Index Of Refraction For Crown Glass
Kalali
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
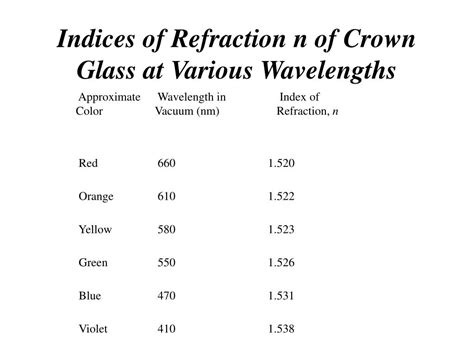
Table of Contents
Index of Refraction for Crown Glass: A Deep Dive
The index of refraction, a fundamental optical property, dictates how light bends when passing from one medium to another. Crown glass, a widely used type of glass known for its relatively low dispersion and high transparency, exhibits a specific index of refraction that makes it suitable for a broad range of applications. This article delves into the intricacies of the refractive index of crown glass, exploring its variations, measurement techniques, practical implications, and significance in diverse fields.
Understanding the Index of Refraction
The index of refraction (n) is a dimensionless number that represents the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum (c) to the speed of light in a given medium (v): n = c/v. A higher index of refraction indicates that light travels slower in that medium compared to a vacuum. This change in speed is responsible for the phenomenon of refraction – the bending of light as it crosses the boundary between two media with different refractive indices.
Factors Influencing the Refractive Index of Crown Glass
The refractive index of crown glass isn't a fixed value; it's influenced by several factors:
-
Wavelength of Light: Crown glass, like most materials, exhibits dispersion, meaning its refractive index varies with the wavelength of light. Shorter wavelengths (e.g., violet) experience a higher refractive index than longer wavelengths (e.g., red). This is why prisms can separate white light into its constituent colors. This wavelength dependency is often described using the Abbe number, a measure of a material's dispersion. Lower Abbe numbers indicate higher dispersion.
-
Temperature: Temperature fluctuations affect the refractive index. Generally, an increase in temperature leads to a slight decrease in the refractive index of crown glass. This effect, though relatively small, needs to be considered in precision optical applications.
-
Composition: The precise chemical composition of the crown glass significantly influences its refractive index. Different types of crown glass, containing varying proportions of silica, soda, lime, and other additives, will have slightly different refractive indices. Special crown glasses, formulated with specific additives, can be designed for specific refractive index requirements.
-
Pressure: While less significant than temperature and composition, pressure changes also exert a subtle effect on the refractive index of crown glass.
Typical Refractive Index Values for Crown Glass
While precise values vary based on the specific type and composition of crown glass, common refractive indices for crown glass at the sodium D-line (589.3 nm), a standard wavelength for optical measurements, fall within the range of 1.51 to 1.52. It's crucial to note that this is an approximation, and the manufacturer's specifications should always be consulted for precise values for a particular type of crown glass. Data sheets often provide refractive index values for multiple wavelengths to account for dispersion.
Common Types of Crown Glass and their Refractive Indices
Various types of crown glass exist, each tailored for specific applications. Here are a few examples:
-
Borosilicate Crown Glass: Known for its excellent chemical resistance and low thermal expansion, its refractive index typically falls within the lower end of the 1.51 to 1.52 range.
-
Light Crown Glass: This type of crown glass, designed for applications requiring high transmission, often has a refractive index near the lower end of the typical range.
-
Dense Crown Glass: With a slightly higher refractive index, dense crown glass offers increased refractive power, making it suitable for lenses requiring stronger focusing.
It's imperative to consult the manufacturer's specifications for the exact refractive index of the specific crown glass being used in a particular project.
Measuring the Refractive Index of Crown Glass
Precise measurement of the refractive index is vital in optical design and manufacturing. Several methods are commonly employed:
-
Refractometry: This involves measuring the critical angle of total internal reflection at the interface between the crown glass and a known medium, typically air. The refractive index is then calculated using Snell's Law.
-
Interferometry: This highly precise technique utilizes the interference patterns produced by light waves passing through the crown glass sample and a reference beam. The refractive index is determined from the analysis of the interference pattern.
-
Ellipsometry: Ellipsometry measures changes in the polarization of light reflected from the surface of the crown glass. This information is used to calculate the refractive index and other optical parameters.
These techniques provide accurate measurements critical for quality control and ensuring the performance of optical components.
Applications Leveraging the Refractive Index of Crown Glass
The relatively low dispersion and high transparency of crown glass, coupled with its readily available refractive index range, make it an ideal material for a plethora of applications.
Optical Lenses and Prisms
Crown glass is extensively used in the manufacturing of lenses for cameras, eyeglasses, microscopes, telescopes, and other optical instruments. Its predictable refractive properties are crucial for accurate image formation. Crown glass is often paired with flint glass (having a higher refractive index and dispersion) in achromatic doublets to minimize chromatic aberration.
Optical Windows and Filters
Crown glass serves as an excellent material for optical windows, providing high transmission and protection for sensitive optical components. It can be used in various applications ranging from laser systems to medical imaging devices. Specific doping or treatments might be applied to produce specialized filters for specific wavelengths.
Lighting Applications
The transparency and refractive index of crown glass make it suitable for use in various lighting applications. It can be used to create lenses and diffusers that effectively distribute light sources. The control of light path becomes critical in sophisticated illumination applications.
Conclusion: The Significance of Crown Glass's Refractive Index
The refractive index of crown glass is a critical parameter influencing its performance in a vast array of optical applications. Understanding the factors affecting this value, the typical range of indices, and the measurement techniques employed is essential for optical designers, manufacturers, and researchers. The versatility and readily available nature of crown glass, coupled with its well-characterized optical properties, solidify its important role in numerous technological advancements across various industries. Continuous advancements in glass manufacturing techniques lead to even more precisely controlled refractive indices, allowing for the development of ever-more sophisticated optical systems. Further research into modifying the refractive index through material engineering opens avenues for creating novel optical materials with specialized properties to meet the increasing demands of technological applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Average Iq For A 9 Year Old
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Long Does It Take For Brandy Melville To Ship
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Many Times Does 3 Go Into 30
Jul 13, 2025
-
In What Episode Of Bleach Does Ichigo Ask Orihime Out
Jul 13, 2025
-
How Much Is 4 Oz Chocolate Chips
Jul 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Index Of Refraction For Crown Glass . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.