How Many Sides Does A Trapezoid Have
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
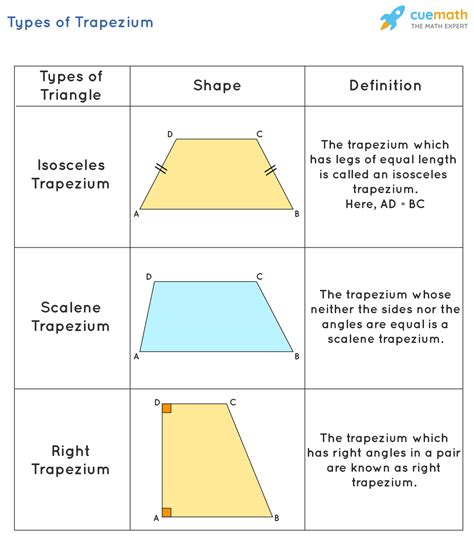
Table of Contents
How Many Sides Does a Trapezoid Have? A Deep Dive into Quadrilaterals
The question, "How many sides does a trapezoid have?" might seem deceptively simple. The answer, of course, is four. However, understanding trapezoids goes far beyond simply knowing their side count. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of trapezoids, exploring their properties, classifications, and applications, ensuring you gain a complete and nuanced understanding of these important geometric shapes.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Defining a Trapezoid
A trapezoid, also known as a trapezium in some parts of the world, is a quadrilateral, meaning it's a two-dimensional closed shape with four sides. But what distinguishes a trapezoid from other quadrilaterals like squares, rectangles, or parallelograms? The defining characteristic of a trapezoid is that it has at least one pair of parallel sides. These parallel sides are called bases, while the other two sides are called legs or lateral sides.
It's crucial to emphasize the "at least one" part of the definition. This means that a trapezoid can have, and often does, only one pair of parallel sides. This contrasts with parallelograms, which have two pairs of parallel sides. This subtle difference is key to understanding the unique properties of trapezoids.
Key Properties of Trapezoids:
- Four Sides: As previously stated, the fundamental characteristic is its four sides.
- At Least One Pair of Parallel Sides: This is the defining characteristic that separates trapezoids from other quadrilaterals.
- Four Angles: Like all quadrilaterals, a trapezoid has four interior angles. The sum of these angles always equals 360 degrees.
- Base Angles: The angles adjacent to each base are called base angles. In an isosceles trapezoid (discussed below), the base angles are congruent (equal in measure).
- Height: The perpendicular distance between the two parallel bases is called the height of the trapezoid. This height is crucial for calculating the area of a trapezoid.
Classifying Trapezoids: Beyond the Basics
While all trapezoids share the fundamental characteristic of having at least one pair of parallel sides, they can be further classified into different types based on their additional properties:
1. Isosceles Trapezoid:
An isosceles trapezoid is a special type of trapezoid where the two non-parallel sides (legs) are congruent (equal in length). This congruence leads to several interesting properties:
- Congruent Base Angles: The base angles of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent. This means that the angles at either end of each base are equal in measure.
- Symmetry: An isosceles trapezoid exhibits a certain symmetry; if you were to fold it along a line connecting the midpoints of its bases, the two halves would perfectly overlap.
2. Right Trapezoid:
A right trapezoid is a trapezoid where at least one of the legs is perpendicular to both bases. This creates a right angle between the leg and the base. This simple addition significantly simplifies some calculations related to the trapezoid's area and other properties.
3. Scalene Trapezoid:
A scalene trapezoid is the most general type of trapezoid. It has no additional properties beyond the basic definition. The sides are all of different lengths, and the angles are all of different measures. This makes it the least symmetrical type of trapezoid.
Calculating the Area of a Trapezoid: A Practical Application
One of the most common practical applications involving trapezoids is calculating their area. The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:
Area = (1/2) * (b1 + b2) * h
Where:
- b1 and b2 are the lengths of the two parallel bases.
- h is the height of the trapezoid (the perpendicular distance between the bases).
This formula is straightforward to use once you've identified the lengths of the bases and the height. Understanding the components of this formula allows for efficient solutions to area-related problems involving trapezoids.
Trapezoids in Real Life: Examples and Applications
Trapezoids, while often overlooked, are surprisingly common shapes found in everyday objects and structures. Recognizing them helps to appreciate their practical significance. Here are some examples:
- Architecture: Many buildings and bridges incorporate trapezoidal designs. The supports of bridges and the shapes of certain roofs often utilize trapezoids for structural stability and aesthetic appeal. Think of the side of a house with a slanted roof – that's a trapezoid!
- Engineering: Trapezoidal shapes are frequently used in engineering designs for various components and structures. Their unique properties often make them optimal for distributing weight and stress.
- Everyday Objects: From picture frames and tabletops to certain types of nuts and bolts, trapezoidal shapes appear in numerous everyday objects. Observe the world around you—you'll be surprised how often you encounter this shape.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers often incorporate trapezoidal shapes to create dynamic and visually interesting compositions. The varied angles and proportions of trapezoids add depth and complexity to their work.
- Nature: While less explicitly apparent than in man-made objects, natural formations can exhibit trapezoidal characteristics, especially when viewed from specific angles. Consider certain geological formations, or even the patterns on some leaves.
Solving Problems Involving Trapezoids: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let's work through a few examples to solidify your understanding of trapezoids and their applications:
Example 1: Finding the Area
A trapezoid has bases of length 5 cm and 9 cm, and a height of 4 cm. Find its area.
Using the formula: Area = (1/2) * (b1 + b2) * h = (1/2) * (5 + 9) * 4 = 28 square cm
Example 2: Identifying Trapezoid Types
A trapezoid has two parallel sides of length 6 cm and 10 cm, and two non-parallel sides of length 5 cm and 5 cm. What type of trapezoid is it?
Since the non-parallel sides are congruent, this is an isosceles trapezoid.
Example 3: Real-World Application
A construction worker needs to calculate the area of a trapezoidal section of a roof. The bases measure 8 feet and 12 feet, and the height is 6 feet. What is the area of the roof section?
Using the formula: Area = (1/2) * (b1 + b2) * h = (1/2) * (8 + 12) * 6 = 60 square feet
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
While this guide covers the fundamental aspects of trapezoids, there are more advanced concepts for those wishing to delve deeper:
- Midsegment Theorem: This theorem states that the segment connecting the midpoints of the two non-parallel sides (legs) of a trapezoid is parallel to the bases and has a length equal to the average of the lengths of the two bases.
- Cyclic Trapezoids: A cyclic trapezoid is a trapezoid that can be inscribed in a circle. This implies specific relationships between its angles and sides.
- Area Calculations using Trigonometry: In cases where only the lengths of the sides and angles are known, trigonometry can be used to calculate the height and area of a trapezoid.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Geometry
While often overshadowed by its more symmetrical quadrilateral cousins, the trapezoid plays a significant role in both theoretical geometry and practical applications. Understanding its properties, classifications, and applications opens doors to a deeper appreciation of geometry and its relevance in the world around us. Remember, the seemingly simple question "How many sides does a trapezoid have?" opens the door to a rich and complex world of mathematical exploration. By understanding the fundamental characteristics of trapezoids and their variations, you can effectively analyze and solve problems involving this versatile geometric shape. So, next time you see a trapezoid, remember that it's much more than just a four-sided figure; it's a powerful tool used in countless ways.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Can You Be A Professor With A Masters
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Bottles Of Water Is 1 Liter
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days In A Million Minutes
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Days Is In 11 Weeks
Jul 14, 2025
-
How Many Grams Are In One Tola Gold
Jul 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Sides Does A Trapezoid Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.