How To Separate Sugar From Water
Kalali
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
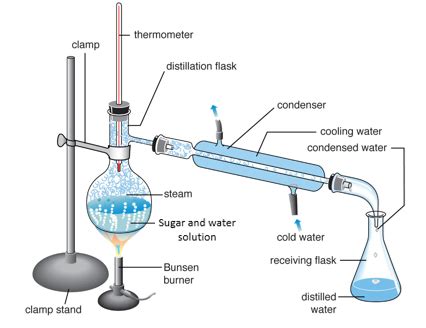
Table of Contents
How to Separate Sugar from Water: A Comprehensive Guide
Separating sugar from water might seem like a simple task, but understanding the underlying principles and choosing the right method can significantly impact efficiency and outcome. This comprehensive guide explores various techniques, from simple evaporation to more advanced methods, helping you choose the best approach based on your needs and resources. We'll delve into the science behind the separation, discuss the pros and cons of each method, and provide practical tips for successful sugar recovery.
Understanding the Sugar-Water Solution
Before diving into separation techniques, it's crucial to understand the nature of a sugar-water solution. Sugar (sucrose) is a soluble solid, meaning it dissolves completely in water to form a homogenous mixture. This means the sugar molecules are evenly dispersed throughout the water, not simply suspended like sediment. This characteristic dictates the methods we can use for separation. We can't simply filter the sugar out; we need to employ techniques that exploit the differences in properties between sugar and water.
Methods for Separating Sugar from Water
Several methods can effectively separate sugar from water. The best choice depends on the scale of the operation, the desired purity of the sugar, and the available resources.
1. Evaporation
This is the most common and arguably simplest method for separating sugar from water, especially for small-scale operations. It relies on the difference in boiling points between water (100°C at standard pressure) and sugar (sugar caramelizes and decomposes before reaching its boiling point).
How it works: The sugar-water solution is heated. As the water boils, it turns into steam and escapes, leaving behind the sugar. The process continues until all the water has evaporated, resulting in solid sugar crystals.
Pros:
- Simple and readily accessible: All you need is a heat source and a container.
- Effective for small quantities: Ideal for home experiments or small-scale projects.
Cons:
- Time-consuming: Evaporation can take a considerable amount of time, especially for larger volumes.
- Energy-intensive: Requires a sustained heat source, leading to higher energy consumption.
- Potential for sugar degradation: Prolonged or excessive heating can caramelize the sugar, altering its color and taste. Careful temperature control is vital.
- Not suitable for large-scale operations: Inefficient and impractical for industrial purposes.
2. Distillation
Distillation is a more sophisticated method that takes advantage of the difference in boiling points between water and sugar. While sugar doesn't have a boiling point in the traditional sense (it decomposes before boiling), water can be boiled off and condensed to collect pure water, leaving behind the sugar.
How it works: The sugar-water solution is heated in a distillation apparatus. The water vaporizes, rises, and then condenses in a separate cooled chamber, resulting in purified water. The sugar remains in the original container.
Pros:
- Produces pure water: This method effectively separates the water, leaving behind the sugar.
- Suitable for larger quantities: Can be scaled up for industrial applications.
Cons:
- Requires specialized equipment: A distillation apparatus is necessary, which can be expensive.
- More complex process: Requires understanding of the distillation process and careful control of temperature and pressure.
- Energy intensive: Like evaporation, it needs a constant heat source.
- Sugar loss possible: Some sugar might be lost through splashing or carryover during boiling.
3. Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a membrane-based separation technique that uses pressure to force water molecules through a semipermeable membrane, leaving behind the sugar. This method doesn't involve heating and is therefore less energy-intensive.
How it works: The sugar-water solution is subjected to high pressure, forcing water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. The membrane allows water molecules to pass through but prevents larger sugar molecules. The resulting purified water is collected on one side, while the concentrated sugar solution remains on the other.
Pros:
- Energy efficient (compared to evaporation and distillation): Lower energy consumption than evaporative methods.
- Relatively high purity: Produces high purity water.
- Suitable for various concentrations: Effective over a range of sugar concentrations.
Cons:
- Expensive equipment: Requires specialized and relatively costly membrane technology.
- Membrane fouling: The membrane can become clogged over time, reducing efficiency and requiring replacement.
- High pressure required: Requires substantial pressure to drive the process.
- Not ideal for all scales: Might not be economically feasible for very small-scale separation.
4. Chromatography
Chromatography is a powerful separation technique used in analytical chemistry and can also be adapted to separate sugar from water. This method exploits the different affinities of sugar and water for a stationary phase.
How it works: The sugar-water solution is passed through a column containing a stationary phase material (e.g., silica gel) that interacts differently with sugar and water molecules. Water will move through the column faster, while the sugar will be retained, allowing for separation.
Pros:
- High resolution: Can achieve very high purity separation.
- Applicable to complex mixtures: Can be used to separate sugar from other dissolved substances.
Cons:
- Highly specialized equipment: Requires specialized chromatographic equipment and expertise.
- Time-consuming: The separation process can be quite lengthy.
- Not cost-effective for large-scale sugar separation: Primarily used for analytical purposes and small-scale purifications.
Choosing the Right Method
The optimal method for separating sugar from water depends on several factors:
- Scale of operation: Evaporation is suitable for small quantities, while distillation or reverse osmosis are better for larger-scale processes.
- Desired purity: Distillation and reverse osmosis generally yield higher purity water compared to evaporation.
- Available resources: The choice will depend on the equipment and resources available.
- Cost considerations: Evaporation is the cheapest, while reverse osmosis and chromatography are more expensive.
Practical Tips for Successful Sugar Recovery
Regardless of the chosen method, these tips can enhance the efficiency and success of sugar separation:
- Start with a clean container: This prevents contamination of the final sugar product.
- Use appropriate heating: Avoid overheating to prevent sugar caramelization. A double boiler or slow, even heat is recommended.
- Monitor the process: Regularly check the progress to avoid over-evaporation or other issues.
- Allow for cooling: Allow the sugar to cool completely after evaporation before handling it.
- Store sugar properly: Store the separated sugar in an airtight container to maintain its quality.
Conclusion
Separating sugar from water offers a practical illustration of fundamental scientific principles. While evaporation remains a simple and accessible option for small-scale separations, more advanced techniques like distillation and reverse osmosis provide greater efficiency and purity for larger-scale or more demanding applications. Choosing the right method requires careful consideration of the factors discussed above, ensuring the successful recovery of sugar while optimizing resource usage. Understanding these methods empowers you to tackle sugar separation tasks effectively, whether in a home experiment or a larger industrial setting. Remember safety precautions and appropriate handling throughout the process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
240 C Is What In Fahrenheit
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 9 8 As A Percent
Mar 15, 2025
-
Convert 2 1 2 To A Decimal
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Much Is 3 4 In Ounces
Mar 15, 2025
-
Como Se Escribe El Cero En Numeros Romanos
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Separate Sugar From Water . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
