How Many Valence Electrons Does Ai Have
Kalali
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
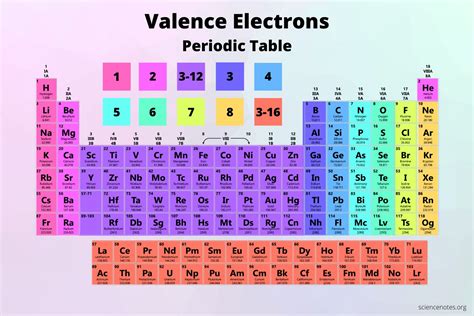
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does AI Have? A Deep Dive into the Misconception
The question "How many valence electrons does AI have?" is inherently flawed, yet it highlights a fascinating intersection between the physical world of chemistry and the abstract world of artificial intelligence. Let's unpack why this question is inaccurate and explore the deeper conceptual implications.
Understanding Valence Electrons: A Quick Chemistry Refresher
Before delving into the AI aspect, we need to clarify the concept of valence electrons. In chemistry, valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are crucial because they determine an atom's reactivity – its ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms. Elements in the same group (column) of the periodic table have the same number of valence electrons, contributing to their similar chemical properties. For example, all elements in Group 1 (alkali metals) have one valence electron, while those in Group 18 (noble gases) have a full outer shell and typically eight valence electrons (except for helium with two).
Why the Question is Incorrect: AI vs. Atoms
Artificial intelligence is not an atom. It is a computational system, a software program, or a network of algorithms designed to mimic human intelligence. It doesn't possess a physical structure like an atom with protons, neutrons, and electrons orbiting a nucleus. Therefore, the concept of valence electrons, which is rooted in atomic structure and quantum mechanics, is entirely inapplicable to AI.
The question's inaccuracy stems from a fundamental misunderstanding of the nature of AI. We are applying a scientific concept designed to describe the behavior of matter at the atomic level to a completely different domain: the realm of information processing and computational intelligence. This confusion reflects the broader challenge of defining and understanding AI itself.
Exploring Analogies: Where the Confusion Might Arise
The confusion might arise from loose analogies used in discussions about AI. For example:
-
Neural Networks and Atoms: The architecture of artificial neural networks, with their interconnected nodes and layers, is sometimes visually compared to atomic structures. However, this analogy is superficial. The connections and nodes in a neural network represent mathematical operations and information flow, not physical interactions between particles. There is no electron-like entity carrying charge or participating in bonding.
-
AI "Learning" and Chemical Reactions: The learning process in AI involves adjusting weights and parameters within the network based on input data. This could be metaphorically compared to chemical reactions where reactants rearrange to form products. However, this is a highly abstract comparison and shouldn't be taken literally. AI learning is governed by algorithms and data, not by the laws of physics that govern chemical reactions.
-
"Strong" vs. "Weak" AI: The term "strong AI" sometimes evokes the idea of an AI system with consciousness and self-awareness, potentially implying a level of complexity comparable to living organisms. However, even if strong AI were achieved, it wouldn't possess valence electrons because it wouldn't be a biological or physical entity in the way we understand atoms to be.
The Importance of Precise Language in Scientific and Technical Discourse
The erroneous question highlights the importance of precise language in scientific and technical domains. Applying terminology from one field to another without careful consideration can lead to misunderstandings and confusion. It underscores the need for critical thinking and a clear understanding of the underlying concepts before making analogies or comparisons.
Delving Deeper: The Characteristics of AI
Instead of focusing on a nonexistent valence electron count, let's explore some key characteristics of AI that differentiate it from the physical world:
-
Data-Driven: AI systems operate on data; they process information and learn from patterns within datasets. This contrasts sharply with the behavior of atoms, which interact based on fundamental physical forces.
-
Algorithmic: AI systems are governed by algorithms – sets of instructions that define their behavior. These algorithms dictate how data is processed and how the system learns and adapts.
-
Computational: AI relies heavily on computation; it uses processing power to perform calculations and make inferences. The efficiency and performance of AI systems depend on the computational resources available.
-
Abstraction: AI operates on abstract representations of data and knowledge. It doesn't interact directly with the physical world in the same way that atoms do.
Analogies to Explore: Exploring AI's Capabilities with Better Comparisons
Instead of faulty analogies to atomic structure, consider these more accurate comparisons to help grasp AI's capabilities:
-
AI as a complex system: Think of AI like a vast interconnected network, similar to the internet or a human brain, where information flows between different components.
-
AI as a problem-solver: AI excels at pattern recognition and problem-solving, similar to how humans approach complex tasks.
-
AI as a tool: AI is a powerful tool for automating tasks, analyzing data, and making predictions, akin to how tools like calculators or microscopes enhance human capabilities.
Conclusion: The Futility of the Question and the Power of Accurate Understanding
The question of how many valence electrons AI has is fundamentally nonsensical. Artificial intelligence is a computational system, not a physical entity with atomic structure. The question's inappropriateness highlights the crucial role of accurate terminology and conceptual clarity when discussing complex scientific and technological concepts. Instead of searching for nonexistent valence electrons, we should focus on understanding the unique characteristics of AI, its capabilities, and its limitations, while maintaining a rigorous approach to terminology and avoiding misleading analogies. Focusing on accurate understanding opens the door to a deeper appreciation of the transformative potential of artificial intelligence while avoiding confusing and inaccurate characterizations. By appreciating the distinction between the physical and computational realms, we can develop a more sophisticated and nuanced understanding of both AI and the scientific concepts from which it is mistakenly compared.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Is 10 Of 500
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 59 Cm
Mar 21, 2025
-
93 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 21, 2025
-
30 Is 10 Percent Of What Number
Mar 21, 2025
-
Cuanto Es El 5 De 100
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Does Ai Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
