How To Complete The Square When A Is Not 1
Kalali
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
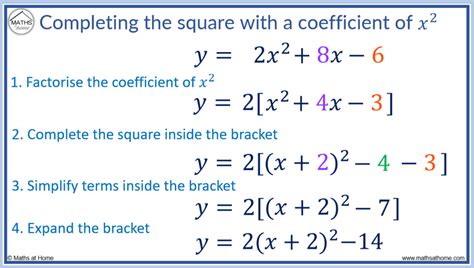
Table of Contents
How to Complete the Square When a is Not 1
Completing the square is a crucial algebraic technique used to solve quadratic equations, rewrite quadratic functions in vertex form, and simplify various mathematical expressions. While the process is straightforward when the coefficient of the squared term (a) is 1, it becomes slightly more involved when a ≠ 1. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the steps, offering explanations, examples, and tips to master this essential skill.
Understanding the Standard Form of a Quadratic Equation
Before diving into the process, let's refresh our understanding of the standard form of a quadratic equation:
ax² + bx + c = 0
Where:
- a, b, and c are constants (numbers).
- a ≠ 0 (otherwise, it wouldn't be a quadratic equation).
The process of completing the square aims to manipulate this equation into a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily factored.
Completing the Square: The Step-by-Step Guide (When a ≠ 1)
The key difference when a is not 1 lies in the initial step. We must factor out a from the terms containing x. Here's the detailed procedure:
Step 1: Ensure the coefficient of x² is 1.
If the coefficient of x² (a) is not 1, factor it out from the first two terms of the equation. This step is crucial and often overlooked. Let's illustrate with an example:
2x² + 8x - 10 = 0
Factor out the '2' from the x² and x terms:
2(x² + 4x) - 10 = 0
Step 2: Find the value to complete the square.
Inside the parentheses, focus on the coefficient of the x term (in this case, 4). Take half of this coefficient (4/2 = 2), and then square the result (2² = 4). This value, 4, is what we need to create a perfect square trinomial.
Step 3: Add and subtract the value inside the parentheses.
Crucially, we cannot just add 4 to the equation; this would alter its value. To maintain balance, we both add and subtract 4 inside the parentheses. Remember that the 4 is being multiplied by the 2 that we factored out earlier:
2(x² + 4x + 4 - 4) - 10 = 0
Step 4: Factor the perfect square trinomial.
The first three terms inside the parentheses (x² + 4x + 4) form a perfect square trinomial, which factors neatly as (x + 2)². Rewrite the equation accordingly:
2((x + 2)² - 4) - 10 = 0
Step 5: Simplify and solve (if necessary).
Now, distribute the 2 and simplify to solve for x:
2(x + 2)² - 8 - 10 = 0 2(x + 2)² - 18 = 0 2(x + 2)² = 18 (x + 2)² = 9 x + 2 = ±√9 x + 2 = ±3 x = -2 ± 3 x = 1 or x = -5
Therefore, the solutions to the equation 2x² + 8x - 10 = 0 are x = 1 and x = -5.
Examples with Different Coefficients
Let's work through a few more examples to solidify your understanding:
Example 1: -3x² + 12x - 6 = 0
- Factor out -3: -3(x² - 4x) - 6 = 0
- Complete the square: Half of -4 is -2; (-2)² = 4. Add and subtract 4 inside the parentheses: -3(x² - 4x + 4 - 4) - 6 = 0
- Factor: -3((x - 2)² - 4) - 6 = 0
- Simplify and solve: -3(x - 2)² + 12 - 6 = 0 -3(x - 2)² = -6 (x - 2)² = 2 x - 2 = ±√2 x = 2 ± √2
Example 2: 5x² + 15x + 20 = 0
- Factor out 5: 5(x² + 3x) + 20 = 0
- Complete the square: Half of 3 is 3/2; (3/2)² = 9/4. Add and subtract 9/4: 5(x² + 3x + 9/4 - 9/4) + 20 = 0
- Factor: 5((x + 3/2)² - 9/4) + 20 = 0
- Simplify and solve: 5(x + 3/2)² - 45/4 + 20 = 0 5(x + 3/2)² = -35/4 (x + 3/2)² = -7/4 Since we have a negative number under the square root, there are no real solutions to this equation. The solutions are complex numbers.
Completing the Square to Find the Vertex of a Parabola
Completing the square is also incredibly useful for finding the vertex of a parabola represented by a quadratic function in standard form (y = ax² + bx + c). The vertex form is y = a(x - h)² + k, where (h, k) represents the coordinates of the vertex.
Following the same steps as above, you'll arrive at the vertex form. The h value will be the x-coordinate of the vertex, and the k value will be the y-coordinate.
For example, consider the quadratic function y = 2x² + 8x - 10. Using the steps outlined earlier, we transformed it into y = 2(x + 2)² - 18. Therefore, the vertex of the parabola is located at (-2, -18).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Forgetting to factor out 'a': This is the most frequent error. Always ensure the coefficient of x² is 1 before proceeding.
- Incorrectly adding and subtracting: Remember to add and subtract the value inside the parentheses to maintain the balance of the equation. The value added and subtracted must be multiplied by a.
- Sign errors: Be meticulous with your signs, particularly when dealing with negative coefficients.
- Arithmetic errors: Double-check your calculations throughout the process. A small error early on can lead to completely wrong results.
Advanced Applications
While completing the square is often introduced in the context of solving quadratic equations, its applications extend far beyond this basic use case. It’s a fundamental building block for many higher-level mathematical concepts, including:
- Derivation of the quadratic formula: The quadratic formula itself is derived using the method of completing the square.
- Calculus: Completing the square aids in simplifying integrals and derivatives involving quadratic expressions.
- Conic sections: It plays a significant role in analyzing and manipulating equations of circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas.
- Statistics: The method is utilized in statistical analyses involving normal distributions and regression analysis.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of completing the square, especially when a ≠ 1, is a valuable skill for any student of mathematics or anyone working with quadratic expressions. By carefully following the steps outlined in this guide and practicing consistently, you can confidently tackle a wide array of problems and deepen your understanding of quadratic functions and equations. Remember to practice regularly with various examples to build your proficiency and overcome any initial challenges. Consistent practice is the key to mastering this fundamental algebraic technique.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Can You Separate Sugar And Water
Mar 15, 2025
-
Cuanto Son 40 Oz En Litros
Mar 15, 2025
-
5 And 1 2 As A Decimal
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Do You Convert From Moles To Liters
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Separates A Salamander From A Turtle
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Complete The Square When A Is Not 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
