In An Ac Circuit The Effective Voltage Is
Kalali
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
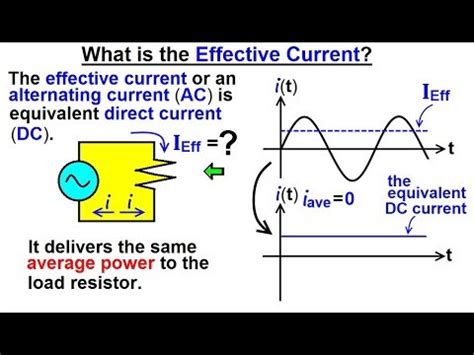
Table of Contents
In an AC Circuit, the Effective Voltage: A Deep Dive
Understanding voltage in alternating current (AC) circuits requires a nuanced approach compared to direct current (DC) circuits. While DC voltage maintains a constant value, AC voltage continuously changes its magnitude and direction. This fluctuation makes simply stating the peak voltage insufficient for characterizing the circuit's power delivery. This is where the concept of effective voltage, also known as root mean square (RMS) voltage, comes into play. This article delves into the intricacies of effective voltage in AC circuits, explaining its calculation, significance, and practical applications.
What is Effective Voltage (RMS Voltage)?
The effective voltage, or RMS voltage, represents the equivalent DC voltage that would produce the same average power dissipation in a resistive load. In simpler terms, it's the DC voltage that would generate the same amount of heat in a resistor as the fluctuating AC voltage. This is crucial because many AC applications, such as heating elements and incandescent lighting, primarily depend on the average power delivered, not the instantaneous voltage.
Unlike the peak voltage, which represents the maximum voltage reached during a cycle, the RMS voltage considers the entire waveform over a complete cycle. This means it accounts for both the positive and negative portions of the sinusoidal waveform, effectively averaging their power contribution.
The Significance of RMS Voltage
The RMS value is essential because it directly relates to the average power dissipated in a resistive load. While the average value of a sinusoidal AC voltage is zero, the average power is not. The RMS voltage provides a more practical measure of the energy delivered by an AC circuit to resistive components. This is why RMS values are used for specifying voltage ratings of household appliances, power systems, and electrical equipment.
Calculating RMS Voltage for a Sinusoidal Waveform
For a pure sinusoidal AC voltage, the RMS voltage is related to the peak voltage (Vp) by a simple mathematical relationship:
VRMS = Vp / √2 ≈ 0.707 * Vp
Where:
- VRMS is the root mean square voltage.
- Vp is the peak voltage.
This formula arises from the mathematical process of calculating the root mean square. The process involves squaring the instantaneous voltage values, averaging them over a complete cycle, and then taking the square root of the average. The √2 factor emerges directly from this mathematical derivation, specifically from the integration of the squared sine wave over one period.
Beyond Sinusoidal Waveforms: RMS in Complex AC Circuits
While the formula above applies specifically to pure sinusoidal waveforms, the concept of RMS voltage extends to more complex AC waveforms, such as those containing harmonics or exhibiting non-sinusoidal shapes. In such cases, the calculation becomes more intricate, often requiring integration techniques to determine the RMS value accurately.
The general formula for calculating the RMS voltage for any periodic waveform is:
VRMS = √[ (1/T) ∫₀ᵀ v(t)² dt ]
Where:
- VRMS is the RMS voltage.
- T is the period of the waveform.
- v(t) is the instantaneous voltage as a function of time.
- ∫₀ᵀ represents the definite integral from 0 to T.
This formula highlights that the RMS value fundamentally involves calculating the average of the square of the instantaneous voltage over a complete cycle. This is a more general approach applicable to any periodic waveform, not just a simple sine wave.
Practical Applications of RMS Voltage
The RMS voltage is fundamental in various electrical and electronic applications. Here are a few key examples:
1. Household Power Supply
Standard household AC power outlets provide an RMS voltage, typically 120V in North America and 230V in many parts of Europe and Asia. These RMS values are the effective voltages that drive appliances and lighting.
2. Audio and Signal Processing
In audio and signal processing, RMS voltage (often represented as RMS level) is used to measure the effective power or amplitude of audio signals. This is critical for avoiding signal clipping and ensuring accurate reproduction of sounds. RMS meters are commonly used in recording studios and audio equipment to monitor signal levels.
3. Power Measurement and Calculations
The RMS voltage is essential in electrical power calculations. The power (P) dissipated in a resistor is given by:
P = VRMS² / R
Where R is the resistance. This formula shows the direct relationship between the RMS voltage and the average power dissipated. This is the cornerstone formula for power calculations in AC circuits.
4. Power Electronics
In power electronics applications involving AC-DC conversion (rectifiers) or DC-AC conversion (inverters), the RMS voltage of the input or output waveform is crucial for designing efficient and reliable systems. Understanding the RMS voltage allows engineers to correctly size components and predict power losses.
5. Electrical Safety
Accurate determination of RMS voltage is critical for ensuring safety in electrical systems. Incorrect assumptions about voltage levels can lead to equipment damage, electrical shock, or fire hazards. Proper measurement and understanding of the RMS voltage are crucial for maintaining safety standards.
Differentiating RMS Voltage from Peak Voltage and Average Voltage
It's crucial to differentiate RMS voltage from other voltage measures in AC circuits:
-
Peak Voltage (Vp): This represents the maximum instantaneous voltage reached during a cycle. It is simply the amplitude of the waveform.
-
Average Voltage (Vavg): For a symmetrical AC waveform like a sine wave, the average voltage over a complete cycle is zero. The average voltage only becomes meaningful for non-symmetrical waveforms.
-
RMS Voltage (VRMS): This represents the equivalent DC voltage that would produce the same average power in a resistive load. It's the most practical measure of voltage in AC circuits for power calculations.
The key takeaway is that while peak voltage indicates the maximum voltage, RMS voltage provides the effective voltage that dictates the power delivered to the load. This is why RMS voltage is predominantly used in power calculations and appliance ratings.
Measuring RMS Voltage
Measuring RMS voltage requires specialized instruments, primarily digital multimeters (DMMs). Many DMMs have a dedicated RMS voltage measurement function that provides accurate readings for both sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal waveforms. It is important to note that some cheaper multimeters only provide accurate RMS readings for true sine waves; for complex waveforms, a true-RMS multimeter is necessary.
Traditional analog multimeters typically measure average voltage, which is only useful for determining RMS in specific cases (like pure sine waves). For any non-sinusoidal waveform, an analog meter will not accurately reflect the power-related RMS value.
Conclusion: The Practical Importance of RMS Voltage in AC Circuits
In conclusion, understanding the concept of effective voltage (RMS voltage) is paramount for anyone working with AC circuits. It's not just a theoretical concept; it is a fundamental quantity used in numerous practical applications, ranging from household power to sophisticated electronics. Its ability to accurately represent the power delivery capabilities of an AC voltage source makes it indispensable for electrical engineers, technicians, and anyone dealing with AC circuits. The proper understanding and application of RMS voltage are critical for designing safe, efficient, and reliable electrical systems. While peak and average voltages provide some information, only RMS voltage directly reflects the effective power, making it the cornerstone of AC circuit analysis and design.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Natural Phenomenon Is The Best Example Of Periodic Behavior
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 0 08 As A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Cups In 3 1 2 Quarts
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Number Is 15 Of 80
Mar 17, 2025
-
136 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In An Ac Circuit The Effective Voltage Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
