the object.
For more distant objects, where parallax becomes less accurate, other methods are used. These include analyzing the object's brightness, spectral characteristics, and other physical properties to infer its distance. Each method has its limitations and uncertainties, but through careful observation and analysis, astronomers continue to refine their measurements of cosmic distances.
The Expanding Universe and Cosmic Distances
Our understanding of cosmic distances is also intimately linked to our understanding of the expanding universe. The universe is not static; it's continuously expanding, meaning the distances between galaxies are increasing over time. This expansion influences how we measure and interpret cosmic distances, requiring careful consideration of cosmological models and the expansion rate of the universe.
Beyond Light-Years: Other Units of Cosmic Distance
While light-years are commonly used, other units are employed to measure even greater cosmic distances. These include:
- Parsecs (pc): One parsec is approximately 3.26 light-years. Parsecs are often used in astronomical calculations due to their convenient relationship with parallax measurements.
- Kiloparsecs (kpc): Equal to 1,000 parsecs, this unit is commonly used for distances within galaxies.
- Megaparsecs (Mpc): Equal to 1 million parsecs, this unit is frequently used to measure distances between galaxies and galaxy clusters.
- Gigaparsecs (Gpc): Equal to 1 billion parsecs, this unit represents incredibly vast distances within the observable universe.
The Importance of Understanding Cosmic Distances
Understanding the vast scales of cosmic distances is crucial for numerous reasons. It allows us to:
- Improve our understanding of the universe's structure and evolution: By measuring distances, we can map the distribution of galaxies, stars, and other celestial objects, providing insights into the large-scale structure of the universe.
- Refine cosmological models: Accurate distance measurements are essential for testing and refining our cosmological models, which attempt to explain the origin, evolution, and ultimate fate of the universe.
- Advance our search for extraterrestrial life: Knowing the distances to other stars and planets helps us prioritize targets for the search for extraterrestrial life and assess the feasibility of interstellar travel.
- Expand our knowledge of fundamental physics: Studying the vast distances and objects in the universe can lead to breakthroughs in our understanding of fundamental physics, such as gravity, dark matter, and dark energy.
In conclusion, while the Earth is not 0.0000158 light-years from the Sun – a figure that's practically meaningless in this context – understanding the concept of light-years, alongside astronomical units, is vital for grasping the sheer scale of the cosmos. The Earth-Sun distance, expressed in AU, highlights the delicate balance that allows life to flourish on our planet. Exploring these vast distances and the methods used to measure them not only expands our knowledge of the universe but also deepens our appreciation for our unique place within it. The journey to understand these cosmic scales is ongoing, driven by scientific curiosity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge about the universe we inhabit.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Hours Is 95 Minutes
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 7 Of 12
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Oz Is 4 Pounds
Apr 05, 2025
-
106 Inches Is How Many Feet
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Long Is 50 Inches In Feet
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Light Years Is Earth From The Sun . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
