How To Turn An Improper Fraction To A Proper Fraction
Kalali
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
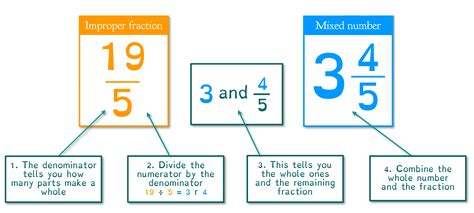
Table of Contents
How to Turn an Improper Fraction to a Proper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Improper fractions, those where the numerator is larger than the denominator, can seem daunting at first. But converting them to proper fractions (a whole number and a proper fraction) is a fundamental skill in mathematics with broad applications. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to master this conversion, regardless of your current math proficiency. We'll explore the process step-by-step, offer practical examples, and even delve into the underlying reasons why this conversion is so crucial.
Understanding Improper and Proper Fractions
Before we dive into the conversion process, let's clarify the difference between improper and proper fractions:
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is greater than or equal to the denominator (the bottom number). Examples include 7/4, 5/5, and 11/3.
-
Proper Fraction: A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator. Examples include 1/2, 3/4, and 2/5.
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. For example, 1 ¾, 2 ⅓, and 3 ²/₅. This is the result we aim for when converting an improper fraction.
The Process of Converting an Improper Fraction to a Mixed Number
The core of converting an improper fraction to a mixed number lies in division. Here's the step-by-step process:
Step 1: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
This is the most crucial step. Simply divide the numerator (the top number) by the denominator (the bottom number).
Step 2: Determine the Whole Number
The quotient (the result of the division) represents the whole number part of your mixed number.
Step 3: Determine the Remainder
The remainder from the division becomes the numerator of your proper fraction.
Step 4: Keep the Original Denominator
The denominator of your proper fraction remains the same as the original improper fraction's denominator.
Step 5: Combine the Whole Number and the Proper Fraction
Finally, combine the whole number obtained in Step 2 and the proper fraction obtained in Steps 3 and 4 to form your mixed number.
Illustrative Examples: Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Let's solidify our understanding with several examples:
Example 1: Converting 7/4
- Divide: 7 ÷ 4 = 1 with a remainder of 3.
- Whole Number: The quotient is 1.
- Remainder: The remainder is 3.
- Denominator: The denominator remains 4.
- Mixed Number: Combining these, we get 1 ¾.
Therefore, 7/4 = 1 ¾
Example 2: Converting 11/3
- Divide: 11 ÷ 3 = 3 with a remainder of 2.
- Whole Number: The quotient is 3.
- Remainder: The remainder is 2.
- Denominator: The denominator remains 3.
- Mixed Number: Combining these, we get 3 ⅔.
Therefore, 11/3 = 3 ⅔
Example 3: Converting 15/5
- Divide: 15 ÷ 5 = 3 with a remainder of 0.
- Whole Number: The quotient is 3.
- Remainder: The remainder is 0. Since the remainder is 0, there's no fractional part.
- Mixed Number: This simplifies to just the whole number 3.
Therefore, 15/5 = 3
Example 4: Converting a larger improper fraction: 127/12
- Divide: 127 ÷ 12 = 10 with a remainder of 7.
- Whole Number: 10
- Remainder: 7
- Denominator: 12
- Mixed Number: 10 ⁷/₁₂
Therefore, 127/12 = 10 ⁷/₁₂
Why is Converting Improper Fractions Important?
The conversion of improper fractions to mixed numbers is more than just a mathematical exercise. It's a crucial skill with several important applications:
-
Real-world problem solving: Many real-world scenarios involve fractions. For instance, measuring ingredients in a recipe, calculating distances, or dividing resources often result in improper fractions. Converting to mixed numbers makes these results much easier to understand and apply. Imagine a recipe calling for 7/4 cups of flour; 1 ¾ cups is far more practical to measure.
-
Simplifying calculations: Working with mixed numbers is often simpler than working with large improper fractions, particularly in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions.
-
Improved understanding of quantity: Mixed numbers provide a clearer representation of quantities. Understanding that 11/3 represents 3 and ⅔ provides a better grasp of the magnitude than the improper fraction itself.
-
Foundation for advanced mathematics: The concept of converting improper fractions forms a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts, such as algebra, geometry, and calculus.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
While the process is straightforward, here are a few common mistakes to watch out for:
-
Incorrect Division: Double-check your division to ensure accuracy. A minor error in division will lead to an incorrect mixed number.
-
Forgetting the Remainder: Remember that the remainder is crucial; it forms the numerator of the proper fraction.
-
Incorrect Denominator: Always keep the original denominator. It doesn't change during the conversion process.
-
Not simplifying the final answer: If the resulting proper fraction can be simplified (reduced to its lowest terms), remember to do so. For instance, 6/8 should be simplified to 3/4.
Advanced Applications and Further Exploration
Beyond the basics, this skill is fundamental in various mathematical contexts:
-
Working with fractions in algebra: Solving algebraic equations involving fractions often requires converting between improper and mixed numbers for simplification.
-
Geometry and Measurement: Calculating areas, volumes, and other geometric properties often involves fractions, making conversion essential for accurate results.
-
Data analysis and statistics: Many statistical calculations involve fractions, and converting improper fractions can make interpreting the results easier.
-
Computer programming: Programming languages often require handling fractions, and efficient conversion algorithms are crucial for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers is a fundamental mathematical skill with widespread applications. By mastering the simple steps outlined in this guide, you'll significantly improve your mathematical abilities and gain a clearer understanding of how fractions work. Remember to practice regularly, pay close attention to the division process, and always double-check your work. With consistent practice and attention to detail, you'll confidently navigate the world of fractions and unlock their practical applications in various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Is 20 Of 300
May 09, 2025
-
Living And Nonliving Things In An Ecosystem
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 60 Out Of 100
May 09, 2025
-
36 Is 15 Of What Number
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 0 09 As A Fraction
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Turn An Improper Fraction To A Proper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.