How Many Pi Bonds Are Present In Acetylsalicylic Acid
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
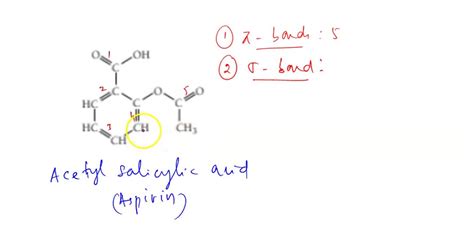
Table of Contents
How Many Pi Bonds Are Present in Acetylsalicylic Acid? A Detailed Analysis
Acetylsalicylic acid, more commonly known as aspirin, is a ubiquitous drug celebrated for its analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory properties. Beyond its medicinal significance, aspirin also presents a fascinating case study in organic chemistry, particularly regarding its bonding structure. Understanding the number of pi bonds present requires a thorough examination of its molecular structure. This article will delve deep into the chemical structure of acetylsalicylic acid, elucidating the concept of pi bonds and ultimately determining the precise number present within the molecule.
Understanding Pi Bonds
Before we embark on analyzing acetylsalicylic acid, let's establish a clear understanding of pi bonds. Chemical bonds arise from the interaction of atomic orbitals. A sigma (σ) bond is formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in a strong, single bond. However, pi (π) bonds are formed by the sideways overlap of p-orbitals, resulting in a weaker bond that exists in addition to a sigma bond. This means pi bonds are always found in conjunction with a sigma bond, forming a double or triple bond.
- Double bonds: Consist of one sigma bond and one pi bond.
- Triple bonds: Consist of one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
Pi bonds are crucial in determining the shape and reactivity of molecules. Their presence leads to restricted rotation around the bond axis, influencing the molecule's overall three-dimensional structure. Furthermore, the electron density in pi bonds is more readily available for reactions, making molecules containing pi bonds often more reactive than those with only sigma bonds.
The Structure of Acetylsalicylic Acid
Acetylsalicylic acid possesses the chemical formula C₉H₈O₄. Its structure is comprised of a benzene ring, an ester group (-COO-), and a carboxylic acid group (-COOH). Let's dissect the structure to identify the presence of pi bonds:
1. The Benzene Ring: The benzene ring is a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds. However, this depiction is a simplification. The actual bonding in benzene is best represented by resonance structures, implying delocalized pi electrons shared across all six carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in the benzene ring is sp² hybridized. This means each carbon atom contributes one p-orbital to the delocalized pi system above and below the plane of the ring. Consequently, the benzene ring contributes three pi bonds to the total count in acetylsalicylic acid. It's crucial to understand that these are not localized double bonds; rather, they represent a continuous cloud of electron density above and below the ring plane.
2. The Ester Group (-COO-): The ester group links the acetyl group (CH₃CO-) to the salicylate part of the molecule. The carbonyl group (C=O) within the ester contains a double bond – consisting of one sigma bond and one pi bond. Therefore, the ester group contributes one pi bond.
3. The Carboxylic Acid Group (-COOH): The carboxylic acid group also includes a carbonyl group (C=O), identical to the one in the ester group. Therefore, the carboxylic acid group contributes one pi bond.
Calculating the Total Number of Pi Bonds
By summing up the contributions from each part of the molecule:
- Benzene ring: 3 pi bonds
- Ester group: 1 pi bond
- Carboxylic acid group: 1 pi bond
Total: 3 + 1 + 1 = 5 pi bonds
Therefore, there are a total of five pi bonds present in a molecule of acetylsalicylic acid.
Further Exploration of Pi Bonds in Aspirin's Reactivity
The presence of these pi bonds significantly impacts aspirin's chemical reactivity. The delocalized pi electrons in the benzene ring make it susceptible to electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. This is exploited in various chemical modifications and syntheses involving aspirin. Similarly, the carbonyl pi bonds in both the ester and carboxylic acid groups are reactive sites, participating in reactions such as hydrolysis and esterification.
The understanding of pi bond distribution within the acetylsalicylic acid molecule is vital for:
- Drug design and development: Modifying the molecule's structure to enhance or alter its pharmacological properties often involves altering the pi bond system.
- Metabolic studies: Understanding how the molecule interacts with enzymes in the body often relies on knowledge of the reactive pi bond sites.
- Analytical chemistry: Spectroscopic techniques, such as infrared (IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, can be used to detect the presence and characteristics of pi bonds, thereby assisting in identifying and characterizing acetylsalicylic acid.
Conclusion: The Significance of Pi Bonds in Acetylsalicylic Acid
The seemingly simple question, "How many pi bonds are in acetylsalicylic acid?", opens a window into the complex world of organic chemistry. By carefully analyzing the molecular structure and understanding the nature of pi bonds, we arrive at the definitive answer: five pi bonds. These pi bonds are not merely structural features; they are crucial determinants of the molecule's reactivity, its interactions with other molecules, and ultimately its pharmacological activity. This detailed exploration demonstrates the fundamental importance of understanding molecular bonding in comprehending the properties and behavior of pharmaceutical compounds like aspirin. The presence and location of these pi bonds are critical parameters in various applications, from synthetic modifications to pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies. A thorough understanding of pi bonds within the acetylsalicylic acid molecule offers invaluable insights into its multifaceted nature and medicinal applications. The exploration of this topic extends beyond a simple count; it underscores the intricate relationship between molecular structure and functionality. Furthermore, the analysis presented here serves as a valuable learning tool for students and researchers alike, reinforcing the fundamental principles of organic chemistry and its relevance to medicinal chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Multiple Of 16
May 09, 2025
-
How Much Is 160 Ounces Of Water
May 09, 2025
-
1 8 Inch Equals How Many Mm
May 09, 2025
-
What Percent Is 7 Of 30
May 09, 2025
-
100 Cm Equals How Many Meters
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Pi Bonds Are Present In Acetylsalicylic Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.