How Many Valence Electrons Does Ar Have
Kalali
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
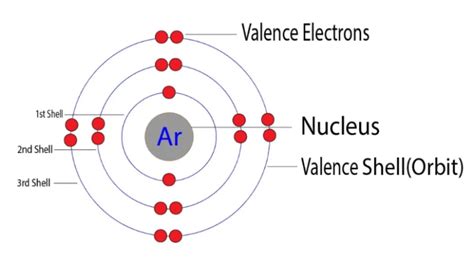
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does Argon Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure and Chemical Behavior
Argon (Ar), a noble gas residing in Group 18 of the periodic table, holds a unique position in chemistry due to its complete valence shell. Understanding its electron configuration is key to grasping its inert nature and its applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of argon's valence electrons, exploring its atomic structure, chemical properties, and the implications of its filled valence shell.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Reactivity
Before focusing on argon, let's establish a fundamental concept: valence electrons. These are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom, also known as the valence shell. They are the electrons most involved in chemical bonding and interactions with other atoms. The number of valence electrons determines an element's reactivity and how it will bond with other elements. Atoms strive for stability, often achieved by having a full valence shell, usually containing eight electrons (the octet rule, with some exceptions).
Argon's Electronic Structure: A Noble Gas Configuration
Argon's atomic number is 18, meaning it possesses 18 protons and 18 electrons in a neutral atom. These electrons are distributed across different energy levels or shells. Following the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, the electronic configuration of argon is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶.
Breaking Down Argon's Electron Configuration:
- 1s²: Two electrons occupy the first energy level (n=1), in the 's' subshell.
- 2s²: Two electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2), in the 's' subshell.
- 2p⁶: Six electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2), in the 'p' subshell.
- 3s²: Two electrons occupy the third energy level (n=3), in the 's' subshell.
- 3p⁶: Six electrons occupy the third energy level (n=3), in the 'p' subshell.
Identifying the Valence Electrons:
The outermost shell in argon's configuration is the third energy level (n=3), which contains the 3s and 3p electrons. Adding these electrons together (2 + 6 = 8), we find that argon has 8 valence electrons. This complete octet is the reason for argon's exceptional stability and inertness.
The Significance of a Full Valence Shell: Inertness and Stability
The presence of eight valence electrons in argon's outermost shell results in exceptional stability. Atoms tend to react to achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of a noble gas. Argon, already possessing this stable configuration, has little tendency to gain, lose, or share electrons. This explains its chemical inertness.
Comparing Argon to Other Elements:
Consider elements like sodium (Na), with one valence electron, and chlorine (Cl), with seven valence electrons. Sodium readily loses its valence electron to achieve a stable configuration, forming a positive ion (Na⁺). Chlorine readily gains an electron to complete its octet, forming a negative ion (Cl⁻). This electron transfer leads to the formation of the ionic compound sodium chloride (NaCl), or table salt. Argon, however, has no such driving force to react, as it already has a complete octet.
Argon's Unique Properties and Applications: A Result of Its Valence Electron Configuration
Argon's inertness, a direct consequence of its filled valence shell, makes it incredibly useful in various applications:
1. Inert Atmosphere Creation:
- Welding and Metallurgy: Argon's inertness prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions during welding and metal processing. Creating an argon atmosphere around the molten metal protects it from contamination.
- Chemical Reactions: Argon provides a non-reactive environment for carrying out sensitive chemical reactions that would otherwise be affected by oxygen or nitrogen.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: In the production of semiconductors, argon's inertness is crucial in preventing contamination and maintaining the integrity of the delicate structures.
2. Lighting Applications:
- Incandescent Lighting: Argon is used in incandescent light bulbs to reduce the rate of filament evaporation and extend the bulb's lifespan. Its inertness prevents the filament from reacting with oxygen.
- Fluorescent Lighting: Argon is a common component of the gas mixture inside fluorescent tubes, where it facilitates the ionization process needed to produce light.
3. Medical and Scientific Applications:
- Laser Technology: Certain argon lasers are used in various medical procedures like eye surgery and dermatology.
- Dating Techniques: Argon-argon dating is a radiometric dating technique used in geochronology to determine the age of rocks and other geological materials.
Beyond the Octet Rule: Exceptions and Nuances
While the octet rule provides a useful framework for understanding chemical bonding, it's not without exceptions. Some elements, particularly those in higher periods of the periodic table, can have more or fewer than eight electrons in their valence shells and still achieve stability. However, argon, being a relatively simple atom in the second period, adheres perfectly to the octet rule.
Conclusion: The Importance of Valence Electrons in Determining Chemical Behavior
The number of valence electrons an atom possesses is a fundamental factor determining its chemical properties and reactivity. Argon, with its eight valence electrons and complete octet, exhibits remarkable inertness. This unique characteristic underpins its widespread applications in diverse fields, from welding to medical technology. Understanding the relationship between electron configuration and chemical behavior is crucial for comprehending the behavior of all elements in the periodic table. Argon serves as a perfect example of how a full valence shell leads to exceptional stability and unique applications, highlighting the importance of valence electrons in chemistry. Furthermore, studying argon's electron configuration helps solidify a fundamental understanding of atomic structure and the basis of chemical bonding. This knowledge forms the bedrock of further exploration in chemistry and related fields. The seemingly simple question, "How many valence electrons does argon have?" opens a door to a wealth of understanding within the fascinating world of atomic structure and chemical behavior.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Double Of 1 4 Cup
Jul 10, 2025
-
Prepare Me A Body And I Will Redeem Man
Jul 10, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is A Meter Stick
Jul 10, 2025
-
Soundtrack To Step Up 2 The Streets
Jul 10, 2025
-
Keebler Club And Cheddar Crackers Expiration Date
Jul 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Does Ar Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.