How Many Mm Is A Quarter
Kalali
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
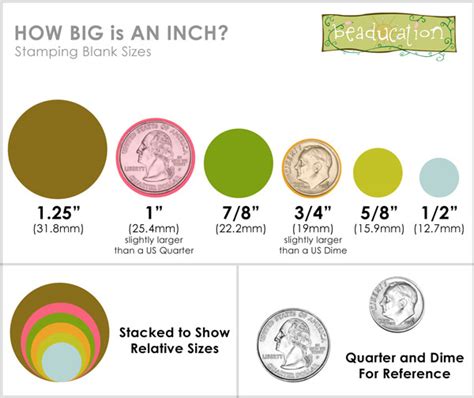
Table of Contents
How Many MM is a Quarter? A Comprehensive Guide to US Coin Measurements
The seemingly simple question, "How many mm is a quarter?" opens a fascinating exploration into the world of measurement, numismatics, and the intricacies of the US monetary system. While a quick Google search might provide a single answer, understanding the nuances requires a deeper dive. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the history, variations, and practical applications of knowing the precise dimensions of a US quarter.
Understanding the US Quarter
Before jumping into millimeters, let's establish a firm understanding of the US quarter dollar. This iconic coin, representing 25 cents, boasts a rich history and distinct design features. Its composition, size, and weight have remained relatively consistent over time, although minor variations exist depending on the minting year.
Historical Context: A Brief Overview
The quarter dollar, officially known as the quarter, has been a staple of the US monetary system since 1796. While its design has evolved over the years, with different commemorative and state quarters introduced periodically, the basic specifications have largely remained constant. Understanding this historical context is crucial to appreciating the slight variations you might encounter when measuring individual quarters.
Composition and Manufacturing: The Science Behind the Coin
The composition of a US quarter has also changed over time. Currently, quarters are made of copper-nickel clad composition. This means a core of pure copper is clad in a layer of cupro-nickel alloy, resulting in a coin that is both durable and cost-effective to manufacture. The manufacturing process is incredibly precise, aiming for consistent dimensions and weight across all minted coins. However, minute variations can occur due to the manufacturing process itself.
From Inches to Millimeters: Conversion and Precision
Now, let's address the core question: how many millimeters are in a quarter? A standard US quarter has a diameter of approximately 24.26 millimeters (mm). This is derived from the official measurements of 0.955 inches (the diameter), using the standard conversion factor of 25.4 millimeters per inch.
Understanding the "Approximately"
It's crucial to note the word "approximately." While the official specification aims for 24.26 mm, minor variations are inevitable due to the manufacturing process. Individual quarters might measure slightly more or less than this, although the difference would be minuscule, usually within a fraction of a millimeter.
Measurement Techniques: Ensuring Accuracy
Measuring a quarter's diameter accurately requires precision instruments. While a ruler might provide a rough estimate, a caliper or micrometer would be necessary for obtaining a highly accurate measurement. These instruments allow for more precise readings, accounting for the subtle variations in individual coins.
The Importance of Precision Measurement in Various Fields
The precise measurement of a quarter, while seemingly insignificant, holds practical importance in several fields:
-
Numismatics (Coin Collecting): Collectors often meticulously measure and weigh their coins for grading and authentication purposes. Slight deviations from the standard dimensions can affect a coin's value and rarity.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: The precise dimensions of coins, including the quarter, serve as a benchmark in precision manufacturing processes. Understanding and controlling tolerances is crucial in industries requiring high accuracy.
-
Scientific Experiments: In some scientific experiments, coins can act as standardized weights or objects. In such scenarios, precise measurements become critical for achieving accurate and reliable results.
-
Quality Control: Manufacturing facilities utilize precise measurements to ensure the quality of their products. Deviations from the standards can indicate potential issues within the manufacturing process.
Variations and Exceptions: Considering the Unpredictable
While the standard diameter of a quarter is 24.26 mm, it's important to acknowledge that exceptions and variations exist. These variations stem primarily from:
-
Wear and Tear: Over time, a quarter in circulation might experience wear and tear, slightly reducing its diameter. This is especially noticeable in heavily circulated quarters.
-
Manufacturing Tolerances: As mentioned, even with advanced manufacturing techniques, slight variations in the dimensions are unavoidable. These minute differences are usually within acceptable tolerances, but they still exist.
-
Commemorative Quarters: The designs of commemorative quarters are varied and might introduce subtle differences in the thickness or even diameter, though generally remain within the standard tolerances.
-
Foreign Currency Coins: It's imperative to remember that the 24.26 mm diameter specifically applies to the US quarter. Other countries' 25-cent coins or coins of similar value might have vastly different dimensions.
Beyond Diameter: Exploring Other Dimensions
While diameter is the most commonly discussed dimension, a complete understanding requires considering other measurements:
-
Thickness: The thickness of a US quarter is approximately 1.75 mm. Similar to the diameter, slight variations might exist due to manufacturing tolerances.
-
Weight: The weight of a US quarter is approximately 5.67 grams. This measurement, like the others, can exhibit minor variations.
Practical Applications: Utilizing Quarter Dimensions
Knowing the precise dimensions of a quarter can be surprisingly useful in various situations:
-
DIY Projects: In crafting or DIY projects requiring specific measurements, a quarter can serve as a convenient and readily available reference point.
-
Estimating Distances and Sizes: In the absence of a ruler, a quarter can be used as a rough estimation tool for small distances and sizes.
-
Educational Purposes: The quarter's dimensions can be used in educational settings to illustrate concepts related to measurement, conversion, and precision.
Conclusion: The Significance of Precise Measurement
The seemingly simple question of "How many mm is a quarter?" unveils a multifaceted exploration encompassing history, manufacturing processes, and practical applications. While the answer is approximately 24.26 mm, understanding the potential variations, measurement techniques, and the significance of precision in different fields adds depth and context to this seemingly straightforward query. Whether you're a coin collector, an engineer, a scientist, or simply curious about the details of everyday objects, grasping the nuances of a quarter's dimensions provides a valuable understanding of the world around us. The attention to detail in understanding these precise measurements extends beyond simple curiosity and into practical applications across diverse fields. Remember that while 24.26 mm serves as a useful benchmark, always account for potential variations for accurate results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Are Golgi Apparatus In Prokaryotic Cells
Apr 03, 2025
-
12 Out Of 20 As Percentage
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Meters In 2 Km
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 50 Is 30
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Liters Is 8 Gallons
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Mm Is A Quarter . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
