Is -10 A Rational Number Or Irrational
Kalali
Mar 13, 2025 · 4 min read
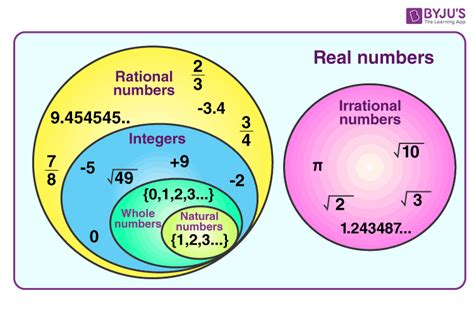
Table of Contents
Is -10 a Rational Number or Irrational? A Deep Dive into Number Classification
The question, "Is -10 a rational number or irrational?" might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding the answer requires a solid grasp of fundamental mathematical concepts. This article will delve into the definitions of rational and irrational numbers, explore the properties of -10, and ultimately provide a definitive answer, along with a broader understanding of number classification. We'll also examine some common misconceptions and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Rational Numbers
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, and 'q' is not equal to zero. This seemingly simple definition encompasses a vast range of numbers. Let's break it down:
-
Integers: These are whole numbers, including positive numbers (1, 2, 3...), negative numbers (-1, -2, -3...), and zero (0).
-
Fraction: A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's a ratio of two numbers.
The key here is that the fraction must be able to represent the number exactly. This is crucial when distinguishing between rational and irrational numbers.
Examples of Rational Numbers:
-
1/2: This is a classic example. One-half is a rational number because it's expressed as a fraction of two integers.
-
-3/4: Negative fractions are also rational.
-
5: The integer 5 can be expressed as a fraction: 5/1. All integers are rational numbers.
-
0.75: This decimal can be written as 3/4, thus making it a rational number. Any decimal that terminates (ends) or repeats is rational.
-
-2.666...: This repeating decimal can be expressed as a fraction (-8/3), making it rational.
Understanding Irrational Numbers
Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers (p/q). Their decimal representations are non-terminating and non-repeating, meaning they go on forever without ever settling into a repeating pattern. This infinite and unpredictable nature is what distinguishes them from rational numbers.
Examples of Irrational Numbers:
-
π (Pi): This famous constant, representing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, is approximately 3.14159... but the decimal expansion continues infinitely without repeating.
-
√2 (Square root of 2): This number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its decimal approximation is 1.41421..., again, continuing infinitely without repeating.
-
e (Euler's number): Another important mathematical constant, approximately 2.71828..., with a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansion.
-
The Golden Ratio (φ): Approximately 1.618..., an irrational number with significant appearances in geometry and art.
Classifying -10
Now, let's address the central question: is -10 a rational number or irrational?
The number -10 is an integer. As we established earlier, all integers are rational numbers because they can be expressed as a fraction: -10/1.
Therefore, -10 is a rational number.
Common Misconceptions about Rational and Irrational Numbers
Several common misunderstandings can arise when classifying numbers:
-
Negative numbers are irrational: This is false. Many negative numbers are rational (like -10), while some are irrational (like -√2). The sign of a number doesn't determine its rationality.
-
All decimals are irrational: This is incorrect. Terminating decimals (like 0.5) and repeating decimals (like 0.333...) are rational because they can be expressed as fractions. Only non-terminating, non-repeating decimals are irrational.
-
Irrational numbers are somehow "less real": This is a misconception. Both rational and irrational numbers are equally valid and important parts of the number system. They form the foundation of many mathematical concepts and applications.
Practical Applications and Further Exploration
Understanding the distinction between rational and irrational numbers has significant practical applications across various fields:
-
Computer Science: Representing irrational numbers in computers often involves approximations, as their infinite decimal expansions cannot be stored exactly.
-
Engineering: Precise calculations in engineering often require understanding the limitations of representing irrational numbers.
-
Physics: Many physical constants, like the speed of light, are often approximated as rational numbers for practical calculations.
-
Mathematics: The study of rational and irrational numbers is fundamental to higher-level mathematics, including calculus and analysis.
Conclusion: -10 is Definitely Rational
In conclusion, the number -10 is definitively a rational number. It meets the criteria for rationality: it can be expressed as a fraction (-10/1) where both the numerator and denominator are integers, and the denominator is not zero. Understanding the definitions of rational and irrational numbers, along with recognizing the properties of integers and fractions, is crucial for accurate mathematical classification. By grasping these core concepts, you can confidently classify various numbers and appreciate the rich structure of the number system. This understanding forms the bedrock for more advanced mathematical exploration and application across various scientific and technical fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Does It Take To Count To One Billion
Jul 06, 2025
-
Why Did The Kangaroo See A Psychiatrist
Jul 06, 2025
-
How Long Would It Take To Walk To China
Jul 06, 2025
-
Step Up To The Streets Final Dance
Jul 06, 2025
-
How Many Grams Is Half An Oz
Jul 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is -10 A Rational Number Or Irrational . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.