How To Convert Negative Fractions To Decimals
Kalali
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
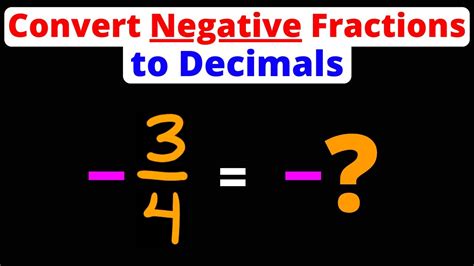
Table of Contents
How to Convert Negative Fractions to Decimals: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics, and understanding how to handle negative fractions is crucial for mastering this concept. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process step-by-step, providing clear explanations, examples, and tips to help you confidently convert any negative fraction to its decimal equivalent. We'll also explore different methods and address common challenges, ensuring you gain a solid understanding of this essential mathematical operation.
Understanding Negative Fractions
Before diving into the conversion process, let's solidify our understanding of negative fractions. A negative fraction simply represents a portion of a whole number that is less than zero. It's indicated by a minus sign (-) placed before the fraction. For instance, -⅓, -2/5, and -7/8 are all examples of negative fractions. The negative sign applies to the entire fraction, not just the numerator or denominator.
Think of it this way: a fraction represents a division problem. The numerator is divided by the denominator. If the result of that division is negative, then the fraction itself is negative.
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method for converting a negative fraction to a decimal is through long division. This method works for all types of fractions, both simple and complex. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Ignore the negative sign initially. Focus solely on the numerical values of the numerator and denominator.
Step 2: Perform long division. Divide the numerator by the denominator. Remember the process of long division: how many times the denominator goes into the numerator, subtracting, bringing down the next digit, etc.
Step 3: Add the negative sign. Once you've obtained the decimal result from the long division, simply add the negative sign in front of it.
Example: Convert -¾ to a decimal.
- Ignore the negative sign: We'll focus on ¾.
- Long Division: 3 divided by 4. This gives us 0.75.
- Add the negative sign: The decimal equivalent is -0.75.
Example with a Remainder (Repeating Decimal): Convert -²/₃ to a decimal.
- Ignore the negative sign: Focus on ²/₃.
- Long Division: 2 divided by 3. This results in a repeating decimal: 0.6666... We can represent this as 0.¯6.
- Add the negative sign: The decimal equivalent is -0.¯6.
Method 2: Converting to an Equivalent Fraction with a Denominator of 10, 100, 1000, etc.
This method is particularly useful for fractions with denominators that are factors of powers of 10. If you can convert the fraction to an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 10, 100, 1000, etc., the decimal conversion becomes much simpler.
Step 1: Identify the denominator. Check if the denominator is a factor of 10, 100, 1000, or another power of 10.
Step 2: Convert to an equivalent fraction. If the denominator is a factor, multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the appropriate number to obtain a denominator that is a power of 10.
Step 3: Write as a decimal. Once you have a denominator that is a power of 10 (e.g., 10, 100, 1000), the decimal representation is easily obtained. The number of zeros in the denominator corresponds to the number of places after the decimal point.
Step 4: Add the negative sign. Remember to add the negative sign to the final decimal result.
Example: Convert -²/₅ to a decimal.
- Identify the denominator: The denominator is 5, which is a factor of 10.
- Convert to an equivalent fraction: Multiply both numerator and denominator by 2: (-2 x 2) / (5 x 2) = -⁴/₁₀
- Write as a decimal: -⁴/₁₀ = -0.4
- Negative Sign: The decimal is already negative, so no further action is needed.
Example (More Complex): Convert -¹²/₂₅ to a decimal.
- Identify the denominator: The denominator is 25, which is a factor of 100.
- Convert to an equivalent fraction: Multiply both numerator and denominator by 4: (-12 x 4) / (25 x 4) = -⁴⁸/₁₀₀
- Write as a decimal: -⁴⁸/₁₀₀ = -0.48
- Negative Sign: The decimal is already negative.
Method 3: Using a Calculator
The simplest method, especially for complex fractions, is to use a calculator. Simply enter the fraction with the negative sign, and the calculator will compute the decimal equivalent. Most calculators will handle both simple and complex fractions accurately. Remember to ensure that the calculator is properly interpreting the negative sign, and that you are entering the fraction correctly (often as -numerator/denominator).
Dealing with Repeating Decimals
When converting certain fractions, you may encounter repeating decimals. These decimals have a sequence of digits that repeat infinitely. For example, -¹/₃ converts to -0.¯3, indicating that the digit 3 repeats indefinitely. In these cases, you can:
- Use the bar notation: The bar above the repeating digits indicates the repeating sequence. This is the most concise way to represent repeating decimals.
- Round to a specified number of decimal places: Depending on the context, you might round the repeating decimal to a certain number of decimal places (e.g., rounding -0.¯3 to -0.33). Be mindful that rounding introduces a small degree of inaccuracy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Forgetting the negative sign: This is the most common error. Always remember to include the negative sign in your final answer.
- Incorrect long division: Double-check your long division steps to avoid errors.
- Misinterpreting repeating decimals: Understand how to correctly represent repeating decimals using bar notation or rounding.
- Improper calculator use: Ensure you are entering the fraction correctly into your calculator, especially regarding the placement of the negative sign.
Practice Makes Perfect
The best way to master converting negative fractions to decimals is through consistent practice. Start with simple fractions and gradually move to more complex ones. Use a combination of the methods described above to build your understanding and confidence. Regular practice will not only improve your accuracy but also enhance your speed and efficiency in performing these conversions.
Applications of Negative Fraction to Decimal Conversion
The ability to convert negative fractions to decimals is crucial in various fields, including:
- Science: Many scientific calculations involve fractions, and converting them to decimals is necessary for computations and data analysis.
- Engineering: Engineering projects often require precise measurements, and decimal representation is often preferred for calculations and design specifications.
- Finance: Negative fractions represent losses or debts in financial calculations. Converting them to decimals simplifies financial reporting and analysis.
- Computer Programming: Many programming languages require decimal representation for numerical calculations.
- Everyday Life: This skill is applicable in various everyday situations, from calculating discounts to measuring ingredients in recipes.
By mastering the techniques explained in this comprehensive guide, you'll be well-equipped to confidently convert any negative fraction to its decimal equivalent, enhancing your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities across various applications. Remember, practice is key, and with consistent effort, you'll develop fluency in this essential mathematical process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Times Does 3 Go Into 30
Jul 13, 2025
-
In What Episode Of Bleach Does Ichigo Ask Orihime Out
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Much Is 4 Oz Chocolate Chips
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Many Times Does 9 Go Into 70
Jul 13, 2025
-
4 Pics 1 Word Cheat 8 Letters
Jul 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Convert Negative Fractions To Decimals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.